Causes of domestic tomato fruit
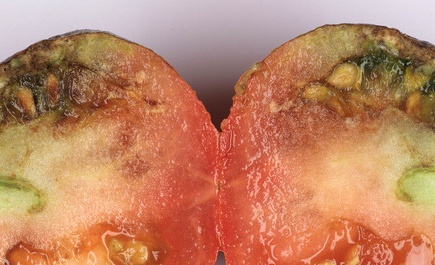
Very often, green tomatoes during storage are covered with brown spots, becoming unsuitable for food and processing. Information about the main diseases of the tomato, methods of their treatment and prevention will help save the harvest.
Symptoms
 Consider the first symptoms of the disease can be on green tomatoes. On the surface of the fruit flattened or bumpy patches of brown, brown-gray tint are formed. When tomatoes ripen, the color of these areas remains gray-brown or yellow, this causes uneven ripening of the fruit. On the cut, the flesh has a dark brown color.
Consider the first symptoms of the disease can be on green tomatoes. On the surface of the fruit flattened or bumpy patches of brown, brown-gray tint are formed. When tomatoes ripen, the color of these areas remains gray-brown or yellow, this causes uneven ripening of the fruit. On the cut, the flesh has a dark brown color.
Diseases of tomatoes, in which the fruits deteriorate:
- bronze;
- mosaic;
- Alternaria;
- fomoz;
- anthracnose;
- late blight;
- brown spot;
- peak rot.
The reasons
Factors causing tomato diseases are in the environment. Tomato health is affected by soil quality. It becomes the cause of fungal diseases, if it has a high concentration of nitrogen, little potassium.
Every autumn, the greenhouse (structure, soil) is treated with a solution of copper sulfate 1 cup per 10 liters of water.
The activity of pathogenic microorganisms increases with high humidity of the soil and air, if sharp fluctuations in the average daily temperature are observed. Poor lighting, dense soil, poorly conducting moisture, air reduce the immunity of plants.
Carriers, pathogens
Vertex rot of fruits is the result of agrotechnical blemishes plus genetic predisposition of the variety. Other diseases are caused either by a fungus (late blight, fomoz, anthracnose, Alternaria, brown spot), or by a virus (mosaic).
Treatment
 At the first signs of a fungal disease, the soil moisture is normalized, and airing stops the watering. The treatment is carried out using modern fungicides:
At the first signs of a fungal disease, the soil moisture is normalized, and airing stops the watering. The treatment is carried out using modern fungicides:
- Fitosporin M.
- Kvadris.
- Fundazol.
- Acrobat.
Treatment of tomatoes with systemic agents alternates with treatment with copper-containing preparations Abigak-peak, modified Azophos.
Prevention
Spores of fungi remain in the soil, on plant debris. They are deposited on the structural elements of the greenhouse. One of the basic rules of a healthy garden is crop rotation, the correct alternation of crops. To prevent the crop from spoiling, tomatoes are not planted in the open ground after potatoes, peppers, eggplant, and tomatoes.
In greenhouses, where this crop is grown annually, the soil (top layer) is renewed every 2-3 years, the used soil is sent for resuscitation into a compost pile. Observe preventive measures:
- seedlings are planted in accordance with the recommended planting scheme;
- a plot for tomatoes is taken in a well-lit part of the garden;
- seeds are planted before planting, the soil is disinfected.
Resistant varieties
Modern hybrids are resistant to most fungal diseases. A good selection of seeds guarantees a quality crop of tomatoes. To help summer residents list of resistant varieties of tomato:
- Firebird F1.
- Boheme F1.
- Chio-chio-san.
- Apple Russia.
- Raspberry giant.
The choice of early ripe varieties of tomatoes reduces the likelihood of disease. Compliance with the rules of crop rotation, balanced fertilizing, the correct irrigation scheme is the basis of a good harvest.





