Such a disease as late blight or brown rot, a common phenomenon in summer cottages. This infection mainly appears in the middle of the summer season and is able to destroy all nightshade crops. To avoid infection of vegetables, some gardeners try to grow early ripe fruits in order to clean up the area to activate late blight. Others, day after day, spray plants with all kinds of solutions, in the hope that brown rot will bypass their garden.

Unfortunately, planting solanaceous vegetables ahead of schedule and avoiding late blight can only be done in the south, and only if by this time the temperature of the earth reaches the desired level. In northern cities, sowing of planting material in open ground sometimes has to be postponed, because in the middle zone of the globe the weather is not predictable and plantings should be treated very carefully so as not to cause the death of seedlings. Based on this, it can be assumed that the timing of harvesting can also move slightly, which means late blight will already destroy plants.
If tomatoes and other vegetables that grow above the ground can be harvested ahead of schedule and removed to a dark place before ripening, then this trick will not work with potatoes and the potato root crop may soon die. To prevent this from happening, let's learn more about our phytophthora enemy and find out how to deal with it so as not to harm the potato tubers.
Content
Symptoms of late blight

If you closely monitor the appearance of the tops of potatoes, then determining the presence of late blight is not difficult. Initially, green leaves are susceptible to brown rot. A dark spot of dirty gray color is rapidly developing, covering the entire leaflet. Affected areas quickly dry up, begin to crumble. With a thorough examination, on the lower edge of the leaflet you can see a cobweblike formation of white color, which is more like plaque. Inside this plaque, an active development of fungal infections occurs.
If infection is not prevented at the time, late blight will continue to have a negative effect on the potato, destroying the stem. Soon the infection process will reach the potato tubers. Gray spots first appear on the peel, then brown rot affects the fetus from the inside. The flesh of the potato blackens, begins to decompose. In a cut form, you can notice rusty necrosis, which quickly spreads throughout the root crop.
The causes of brown rot
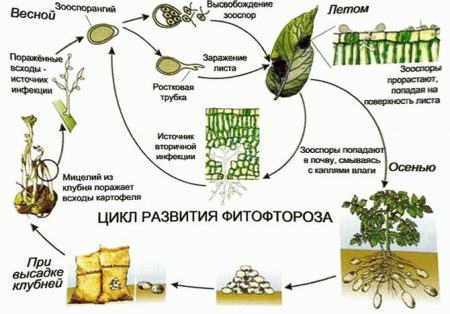
Blight spores can appear on the site for various reasons. The most common are infected plant debris or the migration of the disease by air from a neighboring garden. There have been cases when phytophthora spores were brought into the ground with the addition of new soil. However, brown rot is not activated without favorable conditions, which can serve as:
- High humidity. A few years ago it was revealed that late blight spores die at high temperatures or in direct sunlight. Therefore, it is so important to water the plants precisely under the root, avoiding moisture from entering the tops.
- Weakened plants. It is not without reason that they say that when choosing seedlings, it is better to give preferences to strong and healthy bushes, since weak and stunted seedlings are more often exposed to various diseases due to weakened immunity. Mineral top dressing of plants at an early stage and natural hardening of planting material can correct the situation.
- Thick planting. For each vegetables, there is a measure of planting the material in open ground, not observing the basic rule leads to the fact that the plants are too close to each other and, therefore, in such thickets, bacterial spores develop faster. To prevent this from happening, maintain a certain distance when sowing, thin out plants more often, with a dense planting.

Even with all the above recommendations, the occurrence of late blight on the site is still possible. Ideal conditions for the development of brown rot can create nature itself. Indeed, rainy and cool summers are the best option for late blight. To get rid of this ailment, special drugs will help you.
How to deal with late blight
A dangerous disease can spread to other vegetables if you do not isolate the source of ignition in time. In the fight against late blight, many drugs are good, but we will talk about the most effective.
Folk remedies
Chemical agents are much more effective in controlling fungal diseases, but they cost a lot of money and some drugs simply cannot be used during flowering. Therefore, during the period of flowering and the formation of potatoes, it is better to use the methods that our ancestors used.
- Infusion of garlic and potassium permanganate.

An excellent combination of garlic flavor and antibacterial agents will protect the plant from fungus for a long period. To obtain the desired mixture, it is enough to pour 100 g of chopped garlic in a glass of warm water. Withstand the infusion for a day, strain through a sieve. Pour garlic tincture into a bucket with 10 l of water and add 1 g of manganese. Mix everything thoroughly, water the plants. Half a liter of liquid is enough for one bush.
- Milk serum.
Dilute the fermented milk product with settled water in a ratio of 1: 1 and spray the tops of potatoes. To get a good result, the procedure is recommended twice a week.
- Ash.
An excellent tool that eliminates not only various diseases, but also prevents the appearance of larvae. A week after planting potato seed, cover the top layer with powdered ash. After a couple of weeks, repeat the powdering.

- Yeast.
You can treat diseased bushes with ordinary yeast, the packaging (100 g) of which must be diluted in 10 liters of water. At the first signs of late blight, water the bushes with the resulting solution. Repeat spraying after two weeks, if necessary.
- Horsetail.
Horsetail is actively fighting brown rot. Pour 100 g of dry product with a liter of water, boil on a moderate flame for half an hour, dilute with 5 liters of settled water. Spray potato tops twice a month.
Furicidal preparations
Furgincides are among the chemicals in the pesticides group. This type of drug was created to prevent and treat fungal diseases. Furnincides are divided into several groups that are responsible for a particular effect on the plant, for example:
- protective. The main objective of protective preparations is aimed at the preventive treatment of plants in order to avoid the appearance of fungi and spores;
- medicinal furgincides treat an already diseased plant;
- systemic - absorbed into plants, providing a protective effect from the inside;
- contact. They have only a protective effect, are easily washed off with water;
- disinfectants are used before sowing, processing planting material in a liquid to protect the plant and increase the immune system of the roots.
List of the most popular drugs.
- Topaz.
Refers to systemic furnicides.Processing plants during flowering is prohibited. The chemical preparation is dangerous for the life of animals and humans, therefore only the tops are processed. Avoid getting the product on the fruit. Before eating vegetables, it is recommended to thoroughly rinse the product under running water.
- Fitosporin-M.

Biofungicide has a protective effect on plants. Low toxicity. Used to process planting material. Mostly sold as pasta.
- HOM.
The drug fights diseases, so they are already treated with diseased bushes. Avoid getting HOMA into water bodies, as it has a detrimental effect on fish and other aquatic inhabitants. The last spraying with this solution should occur three weeks before harvesting.
- Copper sulfate.
The main purpose of this drug is disinfection of wounds and the fight against brown rot. Dilute 50-100 g of this product in 10 l of water, stir the resulting solution until the crystals are dissolved, spray the plants.
- Bordeaux mixture.

The Bordeaux mixture, which includes copper and lime, copes well with its protective task. However, preparing this liquid for watering plants is not so simple. The slightest mistake can change the structure, ruining the potatoes.
First of all, it is necessary to breed copper sulfate in warm water. Then add cool liquid so that the total container is 5 l of solution. In another bowl in a liter of water, dilute the lime, then add liquid to 5 liters. Filter the lime water through a sieve. Gently pour the solution of copper sulfate into the lime, constantly stirring with a wooden stick. Use the product as directed.
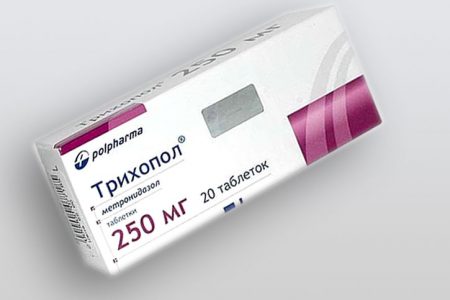
Trichopol
This tool can be called a good find for gardeners. Trichopolum, the active substance of which is metronidazole, does not harm anyone's fruits and human body. Most often, the product is sold in the form of tablets, which must be dissolved in a small amount of warm water, and then add another 10 l of clear liquid. Spraying the bushes is carried out after preparation of the solution.
Preventative measures
Phytophthora on potato bushes may appear suddenly, so that this does not happen, a number of preventive measures must be taken to protect the tubers and tops from brown rot.
- In addition to the main factors, the development of fungal diseases is also affected by the choice of landing site. When sowing potatoes, it is important to choose a site where there is no shadow and moisture does not stagnate.
- Plant rotation plays an important role, since late blight mainly affects nightshade crops; therefore, it is strictly forbidden to plant potato root crops in place of tomatoes, eggplants, and other vegetables belonging to the list of nightshade.
- Choosing a healthy planting material and warming it up will eliminate spores in tubers and give good yield.
- The introduction of potash fertilizers at an early stage of plant development will protect the plantings from brown rot.
- Hilling seedlings favorably affects the sprouts and protects them from diseases.
- If weather forecasters promise that the end of the summer season will end with prolonged rains, then it is better to dig up the crop and put it in a dry dark place for ripening.
- After harvesting, it is important to dig out all the weeds and remove the remaining debris from the site, which could serve as a source of infection for next year.
Performing a series of preventive measures, your seedlings will be under reliable protection.
Varieties of potato resistant to late blight
In order to collect a rich potato crop and not think about the fact that the plant can be infected with late blight, we recommend that you plant only proven potato root crops in the summer cottage, which have strong immunity and are not afraid of a disease such as brown rot. We present you a list of the most popular varieties of potatoes.
- Spring.
Potatoes with an unusual name refer to early ripening species. The high yield of the variety and the resistance to many diseases makes Spring the best seller. The oval shape of the fruit in a light pink peel to the taste of many gardeners. In the context of the vegetable has a white flesh. Potato lends itself to any kitchen test and perfectly complements dishes.
- Blue.

Why the variety was called "Blue" is probably known only to breeders. After all, the appearance of the potato has rounded tubers in a light brown peel. The white flesh remains unchanged even after heat treatment. From this vegetable you get delicious mashed potatoes and excellent home-made chips.
- Nevsky.
The delicate taste of rounded white tubers, covered with white-yellow peel, has been in great demand among gardeners for many years. The variety is resistant to many diseases and pests. Good keeping quality of fruits allows you to stock up on crops for future use.
- Red scarlett

Smooth, pink oval-shaped root vegetables with excellent gustatory qualities have a number of advantages. The variety is well stored for a long time, the presentation, even after long storage, remains unchanged. In cooking, Red Scarlett is used in all directions.
- Luck.
The early ripe variety gives rounded fruits in a light peel and with a yellowish flesh. High productivity and excellent keeping quality to the liking of many gardeners, so this type of "Good Luck" is also the main guest in the suburban areas.
Any of the above varieties is suitable for the cultivation of potatoes in different regions of the country. Each species has a high degree of protection against late blight, however, without preventive measures, even these varieties can undergo brown rot disease. Therefore, carefully monitor the planted bushes in time to prevent infection of the tops.
Potato storage rules

A lot depends on the proper storage of potato root crops after harvesting, including storage periods. To prevent the fruits from spoiling ahead of time, it is recommended to use the following tips.
- Dark room.
Darkness in the room plays an important role in storing potatoes. If there is light, the tubers will begin to germinate, therefore, such a crop will not lie for long, and will soon begin to deteriorate. The best place to bookmark potatoes is the cellar or basement.
- Temperature mode.

The ideal indoor temperature is 2-3 degrees. With this mark, the fruits will not sprout or deteriorate.
- Dryness.
The room where the potatoes will be stored should be dry, otherwise this place will be a beneficial environment for the propagation of spores and viruses. By the way, you need to lay potato tubers in a dry form.
- Container for storage.
As "utensils" you can use wooden or plastic boxes. It is convenient to store potatoes in them and it is easier to find damaged fruits.

Frequently Asked Questions for New Gardeners
Those who grow potatoes for the first time in their garden often have a series of questions, the answers to which are sometimes difficult to find. We decided to save your valuable time and give answers in advance to questions that will certainly arise in the future.
How to treat phytophthora during flowering
As already mentioned, not all methods are allowed during the flowering of potatoes. In addition to folk recipes, you can also use drugs such as:
- Arcedil (50 g per 10 l of water);
- Ridomil MC (25 g per 10 l of water);
- Oskikhih (20 g per 10 liters of water).
The use of each solution is allowed during the flowering period.It is recommended to water the plants after the stem reaches 15-20 cm in height. As a preventative measure, treat the tops twice a month.

How to process potatoes after flowering
At the end of flowering of the potato culture, it is recommended to replace the previous solutions with the following:
- Ditamin M-45 (20 g per 10 liters of water);
- Copper Chloride (40 g per 10 liters of water);
- Cuproxate (25 g per 10 liters of water).
Water the plants twice a month, three weeks before harvesting, stop spraying potato foliage with chemicals and folk remedies.
How to process potatoes in July
An effective method of controlling late blight is a solution of a mixture of copper sulfate, manganese and boric acid. To prepare a vigorous mixture, you need to mix 10 teaspoons of each component in 10 l of water and mix until the crystals are completely dissolved. Then spray the potatoes with the resulting solution and enjoy the result.

Please note that this mixture is allowed to be used once per summer season, and mainly such processing of potatoes is carried out in the month of July.
Conclusion
So that brown rot does not catch you by surprise, we recommend that you start spraying planting material in advance in order to prevent it and carefully monitor the change in the appearance of the leaves. In case of brown spots, immediately use other drugs that will help you to extinguish the fire and save the crop.
It is also worth remembering that presowing treatment of tubers increases the immune system of seedlings and is able to withstand various diseases.



 Description and description of varieties in Belarus with a photo
Description and description of varieties in Belarus with a photo Do I need to pick flowers from potatoes: why do they do it
Do I need to pick flowers from potatoes: why do they do it When to dig potatoes: timing and availability of new potatoes
When to dig potatoes: timing and availability of new potatoes How to grow a good potato crop: various methods and methods, planting and care
How to grow a good potato crop: various methods and methods, planting and care