
The treatment of raspberries for ailments, first of all, is of a preventive nature, which envisages compliance with the rules of agricultural technology. Most often, problems arise when there are well-groomed, neglected gardens in the neighborhood, in years with bad weather or during an outbreak of disease, as well as with a mass population of pests.
Viral diseases
When viruses get to the raspberry plantations, it will be practically impossible to save them. There are several options for their distribution:
- When juice comes from diseased plants to healthy ones.
- Viruses carry sucking insects - aphids, ticks and nematodes.
- You can bring an ailment using a garden tool, which they worked with diseased plants.
- In rare cases, viruses are transmitted through the pollen of infected crops.

Raspberry bushes affected by viruses cannot be propagated, the offspring will also hurt. To protect plants from infection, you can choose varieties that are resistant to viral diseases. The right choice of place, timely watering, top dressing, thinning crop significantly increase the natural immunity of the plant.
All infected stems are cut to the root, most often it is necessary to uproot the whole raspberry, so that the disease does not transfer to neighboring cultures. Then they begin to treat the soil at the site of the former raspberry. Farmayod is used, the drug is bred in high concentrations and the beds are abundantly shed. After autumn cultivation, humus is scattered on the ground, watering with the preparation is repeated in early spring, and phacelia is sown. Raspberries are planted again in a year.
Mosaic
The signs of the mosaic may vary depending on the raspberry variety and the virulence of the pathogen strains. More often, the first symptoms appear on the leaves in the form of yellow spots of irregular shape. At first, necrosis is arranged in a chaotic manner, and towards the end of the summer season, leaf plates are completely strewn with such inclusions, acquire tuberosity, corrugation and irregular shape. Sick shoots can grow normally or stop in development, the bushes become dwarf.

On berries, the virus always manifests itself identically, they are small, dry, taste and aroma are lost, only one acid remains. Productivity, winter hardiness, drought tolerance of plants is greatly reduced. A raspberry tree infected with a mosaic can stand for about 3 or 4 years, then the bushes gradually die off. A bright manifestation of the virus is observed in spring and autumn, in summer in hot weather the mosaic can mask, the bushes look quite healthy, it can be detected only by the condition of the fruits.
It is impossible to cure a mosaic; there are no drugs capable of fighting it. Some gardeners claim that they managed to overcome the disease, but the manifestations of the mosaic can be confused with non-viral chlorosis, which is easily eliminated by iron-containing drugs.
Chlorosis
The first sign is yellowing of the leaves along the main veins, after a short period of time the plates turn completely yellow. Shoots become thin, greatly extended. The fruits dry out, become woody, small, unpleasant in taste.

Cure chlorosis does not work, it must be warned. Processing bushes from sucking insects (vectors) is carried out in early spring, when buds open and at the beginning of flowering. A 3% Nitrafen solution is used; for the second treatment, a 0.1% emulsion of 30% methyl mercaptos is prepared. For the last session, any extended-action insecticide is selected (from aphids, ticks and nematodes).
The same signs accompany non-viral chlorosis, which can develop in poor soil with high humidity or excessive alkalization. Sometimes gardeners complain that non-viral chlorosis appears after irrigation with cold water.
In such cases, the soil is put in order, restore normal acidity (neutral level), stop fertilizing the bushes with superphosphate and manure, periodically loosen. As top dressings, a solution of bird droppings, nitrogen-containing, potassium fertilizers are used. If after normalization of the soil condition the signs of damage will appear for the next season, then the bushes need to be uprooted.
Witch's broom
The people are also called an ailment by a taupe, overgrowth or dwarfism of raspberries. The greatest distribution is in the Non-Chernozem zone of the Russian Federation. A characteristic feature is the formation of a large number (up to 300) of thin shoots, they appear in the form of bunches in one section of the rhizome, the outwardly dense, lush, dwarf bush resembles the tip of a broom. In this case, the height of the plant remains within 20 cm.

The virus can affect both young and adult raspberry bushes, the leaves are smaller, acquire an atypical shape, uneven yellow spots appear on the plates. In some varieties, flower growth is added to the main symptoms (petals are similar to leaf-shaped formations).
The disease has a chronic form, the bushes grow up to 15 years, do not recover and do not die. Signs appear at the same time, persist at all stages of the growing season, even with full observance of agricultural technology, the virus will not disappear, perhaps its manifestations will become less noticeable. The witch's broom spreads very quickly, in the first stages the yield decreases and the quality of the fruit decreases, after 2 or 3 years the bushes cease to produce flower shoots.
The causative agent of the disease is mycoplasma, it is something between a virus and a bacterium. The disease is tolerated by the cicadas, but the main source of infection of healthy raspberries in the area is planting material taken from a diseased plant. How to protect raspberries from broomstick:
- Seedlings are bought only in trusted places, the best resistant varieties are Latam, Alma-Ata, Phoenix, Newburgh and the Golden Queen. Among the most susceptible, one can distinguish such varieties as Kuzmina Novosti, Molling Jewel, Kaliningradskaya, Carnival, Usanka, Vishluha, as well as Glen Klova and Barnaulskaya;
- to prevent the appearance of a circadian plant, raspberries are planted in well-lit, blown places, the pest intensively develops in the shade with high humidity;
- when the buds begin to bloom, during flowering and after harvesting, chemical treatments are carried out against the cicadas by Actellic or any other special preparation.
Improving raspberry immunity to a witch’s broomstick is facilitated by proper care, treatment is a complex process, only scientists are involved in it.
Streak or strip
Stripes or short strokes appear on the stems of annual shoots, the internodes are shortened. The leaves grow very close, the plates twist spirally, pressed against the stem. Affected bushes live no more than 3 years, then dry out. The yield in such plants is minimal, the quality of the berries decreases sharply. It is impossible to alleviate the symptoms or cure raspberries.
Curly hair
The first symptoms are noticeable on the leaves, they become stiff, curl up into a tube, the phenomenon is accompanied by a change in the color of the plate, at first large brown spots appear, with time they dry out. Berries are deformed, acid predominates in taste.

Aphids and nematodes spread the disease, and the virus is also transmitted by poor-quality planting material. There are no treatment methods, the virus spreads quickly, diseased bushes die in 2 years.
Ring spotting
The virus develops very slowly, but it is dangerous because at the initial stages of its manifestation you can only notice in spring or autumn. Leaves acquire small yellow spots, curl, thin out, become very fragile. Bush development slows down.

Severe symptoms are observed in the second year after the lesion, the number of depleted leaves increases significantly, yield decreases. After 3 or 4 years, the raspberry will dry out. The carrier of the disease is a nematode living in the soil. Prevention:
- when the first signs of disease are noticeable, the affected bushes are uprooted, the soil in the entire area with raspberries is treated with nematicides clearly according to the instructions;
- raspberries are not planted after cabbage, tomatoes or strawberries. Legumes will be the best predecessors.
When growing vegetables, siderates help drive nematodes, unfortunately, when planting raspberries, this method will not work.
Fungal diseases
Fungi are the most common and harmful microorganisms that affect raspberries, they make up 80% of all possible ailments. They penetrate the plant tissue through various, even the smallest, injuries. Carriers can be pests, and the disease can also be populated in raspberries with unhealthy seedlings.
Anthracnose
On the leaves along the veins and closer to the edges of the plate, small spots with a gray core and a brown, blurred border are observed. With severe damage, the foci grow together, the leaves curl, crumble. Small depressed ulcers form on the petioles, which grow together over time and crack. The tips of the annual and biennial shoots are also covered with grayish sores with a purple border. The fabric gradually cracks, becomes completely gray.

As the disease spreads, the spots pass to the fruiting branches, ring them, which leads to drying out. Berries are deformed, become one-sided, acquire a brown hue, dry.
On the gray spots, a large number of spores are formed, which develop well in a humid environment. Spores hibernate on affected shoots and leaves, in spring young leaves and branches quickly pick up the disease. Anthracnose is spreading rapidly. Prevention and treatment:
- in the case when the seedlings were bought in unverified places, the planting material is disinfected (rinsed whole) in a 1% solution of copper sulfate;
- severely affected parts of the bush are cut out, they cannot be completely cured, all fallen leaves and berries are removed from the raspberry;
- in early spring, when the buds are still sleeping, the bushes are sprayed with a 3% solution of Nitrafen or 4% with a mixture of Bordeaux fluid. During the period of active vegetation, raspberries are treated with 1% Bordeaux liquid or with drugs such as Ftalan, Kaptan and Tsineb, clearly according to the instructions.
Small areas with raspberries can be treated with antibiotics - Nystatin (100 ml per 10 liters of water) or Griseofulvin 1.5 grams per bucket of water.
Botritis (Gray Rot)
Berries are the first to suffer, separate, soft, brown spots appear on them, they grow rapidly and lead to decay of the fruits, which are covered with a grayish, velvety coating. Ringing brown spots form on the stalk, which leads to the drying of still unripened ovaries.

On the leaves, botritis appears as wide, blurry gray spots. With a severe defeat, elongated spots form on young shoots, branches lose their winter hardiness.The causative agents of gray rot live in plant debris, in the soil and on its surface. Outbreaks of fungus are observed in cold and damp seasons, the main risk is thickened planting, under such conditions, the disease captures all the bushes in just a week. How to treat:
- raspberries are regularly thinned out, fallen leaves, weeds and old mulch are removed, the soil is periodically loosened;
- Strawberries and garden strawberries are not planted next to raspberries;
- in the case when the bushes are not severely affected, all diseased branches are cut, after harvesting the excess and weak shoots are removed at the root, burned;
- before the kidneys swell and before the ovaries appear, they are sprayed with 3% Bordeaux liquid, and the soil between the rows and bushes is treated with a 2% Nitrafen solution. During budding and after picking berries, raspberries are sprayed with colloidal sulfur (100 grams of suspension per bucket of water). Tsineb or Albit is also suitable.
In the event of a massive defeat, raspberries can no longer be saved, the bushes are uprooted, and new seedlings are placed elsewhere.
Verticillus Wilt (Verticillus Wilt)
The disease leads to serious loss of raspberry crop. The fungus lives in soil at a depth of up to 35 cm for about 15 years. The disease penetrates through the roots, the disease spreads very quickly throughout the bush, and after the cold winter and spring the manifestations of the disease are more severe, but the peak (complete drying of the shoots) of the disease reaches its peak in hot, dry weather.

The lower leaves are the first to suffer, it is from them that you can determine the early stage of the disease. The plates turn yellow sharply and immediately fall off. Shoots cease to develop, the bark acquires a bluish tint, the tips of the branches wilt, turn yellow and dry. The bush itself will die within 1 or 2 seasons.
Fungicides before verticillosis are powerless. Soil fumigation (increasing the pathogen population) gives good results, but this method is very costly, it is easier to remove damaged bushes and crush raspberries in another place. There are no varieties resistant to the fungus, therefore, the main prevention will be the observance of agricultural technology and the purchase of seedlings in nurseries with a good reputation.
Rust
The disease is especially dangerous in regions with wet summers. Manifestations of rust are clearly visible - on the outside of the leaves small, rounded, slightly convex, bright orange spots form. After a short period of time, such pads form on the petioles and on the main veins of the plates. On the annual shoots, small gray ulcers with a reddish rim appear, which quickly fuse together and form longitudinal cracks.
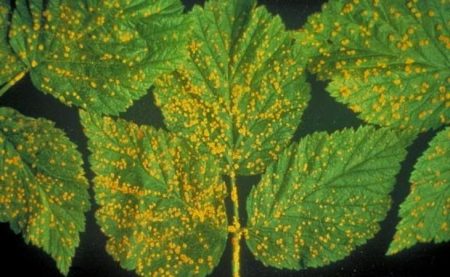
The fungus overwinters on plant debris; in the spring, primary infection of plants occurs. After a couple of weeks on the back of the leaves, light orange, then brown pads form, from which spores come out that infect raspberries in the summer. Under favorable conditions, several generations of fungus appear during the summer and autumn. In dry weather, rust development stops.
In autumn, the leaves become covered with a dark coating (wintering spores), dry and fall off. The disease negatively affects the immunity of raspberries to frost, reduced productivity. How to cure:
- in autumn, cut off all infected parts of the bush and burn;
- leaves can be removed from raspberries or shallow digging with a seal of fallen leaves, soil microflora destroys spores in 30–35 days;
- in spring, raspberry beds mulch manure, the microorganisms in it are also able to destroy rust spores;
- with severe damage to the bushes before budding, the spraying procedure (3% Bordeaux liquid) is combined with top dressing with 2% potassium salt.
In the summer period (before fruit setting), several more sprayings are carried out with a weaker solution of Bordeaux fluid.
Didimella (Spotting purple)
The initial stage of the development of the disease is accompanied by the appearance of blurry spots at the base of the shoots.At first they are greenish-yellow, homogeneous, then they turn brown, the central part is covered with small dark patches. Next spring, the spots brighten. On the leaves, didimella appears as large necrotic spots.

Foci of infection appear on the petioles and fruit branches, they ring shoots, this leads to drying of the berries. Covering scales appear on the kidneys, a significant part of the kidneys freezes over the winter.
Wintering of the fungus takes place in the tissues of the affected parts of the plant, spores spread in spring and summer. First of all, purple spotting affects sick, weakened plants, for example, damaged by gall midge. The disease enhances development in humid weather, and thickened raspberry plantings are considered especially dangerous. How to deal with the disease:
- when the kidneys swell, the bushes are sprayed with 3% Nitrafen solution or 4% with a mixture of Bordeaux liquid;
- before flowering and after full harvest, raspberries are treated with 1% Bordeaux liquid or Phthalanum (see the concentration on the packaging).
Branches with signs of critical damage are cut out, they are removed from the raspberry, along with fallen leaves.
Septoria (White spotting)
The first symptoms become noticeable at the beginning of summer, roundish, brown spots appear on the leaves. Over time, the center of the foci brightens, acquires black dots (mushroom pycnids). The affected areas of the leaf are partially destroyed, over time, the spots grow together, the leaves dry out and fall off.

Septoria is actively developing throughout the growing season of raspberries. The disease spreads rapidly, which contributes to increased humidity at moderate temperatures. Leaves massively dry, fall off, cracks form on the shoots and branches. Plants lose their hardiness, productivity is greatly reduced. The fungus overwinters on the affected parts of the bush and on plant debris. Methods of struggle:
- in autumn, all branches where lesions were observed on the leaves are cut to the root, the leaves are harvested and burned, weakened shoots are also removed;
- 2 weeks before the onset of frost and in early spring, the bushes are sprayed with Tsineb, and the aisles are treated with Nitrafen (2%). For spraying before flowering and after harvesting take 3% Bordeaux liquid or drug Albit, the concentration is specified by the seller.
Spores of the fungus live up to 2 years, while they may not appear at all. In no case should the affected bushes be propagated.
Ulcerative spotting
A common problem that occurs in old stands or with insufficient care. On the basis of young shoots, longitudinal brown spots are observed, which eventually become gray, crack, peel off. The following year, the foci grow, ring shoots. During fruiting, the young shoot dries. Floral branches can also be affected, they turn brown and dry.

Pycnidia hibernate in the affected stems, the primary damage to healthy tissues occurs in the spring. In the cold, rainy summer, the fungus spreads at lightning speed, it does particular harm to weak bushes, or affected by pests. How to cure raspberries:
- after harvesting, pruning is carried out. For the procedure, days with dry weather are selected, first of all, biennial shoots are removed, and also weak and all affected branches are cut;
- in early spring, raspberries are treated with 2% Bordeaux liquid. The following sessions are carried out during the flowering period, and also immediately after it, using drugs such as Impact, Fundazol or Topsin, following the instructions. When all the berries are harvested, raspberries are sprayed with Cuprocin (0, 4%).
When buying seedlings, carefully inspect the stems for flaky areas; in spontaneous markets, infected planting material is quite common.
Powdery mildew
The fungus is manifested on the tops of shoots, leaves and berries. A light gray, cobweb-like plaque forms on the affected organs.On the leaves, foci are observed on both sides of the plate; the berries are as if powdered with flour. Active development of the disease is observed in the summer, favorable conditions - heat with high humidity.

Shoots slow down growth, some plants dry out, yields are greatly reduced, the remaining fruits are smaller, deformed, lose their taste, acquire an unpleasant smell, they are unsuitable for consumption. Treatment and prevention:
- in autumn, the leaves are removed, the affected branches can not be completely uprooted; only the diseased parts of the stem are allowed to be cut;
- bushes must be thinned out, nitrogen-containing fertilizers applied in moderation, the main emphasis is on mineral complexes and organics;
- before flowering and after harvesting raspberries are sprayed with 1% colloidal sulfur.
All fungal diseases develop well in a humid environment, raspberries should be placed in sunny areas with light, permeable soil. Otherwise, the prevention of fungi consists in observing all the rules of agricultural technology. In most cases, chemical treatments cannot be dispensed with, traditional methods of control give a short-term effect.
Bacterial diseases
Another common group of raspberry diseases, it is not extensive, but ailments are found everywhere, in any climatic zone of Russia and other countries.
Root cancer
The popular name of the disease is "goosebump of the roots." Favorable conditions for the development of root cancer are dry weather and long raspberry cultivation in one place. On rhizomes and small roots, at the base of the shoots, tumors are formed, the size of a walnut, sometimes larger. The growths have a tuberous surface, on top they are brown, and inside light, very dense. Bacteria quickly pass from one plant to another, but they do not persist in the soil for a long time, they are destroyed by antagonist microbes in 1 or 2 years.

In the soil, where the acidic medium is 5 pH, the cancer stops developing, but under the influence of the vital activity of plants it quickly recovers, acquires an aggressive form, which causes a sharp, massive lesion of raspberry. In acidic soils, the bacteria die. Cancer penetrates the stems and roots through various injuries.
Sick plants slow down in growth, the roots practically do not develop, the leaves turn yellow, fall off ahead of time, the berries become small, dry out. Significantly reduced productivity, resistance to frost and disease. How to protect raspberries:
- varieties resistant to root cancer do not exist, when buying planting material, the roots and base of the stems are examined carefully, even small atypical growths can be a sign of damage;
- if the plants are not treated, bacteria accumulate in the soil, pathogenicity can be reduced by planting legumes and cereals in the aisles;
- when old bushes are damaged, they are uprooted and thrown away, young plants can still be saved. They are dug up, tumors are cut off, processed in copper sulfate and planted in a new place.
There are no drugs to combat the disease, for the prevention of raspberries, they are promptly fed with phosphorus-potassium and organic fertilizers, in especially dry periods, they are irrigated. Raspberries are not placed in places where crops leached soil grew.
Stem cancer
The disease causes general depression of the bush, bacteria affect the stems and branches of raspberries. On them, growths form in the form of white ridges, later they change color to brown, become hard. Also, the disease manifests itself on the leaves, pedicels and flowers. Sometimes growths ring the stems, but mostly only the lower and middle parts are affected. In the spring, affected kidneys swell, become loose, and die. Cancers break the stem over time.

At high humidity, lesions quickly decompose, a viscous, mucous mass envelops the stem. Bacteria develop inside the branches, often the lesion foci are more extensive than can be seen by external signs. The disease is active all summer and autumn, bacteria winter in the stems, but can persist in the soil. The disease is transmitted with planting material, spreads very quickly.
As in the case of root cancer, there are no chemicals to combat the disease, and preventive measures are of great importance. Sick bushes uproot, even if the stage of development of the bacterium is weak, with a strong defeat for raspberries, another area with healthy soil is isolated. When preparing the soil for planting, it is enriched with manure. In the same place, culture can be planted no earlier than 3 years later.
Raspberry Pests
Pests often cause significant damage to raspberry plantations, especially if timely treatment against them is not carried out. Insects are carriers of diseases, in the process of their life they cause damage to the bushes, through which viruses, bacteria and fungi easily penetrate.
Stem and shoot gall midge
The pest is also called a raspberry mosquito, due to the apparent external similarity. Gall midges harm berries, young stems, cause premature yellowing and falling of leaves. Productivity and immunity of the plant is greatly reduced.

Larvae form annular swellings or growths (galls) on the stems, the outer tissue coarsens and cracks, and the inner one turns into dust. Most often, growths are observed in the lower part of the shoots, the stems become fragile, easily break off. It rarely happens that galls are formed of 5 or 7 pieces at a small distance from each other. If you break a branch at the site of swelling, you can find a small, mobile larva of yellow-green color.
In a certain phase of development, the worms get out of the Gauls and go to the ground, where they pupate and winter. The insect years begin in May, when the soil warms up to 13 degrees. The female lays eggs in cracks and other damage to the bark; over the entire season, it can give several generations. How to drive away an insect:
- during the raspberry growing season, the bushes are inspected for bloating, the lesion site is carefully opened with a knife and a larva is taken out or the stem is cut under the root;
- in the spring, before the swelling of the kidneys, the raspberry is treated with 3% Bordeaux liquid, the procedure will serve as a prophylaxis of didimella, it is noticed that on the bushes affected by the fungus, the gall midge is rampant with particular force;
- nitrogen fertilizers should be applied in moderation, uncontrolled top dressing leads to excessive build-up and cracking of the bark;
- in autumn, the soil around the bushes is dug up and mulched with peat (layer up to 15 cm).
Chemicals do not give good results, since the pest wields in the stems, for extra protection in early spring cut the buds, which are formed at a height of up to 80 cm from the ground, when the shoots grow a little, at the base of the lower green branches cut off all the leaves.
The stem gall midge affects not the fruiting stems of raspberries, but the young shoots. Gauls appear on the side shoots in the form of a small, uneven, brown cone with a smooth or slightly rough surface. Several larvae live inside the swelling at once, here they pupate and winter.
Small mosquitoes with a brown back and transparent wings fly at night. Swelling of raspberry overgrowth can be found between August and November. It is necessary to fight with the stem gall midge as well as with the shoot. It is noticed that the onions and garlic planted around the perimeter of the raspberry, scare away insects. Throughout the season, bushes can be sprayed with infusions and steep decoctions of wormwood or walnut leaves, the gall midges do not like their aroma.
Stem fly
The main harm is caused by larvae; they look like small white worms.Adults lay eggs in the upper leaves of the leaves, the hatched larva bites into young shoots and feeds on delicate tissue, moving down. External signs - the top of the shoot withers, blackens and rots in the longitudinal section of the twig, you can detect the pest itself and its moves.

When the bushes begin to bloom, the larva burrows in the soil, pupates there. In early spring, a small fly with a thin, elongated, segmented body and translucent white-black wings will fly out. The beginning of summer coincides with the period of growth of young shoots. How to drive away an insect, prevention:
- before the start of summer flies, young plants are treated with Actellic or Spark;
- in the autumn, the soil around the bushes is dug up;
- check the condition of young shoots in the spring, a sign of defeat by a fly will be a halt in the development of the upper part of green branches, the growth point is shortened and stops its development. When such specimens are found, they are gradually cut from top to bottom, the entire part of the branch, where there are larvae moves, is removed, the plant remains are immediately removed away from the garden.
With severe damage, the bushes are uprooted, and the soil is dug up. Folk recipes in the fight against the stem fly give a very weak effect.
Shoot aphid
Adult individuals are winged, at the initial stages of development they are wingless. Taurus up to 2 mm in length, light green, matte. The eggs are very small, black, shiny, wintering near the buds, in spring, as soon as the weather is warm, the larvae emerge from them and move to young leaves, feed on their juice.

Over the entire raspberry growing season, several generations of aphids are born. Leaves affected by the pest gradually turn brown, insects move to other branches and to the root shoot. The result of aphid activity is twisting of leaves, curvature and poor development of shoots. The annual growth is reduced, the internodes are greatly shortened, the flowers on the weakened shoots dry out and crumble, the yield and immunity of the bushes decrease. Heat and drought are favorable conditions for the propagation of shoot aphids.  How to fight:
How to fight:
- before the swelling of the kidneys, raspberries are abundantly sprayed with the insecticide Preparation 30, it is intended for the destruction of wintering insect eggs;
- in a small population, the tops of shoots with aphid colonies are cut and burned;
- during flowering, bushes are treated with infusions of tobacco, yarrow or chamomile. The amount of ingredients can be adjusted independently, the main thing is that the finished solutions have a pungent odor, soap is added to the infusions to enhance the effect;
- as soon as the first individuals become noticeable, raspberries are treated with infusion of green soap - 30 grams per liter of water;
- with a severe defeat, it is permissible to treat the bushes with Kinmix, but only before flowering and after picking berries.
Aphid does not appear on its own, well, or this rarely happens, mainly ants bring it. Inspect the raspberry for the presence of anthills, find their moves and try to get rid of the ants first.
Raspberry and strawberry weevil
The first individuals appear in early spring, they feed on young leaves, leaving small holes on them. When a plant throws flowers, female weevils lay one egg at the base of the buds. In total, the insect makes about 100 clutches. The larvae bite into the buds, eat them from the inside, the flower darkens, dries and falls. If you break such a bud, a small white worm with a yellow head will sit in it.

Larvae pupate in fallen flowers; in mid-June a small black beetle with an elongated spout emerges from them. Over the entire season, the pest will give 2 or 3 generations, the first 2 will eat leaves, stems and flowers. Prevention and treatment:
- if the raspberry is small, then in early spring, when the snow has not yet melted, the beds are shed with boiling water, the procedure will not harm the roots, but it will destroy part of the wintering pupae;
- before flowering and after fruiting, the bushes are treated with Karbofos (50 grams per bucket of water), you can use Spark, Confidor or Actellik;
- during flowering and fruit setting, raspberries are sprayed with a strong decoction of tansy, soda (2 tbsp. per bucket of water) or a solution of mustard powder - Art. l for 10 liters of water.
The pest overwinters in fallen leaves, in the autumn they are removed from the site.
Raspberry beetle
Many could observe a rather unpleasant phenomenon - white worms in raspberry berries. The blame for this is a raspberry beetle that lives all year round near bushes of culture. In the spring, insects feed on pollen from weeds, in May, before the raspberries bloom, bugs move to it. The pest lays eggs on young ovaries, as the fruit is poured, the larvae also grow. Berries are deformed, minced and rot.

Adult larvae leave the soil at the end of August, pupate and hibernate at a depth of up to 30 cm.The insect lays up to 40 eggs per season, it can spoil up to 15% of the crop, so the fight against it should be started as early as possible.
What to do:
- in spring, when buds open, the bushes are sprayed with potassium permanganate (0.5 grams per bucket of water). Before flowering use INTA-VIR. As soon as the buds appear, they are treated with Fitoverm or Spark;
- during the formation of buds, some gardeners collect the beetle by hand and destroy, the morning is considered a favorable time for the procedure, when the individuals are still inactive;
- during budding, flowering and the appearance of ovaries, the bug can be scared away by treating the bushes with a strong decoction of flowering tansy - half a bucket of grass is poured with water, boiled for about 20 minutes, filtered. A liter of broth is diluted in 9 liters of water.
For prevention in spring and autumn, the soil in the raspberries is loosened, all weeds are harvested during the season, and onions and garlic are planted around raspberry beds. Under digging or loosening make wood ash, a glass per square meter.
Glassmaker
Raspberry glass-box looks like a small blue-black butterfly with a thin body (yellow stripes are present on the body). The insect begins in June – July; females lay eggs in the soil around raspberry shoots or at the base of the stems. Larvae bite into the branches, making moves, feed on their flesh. Worms can climb the stem or sink to the roots.

In places of damage small swellings form. From the influence of the pest, the raspberry stalks become fragile, stop their development, sometimes the bush fades and dries. Adult caterpillars are white with a yellow head and chest pads, their length reaches 30 mm. The pest hibernates in the stems or on the roots. How to get rid of glassware:
- if possible, mechanical damage to the bark of raspberry stalks should be avoided and weeds should be weeded in a timely manner. The bushes are periodically inspected, the glass-box leaves tubercles on the branches. Affected bushes, weak, dry and prolific stems are cut to the root and burned;
- soil from May to July should be periodically loosened. Before budding, raspberries are treated with Karbofos (60 grams per 10 liters of water). As soon as the first leaves begin to appear, the bushes can be sprayed again with 3% Bordeaux liquid.
Glassmaker is rarely observed in well-groomed raspberries. The pest has a lot of insect enemies that need to be protected. In order not to ruin the natural defenders of raspberries, follow the rules of agricultural technology, use chemistry last.
Ticks
One of the most common pests of raspberries is a spider mite; it does considerable harm to plantations from spring to late autumn. Arachnids, small parasites can be brown, milky, light yellow or pale green. Ticks at any stage of raspberry development live on the back of the leaves, feed on their juice, wrapping these places with a cobweb. On the upper side, the plate becomes roughened, and the places of the bites are highlighted by sores.

First, ticks appear between the veins of leaf blades, in advanced cases they spread throughout the bush and cover it with a continuous web. The plant stops its development. How to fight:
- the tick is not an insect, which means that traditional insecticides against it are powerless. For processing, acaricidal and insectoacaricidal agents are chosen, for example Fufanon, Acrex, Actellic and Antio. You can also use biologics - Akarin, Bitoxibacillin and Fitoverm;
- treatments can be carried out before the fruit sets and after the harvest, chemicals alternate, ticks quickly develop immunity to them;
- of effective folk remedies, we note the garlic infusion - 150 grams of chopped garlic is poured with a liter of water, covered and insisted for 5 days. The resulting concentrate is diluted with water (5 ml per liter of water);
- if the tick affects young shoots of raspberries, the cotton wool is moistened with alcohol, gently wipe the stems and leaves.
If desired, you can cook an infusion of onions or garlic (20 grams of chopped vegetables per liter of warm water, leave for 2 hours). Processing is carried out throughout the season. Without compliance with agricultural technology, the pest cannot be disposed of.
Sawmill raspberry forest and yellow-winged
Sawmills destroy up to 60% of raspberry leaves, insects for the entire growing season of the crop give 3 generations, each takes 35 days to complete development. Kinds:
- Forest sawfly is a hymenopteran insect with transparent wings, the larvae have 8 pairs of legs, the body is green with a dark line on the back, the head and chest are yellow-green. Larvae bite into leaves from the underside.

- Yellow-winged sawfly - imago body length not more than 8 mm, head and chest black-blue, abdomen yellow-brown. The wings are transparent, yellowish at the base, brown in the middle, and darkened towards the apex. Larvae are green with a yellowish head.

A larva or pseudo-caterpillar eats away leaf plates, forms holes on them, sometimes leaves are united from the edges, and in advanced cases they are skeletonized. Basically they do not touch young leaves, eat already ripe. Caterpillars winter in cocoons, in fallen foliage. For years, the insect begins in mid-May. With a strong defeat of raspberries by sawflies, productivity and winter hardiness sharply decrease, shoots practically do not form axillary buds for the next year's crop.
After harvesting and before setting the berries, they are sprayed with drugs such as Karbofos, Kinmiks, Fufanon, Confidor and Fosbetsid. Particular attention is paid to thinning raspberries, harvesting weeds, fallen leaves and old mulch. Before wintering, the soil is loosened. In the summer, when it is impossible to carry out chemical treatments of the caterpillars, they are collected manually, in hot weather they can hide on the back of the leaves.
Raspberry nutcracker
The insect is no longer than 3 mm with a black, thin body, the larva is white, legless up to 1, 5 mm, feeds on stem tissues, gall-like growths form in these places. Damaged stems become brittle. Larvae hibernate in growths, pupate in spring, already at the end of May, adults emerge from the pupae, females lay on young shoots.

How to fight:
- timely trimming of stems with galls (under the root);
- with swelling and blooming of the kidneys, the raspberry is sprayed with Kemifos or Fufanon;
- from folk remedies, dusting with tobacco dust (in May and June) gives a good result.
In order not to confuse the nut grower with other insects, the galls open and inspect the larvae.
Scoop
Raspberries are affected by several types of scoops, they all feed on the berries and leaves of the plant. Pay attention to the most common form - raspberry golden scoop. A moth with a wingspan of up to 3.5 cm. Caterpillars are gray-brown with a white line on the back and gray side stripes. The caterpillar feeds and develops in May, the pest overwinters in plant debris and in the soil overwintering.Vital activity of the pest leads to a decrease in productivity, the growth of shoots slows down due to improper distribution of food.

When the leaves open, raspberry bushes are sprayed with Kemifos, Actellik or Fufanon, the treatment can be repeated until the buds appear. All plant debris is removed in the fall, the earth is loosened.
Fruit mowing
Weevil up to 9 mm in length, body covered with bright, yellow, shiny scales and small villi, the beetle itself is black. Larvae are thick, dense, white, curved with a yellowish head, feed on the juice of grass roots, live in weeds. Pupae are yellowish with distinct legs, wings and proboscis. Beetles come out in early spring, they gnaw the rudiments of leaves and buds. Skosar is a large-eating and very voracious.

You can drive away the pest with the same drugs that are used to combat the scoop, but Actellik gives the best results. The first treatment is carried out before the buds swell, the second when the young leaves bloom, the third before flowering, and the last after harvest. For prevention, weeds are harvested not only in the raspberry, but also around it.
Raspberry flea
The insect is a small, black with a blue tint, bounce beetle. It causes harm from early spring, gnaws small areas on young leaves, leaving behind small ulcers. With the advent of offspring, beetles move to them. Wintering of fleas takes place under the remains of plants in construction waste.

The pest is especially active and voracious in dry, hot weather; during the years of mass reproduction, colonies can greatly weaken fruit-bearing branches, which will certainly affect yield. The period of greatest congestion falls on the last month of spring and at the beginning of the summer season, in the middle of July the second generation is born. Control measures:
- in the spring the bushes are treated with Fufanon;
- with a severe defeat during the period of budding and ripening of berries, you will have to sacrifice the crop and repeat spraying;
- Intestinal poisons give good results - treatment (before buds open) with 0.15% Parisian herbs mixed with 0.2% potassium arsenic.
For prevention, the raspberries are kept clean, weeds removed in a timely manner and all garbage removed.
Two-spotted Cloak
A small beetle with a thick, shortened, stocky body, a black head with a steep forehead pulled into the neck shield. Elytra black with orange, broad transverse spot at apices. The beetle eats from May to June, gnaws young leaves. Control measures include manual collection and destruction of the beetle, as well as preventive and eradicating chemical treatments. Actellik and Fufanon are used against the cryptograss, spraying is carried out before and immediately after the buds open, and also when all the berries are collected.

We repeat, the emergence of diseases on raspberries is often closely associated with the life of pests, and insects are primarily fond of groomed areas. Therefore, do not spare time for raspberries, watch for cleanliness around it. If the problem appears, solve it immediately, now it will be easier for you to recognize and eradicate it.



 Black raspberries in autumn: care and preparation for winter shelter, pruning
Black raspberries in autumn: care and preparation for winter shelter, pruning Features of planting raspberries in the fall and care for it
Features of planting raspberries in the fall and care for it Proper care for raspberries in the fall and its preparation for winter
Proper care for raspberries in the fall and its preparation for winter Care for maintenance raspberries in autumn: pruning and top dressing
Care for maintenance raspberries in autumn: pruning and top dressing