Choosing rabbit breeding with extra income, you can get a delicious dietary meat and a good financial return. Their maintenance does not require large financial investments or time expenditures. The final product obtained from the cultivation may be meat (4-5 kilograms per carcass) and skin. Additional income will be the sale of young animals and manure.
Content
Where to get animals

Buying rabbits is easy. Currently, there are several points where you can buy rabbits:
- On the market;
- farmers;
- on a specialized breeding farm.
Purchasing animals on the market is the most economical option for setting up a rabbit farm. Of the minuses - a low probability of thoroughbred, as well as the almost complete absence of vaccinations in animals.
The purchase of a pedigree animal on a farm is a preferable option. As a rule, farmers have been given all the necessary vaccinations for the animals, but in a small farm it is difficult to observe the genetic purity of the breed, so it is preferable to acquire such animals only for feeding, and not for breeding.
The best option is to buy rabbits in specialized breeding farms. Together with the animal, the buyer receives a vaccination card and a certificate of compliance with the breed.
Species of rocks

By the type of product obtained, all breeds can be divided into three large groups:
- meat direction;
- breeds bred for fur;
- downy breeds.
In addition to the above, there are universal meat-and-skin animal breeds. Rabbits grow medium in size and have medium quality pelts.
Meat breeds

Rabbits are characterized by high fecundity and rate of weight gain by young individuals. The meat breeds of rabbits include:
- Californian.
- Butterfly.
- Soviet chinchilla.
Breeds for fur

Fur rabbits are bred to obtain skins. Their difference is persistent thick fur. The rocks include:
- White giant.
- Viennese blue rabbit.
- Russian ermine.
Down breeds

Down breed rabbits are kept for fluff. The rocks include:
- White downy rabbit.
- Angora rabbit.
- Arctic fox down rabbit.
Pet choice

The breeding stock should be acquired after it becomes clear what kind of products the farm will produce. For meat production, fast-growing animals are purchased, for the production of high-quality skins, rabbits with dense, thick, beautiful fur are purchased; when breeding a down farm, they look at the quality of fluff in animals.
Before acquiring a rabbit of a particular breed, it is necessary to study the characteristic data, color, exterior, average weight and feeding and breeding features.
Signs of healthy specimens:
- a healthy rabbit is very mobile, actively moves, eats feed well;
- the auricles are clean;
- the hair on the face is dry and smooth, on the back is even and shiny;
- the front teeth are well developed and do not interfere with eating food. A sick animal, as a rule, is lethargic, apathetic, eats poorly and reluctantly, the hair on it is ruffled, and parasites can be found in the ears.

When purchasing an animal, it is necessary to find out at what age what vaccinations were given and, if necessary, to make the missing ones.
Signs of inferior animal development:
- abnormal development of the spine. This disease occurs when keeping babies with very low ceilings and high crowding;
- curvature of limbs. This disease occurs due to birth injuries during the round-up or as a result of mutations from closely related crosses;
- lack of weight. The reasons for weight loss can be quite a lot: past illnesses, constant lack of water in drinking bowls, poorly selected feeding diet, cramped cages, lack of milk from the mother rabbit;
- genetic abnormalities. As a result of interbreeding, the animals exhibit signs unusual for this breed: changes in the proportions of the body, ears, limbs, mismatch in the density of the coat, a significant reduction in weight;
- deviations in the color, density and quality of the fur. Animals are born with a coat color that does not meet the standard of the breed. This disease manifests itself as a result of improper breeding of the livestock breeder, or interbreeding.
Rabbit keeping

Currently, there are two main options for keeping animals: cellular and pit.
Cellular rabbits
With this placement option, animals are housed in cages. For adult rabbits and rabbits with litter, individual cages are made, young animals for fattening are kept in a large common cage.
Positive sides:
- careful monitoring of the condition of animals, the ability to instantly respond to diseases;
- the possibility of breeding, 100% protection against unauthorized mating of animals;
- individual cell settlement prevents mass death of animals from viral epidemics;
- cage placement allows for partial automation of animal care and care
Negative sides:
- the purchase of ready-made cells is quite expensive, self-production takes a lot of time;
- breeding rabbits requires a lot of attention from the breeder;
- a lot of space is needed to place the cells.

Cell requirements
Cells are made on a wooden frame from bars with a section of 40 by 40 mm. To protect animals from drafts, the back and sides are sheathed with boards with a thickness of 20-25 millimeters.
The floor for the cage is made of slats or of mesh. The rack floor does not injure the paws of rabbits, but manure is very poorly removed through it. The mesh floor contributes to the purity of the cell, but with a long stay on it in animals there is a curvature of the paws. In a two-story cage under the floor of the upper floor put a tray for collecting feces.
The facade of the cell is made of mesh. A triangular feeder for grass or hay is hung on it. Drinking bowls and feeders for porridge or compound feed are hung on a facade mesh or placed inside a crate.
Cells are mounted on stands at a height of 70-100 centimeters above ground level.
Rabbits are nocturnal animals and in direct sunlight they feel uncomfortable. Therefore, the cells for them are placed either under a canopy or in the shade of buildings.
Pit rabbit keeping

For the pit placement of rabbits on the site, they find a place where there is no access to the surface of groundwater and dig a hole. The standard size of the pit is 2 by 2 meters, the depth of the pit is 1.5 meters. The walls of the pit are strengthened from shedding with slate sheets, the top is closed from precipitation and birds of prey by a canopy. The rabbits placed in the pit begin to dig intensively in all directions of the burrow into which they live. For the convenience of catching animals, the burrow exit into the pit is blocked by a remotely closing shutter.
Animals aged 3-5 months are placed in the prepared pit.
Positive sides:
- the cost of constructing a pit is very low;
- up to 200 rabbits can comfortably live in a standard-size pit;
- rabbits do not require special attention and help during childbirth, because the pits are as close as possible to the natural habitat of these animals;
- feeding all livestock at the same time saves the time and effort needed to service the animals;
- in burrows, animals are warmer in winter frost and cooler in summer cold. A more even temperature regime of keeping positively affects the health of animals;
- rabbits can lick and gnaw the earth, receiving useful minerals in the diet;
- Pit animals allow you to occupy a much smaller area under the farm;
- there are no rats in the pits that can cripple little rabbits;
- rabbits breed without host intervention;
- small rabbits can feed milk any of the lactating rabbits.

Negative sides:
- rabbits mate uncontrollably. This leads to closely related crossbreeding and, gradually, to the degeneration of the tribe;
- it is impossible to engage in tribal work;
- the great difficulty of catching a certain animal in the pit;
- rabbits in the pit often fight. This leads to spoilage of the skins; therefore, exclusively meat or meat-skin breeds are suitable for the pit maintenance;
- in rabbits of downy breeds, when kept in the pit, wool is dirty;
- it is rather difficult to control the condition of animals in the pit; therefore, with diseases it is almost impossible to separate the diseased rabbit into quarantine;
- it is impossible to arrange a separate diet for pregnant females or young fattening animals. All inhabitants of the pit eat the same way.
Feeding rabbits

For the normal functioning of the gastrointestinal tract, a large amount of fiber must be present in the diet of rabbits. Therefore, the main composition of the feed is grass, tree branches, fruits and vegetables. Cereals, legumes and wild herbs are used as greens. In the autumn, from the garden to the very frosts, animals can be fed tops of carrots, beets and cabbage. In winter, animals are fed with hay, brooms, vegetables and silage.
In the cold season, carrots, beets, pumpkins, cabbage, rutabaga, turnips, turnips are added to the diet of rabbits. Before feeding, vegetables are washed, rot is removed and cut into portions.
For better fattening, in addition to the main food (grass, hay or vegetables), rabbits are given an additional grain of cereal or bean crops, loose or granular compound feed, bran, cake. Concentrated feeds have a great energy value, so their dose is increased during intensive feeding or pregnancy.
Part of animal feed can be replaced with food waste. For feeding, you can use bread crusts, peeling vegetables, leftovers from the first courses.
Specific feeding diets depend on the physiological condition of the animals and season:
- young rabbits are given 30-50 g of concentrates, 300-500 g of grass and 150-200 g of succulent feed;
- 70-100 g of concentrates, 500-1200 g of grass, 150-300 g of succulent feed are given to adult animals.
Rabbit case

Before mating, the female is examined, her condition is assessed. There is no point in allowing mating of sick, weakened and poorly fed animals, since they are not able to tolerate healthy offspring. For successful mating, males at the age of 4-5 months and females at the age of 7-8 months are allowed to mate.
Females who after calving eat cubs or refuse to feed them are not allowed for further mating and are subject to culling.
A case is carried out during the period of estrus in rabbits. On average, it lasts 3-4 days, then in the summer there should be a break for a week, in winter - for 10 days. During the hunt, the female sex loop increases and turns pink, the rabbit behaves excitedly and does not eat well. Rabbits are able to mate and produce offspring at any time of the year. Usually one male is kept for 5-10 rabbits. One day a rabbit can fertilize two females.
For mating, the female is planted in the cage to the male, while she is inspected and mastered, the mating process occurs.A sign of the end of the process will be a roll of the male on its side with a quiet rumbling. A control mating is carried out after a few days. If the rabbit does not allow the male to come to her, then she became pregnant.
Pregnancy

The female puppet is transplanted into a larger cage and surrounded with additional care and care. Throughout the pregnancy, the rabbit is tasty and variedly fed. To form future rabbits, meal, meat-bone and fish meal are added to food. In winter, vegetables or silage are necessary, as well as vitamins A and D.
The gestation period lasts 28-35 days. The term depends on the breed of rabbits (small decorative breeds give birth faster), the number of cubs (the more fetuses, the faster the birth) and the age of the female.
A few days prior to the incubation, disinfected mother liquors are installed in standard cells; a soft litter is placed in the nesting compartment of specialized uterine cells.
In the last days of pregnancy and after the rounding, the female drinks a lot, so there must always be a lot of water or snow in the cage.
Immediately after the round, the nest is inspected, the dead rabbits are removed. 8-9 rabbits are left to feed the mother, the rest are transferred to the cage to other rabbits.
The first two weeks the rabbits feed exclusively on mother's milk, then they begin to try what lies in the mother’s feeder.
Rabbits from the mother are planted at the age of 30-40 days.
Rabbit diseases

All diseases of rabbits are divided into infectious diseases and diseases from improper maintenance or feeding. Infectious diseases occur after infection of animals with viruses, at the same time the whole herd can become infected, they are very poorly treated and often lead to death of animals. Diseases arising from malnutrition or maintenance affect an individual animal. Their treatment is useless until the cause of the disease is eliminated. For any disease of animals, you must contact a veterinary clinic.
Diseases from improper maintenance include:
- diseases of the digestive tract;
- bruises, injuries, fractures;
- frostbite;
- sun and heat stroke;
- colds.
Infectious diseases include:
- myxomatosis;
- rhinitis;
- infectious stomatitis.
Disease Prevention, Vaccinations
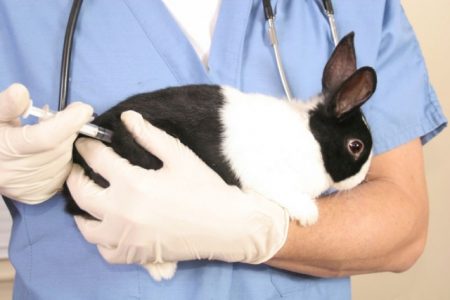
Rabbits are very sensitive to infectious diseases. That is why the best option for acquiring young animals is specialized breeding farms. When buying an animal, the veterinarian issues a veterinary certificate of the absence of infectious diseases.
After acquiring the rabbits, they are placed in a separate isolated cage and kept in quarantine for three weeks; when signs of the disease occur, they are shown to the veterinarian.
As practice shows, infectious diseases are easier to prevent than to cure. That is why it is necessary to observe cleanliness and order in the territory of the rabbit farm. Manure from the cells must be cleaned daily; the cells should be disinfected twice a year with a 5% solution of creolin or 2% solution of formalin. Before transplanting the animal to a new place, as well as before scrolling, treat the cage with a disinfectant solution or burn it with a blowtorch.
Throughout the year (especially in winter) they fight rodents that carry diseases. Rats carry food from the feeders, can attack and bite the little rabbits.
To prevent gastrointestinal diseases, it is necessary to remove half-eaten food and rinse feeders and drinkers once a day. Water for drinking should be clean, it can be taken from trusted sources.
It is necessary to examine animals daily, paying attention to appetite, mobility, and the condition of the coat, nose, eyes, and genitals.
Sick rabbits become inactive, lethargic, the fur becomes dull and disheveled, mucus starts to flow from the nose, and the eyes watery. Animals may also show diarrhea, cramps, and bloating.The rabbits are isolated, if necessary, shown to the veterinarian. All equipment and cells are disinfected.
Vaccinations

Most infectious diseases of rabbits are not treated and almost 100% lead to the death of the animal. Viruses are instantly transferred to other individuals and the farm can become empty in a matter of days. Vaccination reliably protects rabbits from most infectious diseases. All animals must be vaccinated against myxomatosis and viral hemorrhagic disease (HBV). Either separate vaccinations are given from each of them, or a complex vaccine is used.
From VGBK do vaccinations:
- the first time the baby is 6 weeks old and he will gain a mass of 500 grams;
- the second time three months after the first;
- to maintain immunity, the following vaccinations are carried out every six months.
From myxomatosis vaccinations are made:
- the first vaccination is done in the spring, when the kids turn 4 weeks old;
- the second vaccination is carried out 4 weeks after the first;
- further vaccinations are carried out every six months in early spring and early autumn.
From pasteurellosis and paratyphoid, males are vaccinated within 24 hours after their acquisition. Usually they are vaccinated with a complex vaccine, since if two vaccinations are done separately with different vaccines, they must be kept for two weeks between them. Rabies and listeriosis are vaccinated according to the epidemiological situation of the farm location.

There are times when the vaccine does not work:
- animals are infected with helminths;
- rabbits are already infected with the disease from which they are vaccinated;
- the vaccine has expired;
- the vaccine is spoiled due to violation of storage rules;
- delays in revaccination are allowed.
Vaccinations are not allowed for weakened or newly ill animals, as well as pregnant or lactating rabbits.
Slaughter

Slaughter of rabbits is carried out according to the breeding plan. Rabbits of meat breeds are slaughtered as required, fur rabbits are usually slaughtered in November after the end of molting.
For slaughter, animals are lifted by their hind legs and a sharp blow is applied to the head behind the ears with a stick. The hind legs of the carcass are placed in special clamps, eyeballs are removed for better drainage of blood. Around the hock joints of the hind legs make a circular incision of the skin, then the incisions lead along the inside of the hind legs, reducing at the anus. The vertebrae are removed from the tail, the skin is removed from the hind legs and the stocking is pulled down to the head. Fat and films are immediately separated from the skins being removed. The front legs are trimmed along the wrist joint. The skin is cut at the base of the ear cartilage, around the oral cavity and eyes, and finally tightened.
Then it is cleaned of the remains of fat, meat and films, pulled on a special triangular rule and dried in a room at a temperature of 25-35 degrees and air humidity of 30-50%. If the temperature and humidity conditions are not observed, the skins can become brittle and become very saturated with fat. The dried skins are removed from the rules and stored in a place inaccessible to moths and pets.

During long-term storage, the skins of rabbits are caked, so it makes no sense to collect them in large lots, it is better to hand them over to the procurement office as soon as possible.
The skins intended for their needs are sprinkled with salt, rolled up and put away for storage in the refrigerator.
After skinning, the carcass is gutted and cut. For this, the internal organs are removed, the head is cut off at the level of the first cervical vertebra, the front paws along the wrist joint, the hind legs along the hock. The carcass is washed in cold water, then packaged and placed in the refrigerator (if the carcass is sold refrigerated) or in the freezer chest.
Growing decorative rabbits

Dwarf rabbits are common pets. They are very smart, clean, well trained. At present, many breeds are bred, here are some of them:
- Dutch dwarf rabbit.
- Angora dwarf rabbit.
- Dwarf fox rabbit.
- Angora lion.
- Lion's head.
- Lop-eared rabbit ram.
- Dwarf Rusak.
To keep the rabbit in the apartment, a cage of 80 by 80 cm is set. Feeding of decorative rabbits does not differ from feeding of ordinary rabbits.
The mistakes of inexperienced farmers

Breeding rabbits is not an easy process. Animals are very demanding on conditions of detention, feed quality, hygiene. Inexperienced rabbit breeders make the following mistakes:
- A novice farmer often downloads a beautiful business plan from the Internet and believes that he will buy 3-5-7 rabbits, in the first couple of months each of them will bring 10 babies. Immediately after the okrol, he will mate and in six months he will have a large sum from the sale of young meat and 100-200-300 babies. Of course, obtaining such a result from the farm is quite realistic, but in practice it usually turns out that one rabbit does not allow the male to come at all, the second could not give birth, and the third brought only four rabbits. Therefore, starting a rabbit farm should be prepared for failure, disease and hard work.
- It often happens that a novice farmer buys animals of little breed for a lot of money, receives marketable products (skins, young animals), and then finds out that these products are absolutely not in demand in this area, and the proceeds do not compensate for the money spent. Therefore, before deciding to start a rabbit breeding business, you must first decide where and at what price the products will be sold, evaluate profitability, and only then make a decision about buying animals of the right breed.
- Beginning breeders pay little attention to breeding, rarely lead a history of rabbits in rabbits. This leads to closely related crossing and degeneration of the tribe.
- Rabbits are afraid of dampness, drafts, frost. An attempt to save on housing for animals results in crowding, injuries, outbreaks of colds.
- Breeders often forget about vaccinating animals or regret spending money on it. The result of such savings is usually deplorable, with the slightest infection, the entire herd dies.
Cost and Profit

Calculating farm profitability is easy. For the initial acquaintance with this business in mid-spring, you can buy a dozen rabbits - 8 females and two males. The price of 1-2 months old babies is 300-400 rubles per animal, the total acquisition cost will be 3-4 thousand rubles. In 6-8 months from each rabbit it will be possible to get 3 kilograms of meat at a price of 300-350 rubles per 1 kg. In addition to meat from each animal, you can get and sell a skin for 20-30 rubles.
The cost of feed in the spring and summer is negligible; a large amount of grass and a little feed are put in the feeder. For six months, the cost of fed concentrates will be 500-600 rubles.
Consequently, at a cost of 4 thousand rubles for six months of cultivation, the breeder will receive 30 kilograms of meat and ten skins, or, in monetary terms, the revenue will be 9,200 rubles. Also a few by-products of manure will be a byproduct of the farm.
For a dozen rabbits fed for meat, 4-5 cages are quite enough, the manufacturing cost of which is quite low.
With the further development of the farm, males are used for insemination of rabbits, thereby obtaining 60-80 small rabbits, from which 180-240 kilograms of meat can be obtained in six months.
The rabbit farm is a highly profitable business. If the animals are provided with proper living conditions, the necessary vaccination is carried out in a timely manner, they are fed plentifully and variably, the rabbit farm will generate constantly high income.