
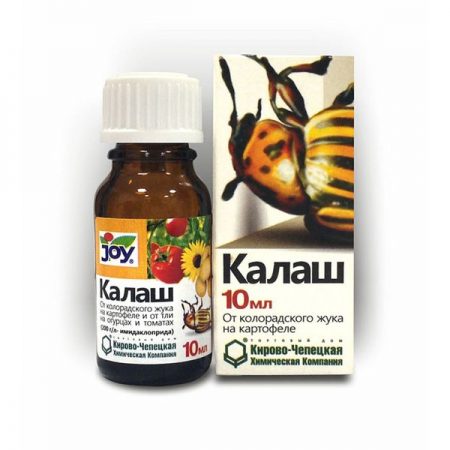
Systemic insecticides are characterized by a contact-intestinal action aimed at sucking insects and some gnawing pests, famous for their effectiveness. The trust of many gardeners won "Kalash" from the Colorado potato beetle, its instructions indicate all the steps for the application necessary for maximum effectiveness in controlling insects.
A great advantage of the tool can be considered its effectiveness after a certain time from the moment of processing the culture. Even in dry, hot and sunny conditions, the treated plants will remain under the reliable protection of the drug.
Content
Description and characterization of the insecticide "Kalash"
The tool belongs to the group of new generation drugs, with a formula that guarantees effective pest control at different stages of their development. Both adult formed individuals and their offspring in the form of larvae will suffer from the remedy.
The substance is famous for a number of advantages compared to other drugs:
- Clash can be used on an ongoing basis and not alternate it with other means.
- Its use is not addictive in insects.
- Culture tubers will not suffer from components.
- The formation and maturation is timely and balanced.
The effect of the drug will not decrease for the next 14 days from the moment of processing the culture. Rains during this period will not affect the effectiveness of the product, since a reliable protective shell will be formed on the culture. It is these benefits that eliminate the need to use Kalash again. After using a new generation of insecticide, the chances of re-infection with the pest are significantly reduced.

Means "Kalash" acts as an antidepressant for culture. This gives her the ability to quickly recover from damage from pests.
The drug Kalash: composition, how it works
Kalash, used from the Colorado potato beetle, according to reviews, shows good results. All thanks to the composition of the drug. A water-soluble concentrated agent acts on the pest due to the active ingredient imidacloprid. This component belongs to the group of neonicotinoids. When a pest enters the body, it affects its nervous system, blocking natural normal impulses in the postsynaptic membrane. After convulsions, the insect beats paralysis, then death awaits him. The mechanism of Kalash influence on the Colorado potato beetle is neurotoxic.

The method of application of the insecticide
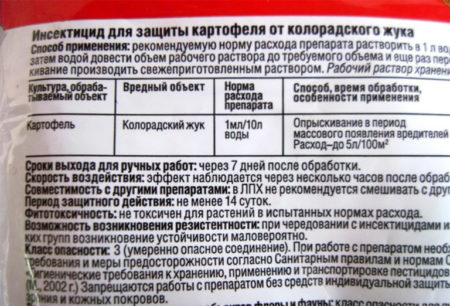
Using the Kalash preparation from the Colorado potato beetle, you need to know exactly how to breed it and how to properly handle the culture with the solution. Only proper processing, in accordance with all the rules specified in the instructions, will lead to a positive result. Kalash is recommended to be used exclusively as part of the plant’s vegetation. This water-soluble concentrate belongs to the third class of toxicity that threatens birds and various animals. The first degree of danger is allocated in relation to the effect of the agent on the bees.
This feature should be considered for those people who are going to use the drug near the location of the hive:
- Before starting spraying, it is important to properly dilute the drug, following strict dosage rules.
- The leaf beetle will suffer from an insecticide if the drug is diluted in the ratio of ampoules per 10 liters of water.
- The finished solution in a volume of five liters can be used on 100 meters of a square garden. Kalash is issued in various forms. The gardener has a choice between a capacity of 100 ml or a capacity of five liters.
With careful spraying and proper dilution of the solution, taking into account all the recommendations, re-spraying may not be necessary. Reliability of the drug after the first use will be guaranteed.
Safety Precautions While Using Kalash
Kalash, as a tool to help get rid of the Colorado potato beetle, should be used strictly according to the instructions:
- The gardener must take care of safety using protective clothing at every step of working with the drug. It prevents the spread of particles of the product on the skin.
- It is important to protect the eyes when using a mask.
- A prerequisite for working with Kalash, as with other insecticides, is the use of a respirator.
- You cannot stop during processing.
- It is forbidden to eat food during the spraying process exactly, like drinking drinks, going to the toilet and smoking breaks. All this poses a great danger to well-being and human health.

Important! No crops or pets are allowed near cultivated crops.
Additional and mandatory precautions are rinsing of the respiratory organs after processing the culture and taking a shower. If chemicals come into contact with the skin, they should be washed off immediately with clean water and soap. If a person suspects poisoning with Kalash, medical professional help is indispensable.
Reviews
Pauline:
“For several years, she collected the Colorado potato beetle by hand. Anyone who fights with him knows that this is a difficult job, which takes a lot of time and takes a lot of energy. A lot of potatoes were planted this year. I can’t imagine what I would do without Kalash. I didn’t use other insecticides, there’s nothing to compare with, but I’m happy with the effectiveness of the drug. ”
Alexey:
“Kalash rescues annually from the Colorado potato beetle that attacks potatoes. One ampoule is enough for me to cultivate the entire plot planted with this crop. “Not much time passes after the treatment so that the first effects of the drug are noticeable.”
Basil:
“I use Kalash primarily because the bug does not get used to it, which means that you don’t have to spend money on other insecticides. It turns out to deal with the pest effectively and economically. This year, I sprayed potatoes just once. The beetle did not return. "
Valeria:
“For my site, the Colorado potato beetle is an eternal problem. Used various insecticides, but decided to stay on Kalash. The product is available, and after two treatments, with a short break between each procedure, you forget about the pest for a long time. I will highly recommend this tool to other gardeners."Kalash praised a neighbor whose culture suffers from the Colorado potato beetle."



 How to make bread infusion for feeding cucumbers
How to make bread infusion for feeding cucumbers Superphosphate: what is it and how to apply it
Superphosphate: what is it and how to apply it What problems can be expected from siderats?
What problems can be expected from siderats? Secrets of the collection, storage and use of eggshells in the garden
Secrets of the collection, storage and use of eggshells in the garden