Juniper is a popular culture among plant growers, which is often planted in personal plots. To obtain new seedlings, gardeners often want to independently carry out the whole process.
Reproduction of juniper by cuttings in the fall is permissible. In a way, this period for the propagation of culture, gives a better result than the standard period - spring and summer seasons. Often, spring and summer are too hot and arid for the juniper, so the survival rate of the cuttings becomes worse.
Content
Types of juniper for cuttings
 Often, after planting one instance of a coniferous plant, a person wants to get new plants, but without money. For such purposes, the preferred option is the cutting of juniper. Thus, from one adult plant you can get such a number of seedlings, which is enough to ennoble the entire house area. But, the juniper propagates not only by cuttings, but also in other ways:
Often, after planting one instance of a coniferous plant, a person wants to get new plants, but without money. For such purposes, the preferred option is the cutting of juniper. Thus, from one adult plant you can get such a number of seedlings, which is enough to ennoble the entire house area. But, the juniper propagates not only by cuttings, but also in other ways:
- seed material;
- dividing the bush;
- layering.
Cuttings are the simplest method that allows you to get a young plant with all the signs of the mother plant. But, not all types and varieties of juniper are permissible to propagate by cuttings, for some, a more natural option is the division of a bush or layering. Cuttings are a good option in the case of a new planting material for the following types of coniferous crops:
- Ordinary - the height of the bush or tree is 5-10 m, the trunk diameter is about 20 cm. The crown is dense, bushy, in the case of shrubs - ovate. The bark is brownish gray. The needles are trihedral, pointed, rich green color. The most popular varieties are Green Carlet, Montana and Depress.
- Verginsky - the ovoid crown, narrowed, with the growth of the specimen becomes more fluffy. The bark of the plant is first greenish, dark, but with age acquires a brownish-scarlet or dark brown color. Small scaly or needle-shaped needles, painted in dark emerald color. Popular varieties of the species - Robusta Green, Gray Oul, Glauka.
- Cossack - a bush, creeping. The height of the bush does not exceed 1.5 m. The species grows rapidly and rapidly. The needles are painted in a dark turquoise color, it is needle-shaped in young plants and scaly in adult specimens. There are tree-like options for Cossack. Their height reaches 4 m.
- Horizontal - a bush of creeping nature. Branches are elongated, shoots are dark turquoise, tetrahedral. The needles are bluish-green. In winter, the needles are often painted brown. Fruits are bluish-black, with a bluish bloom. Popular varieties among gardeners: Andorra Compact, Lime Glow, Prince of Wales, Plumosa.
- Chinese is a tree-like form, the height of the specimen is 8-10 m. A crown of a pyramidal nature, less often - the species is expressed by an open bushy bush. The crust is grayish-red, exfoliating. Needles needles and scaly. The most popular varieties among plant growers are Olympia, Gold Coast (green-golden needle-like leaf blades), Yaponika, and Strakta.
- The middle one is a hybrid of Cossack and Chinese. The shape is bushy, the shoots are curved in an arc. The height of the adult representative is 3-5 m.The most popular varieties are Gold Star and MintJulep.
- Scaly - shrub up to 1.5 m in height. The bark is rich brown, coniferous hard and sharp. Cones are black. The most popular varieties are Blue Star, Roderi, Meyeri.
- Rock - a bushy or tree-like plant, up to 18 m high. The crown of rounded shape, actually begins with the base of the trunk. Young shoots reach a thickness of 1.5 cm. Painted in faded green or light turquoise. Sheet plates are needle-shaped, but more often - scaly. Common varieties are Skyrocket, Springbank and Relens.
This is a general list of species that can be successfully propagated by cuttings.
Popular grades for cuttings
 Depending on the particular variety, juniper can propagate by cuttings easily, but some of the common varieties give better results when dividing the bush or in the case of obtaining new specimens by layering. Among gardeners, the following varieties are common:
Depending on the particular variety, juniper can propagate by cuttings easily, but some of the common varieties give better results when dividing the bush or in the case of obtaining new specimens by layering. Among gardeners, the following varieties are common:
- Mint Julep;
- Meyeri;
- Dream Joy;
- Holger;
- Hit;
- Lime Glow;
- Wiltoni;
- Gold Coast;
- Gold Mordigan;
- Curivao Gold;
- Golden Star.
Full success in the case of cuttings can be obtained using junipers of the following varieties:
- Meyeri - thick turquoise or dark gray-steel needles. Plant height - from 30 to 100 cm. In addition to cuttings, seed propagation is allowed.
- Holger - height up to 80 cm, leaf needle plates are painted in bluish-blue color.
- Curivao Gold is a vigorous variety, it is possible to get it with all the signs of the mother plant only by cuttings.
- Slag - “growth” up to 25 cm, crown - up to 150 cm in diameter. Propagation by seeds, layering and cuttings is allowed.
- Mint Julep is a mint-green color of the crown; new specimens can only be obtained vegetatively - layering and cuttings.
- Viltoni is a bluish-silver crown; when using seeds, the new plant loses the signs of maternal juniper. Only vegetative options for obtaining new Viltoni are suitable.
- Lime Glow - a dwarf, the crown is painted in a bright greenish-yellow color. In the fall season, foliage changes tone to bronze-copper. New copies are obtained by cuttings.
In the beginning of autumn and the propagation of juniper almost in winter - at the end of the autumn season, it has no differences from this process in the spring-summer season.
Drop-off date and procurement rules
 Cuttings are a cheap option for producing young conifers. This method has many advantages:
Cuttings are a cheap option for producing young conifers. This method has many advantages:
- preservation of varietal characteristics;
- the formation of powerful roots;
- high vitality;
- less susceptibility to pests;
- faster growing up;
- rapid survival and active development;
- the survival rate of cuttings is 2 times higher than that of seedlings.
It is possible to use cuttings for obtaining new conifers from spring to the beginning of winter.
Experienced gardeners prefer the autumn season. This is explained by the fact that the evaporation of water from the onset of cold weather does not actually occur, which favorably affects the state of planting material and its development.
Choosing certain dates for landing, you need to focus on climatic conditions. For better rooting of planting material, it is required that the room temperature be at a level of 5 to 25 ° C. Lower temperature indicators or a thermometer mark above the specified limits adversely affect the process of reproduction and can lead to a new plant death.
 You may be interested in:
You may be interested in:To obtain viable and resistant to adverse factors seedlings, blanks are taken exclusively from adult instances of conifers. Juniper must be at least 8 years old. But, it is undesirable that the age of the conifer is more than 10 years.
Depending on the place from which the stem was taken, the young conifer can subsequently develop in different ways. When the apical part of the juniper is cut off, the daughter specimen will tend mainly upward, and in the case of lateral shoots, to the sides. With a vertical crown, the cuts of branches on the cuttings are also performed vertically, and in the case of bushy conifers, side shoots are used.
Instructions for the grower
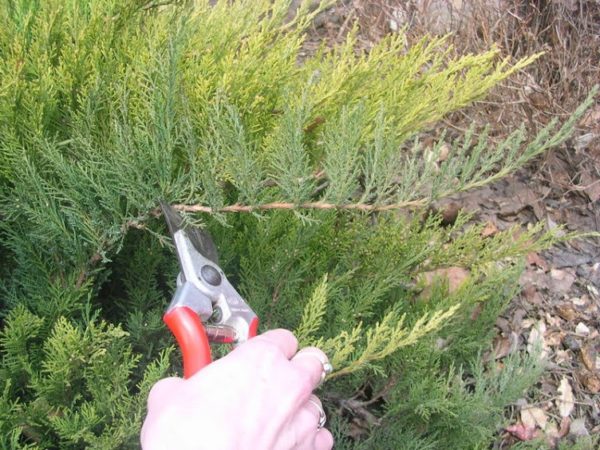 The plant obtained by cuttings, and which are planted in the soil, more easily tolerates the process of acclimatization and is better adapted in unusual conditions. Nevertheless, in order for the plant to receive not only the signs of the mother juniper, but also all the bonuses from the cuttings, it is required to follow a strictly verified algorithm and strictly observe agricultural technology.
The plant obtained by cuttings, and which are planted in the soil, more easily tolerates the process of acclimatization and is better adapted in unusual conditions. Nevertheless, in order for the plant to receive not only the signs of the mother juniper, but also all the bonuses from the cuttings, it is required to follow a strictly verified algorithm and strictly observe agricultural technology.
Material preparation
Before propagation of the juniper it is required to choose the right material for planting. In this case, powerful and healthy conifers will grow from cuttings. The main rules for the preparation of planting material are as follows:
- Experienced growers use 8-year-old junipers to preserve all the signs of a cuttings donor.
- The shoot cuttings are often cut off from the middle part of the mother conifer in the case of bush forms. In the case of columnar varieties, only apical shoots are used.
- Not lignified shoots are selected. Semi-lignified can be used, but more often young, still green, branches are used as planting material.
- Cut the shoot to the stalk in the early morning hours, when all areas of the juniper are full of moisture.
- In the course of cutting off the shoot, you need to capture part of the branch on which the stalk had previously grown, creating a “heel”. This contributes to easier and faster rooting.
- The optimal length of the cut shoot is 12 cm, but longer ones are also allowed - up to 25 cm inclusive.
- All work is performed with sharpened and sterile garden tools.
Preparing the cuttings involves 3 stages:
- The needles are cut with a sharp blade - the bark should not be damaged. Leave only apical, which are required for normal air exchange.
- The lower section is treated with a drug that stimulates the growth of the root system.
- After 1 day, the stalk-blank is placed in the prepared substrate.
Juniper is not recommended to root in water. In a humid environment, the bark begins to exfoliate from this conifer, which adversely affects the viability of planting material.
Substrate
 In many respects, the success of rooting depends on the soil mixture in which the juniper planting material is placed. The substrate should have the following characteristics:
In many respects, the success of rooting depends on the soil mixture in which the juniper planting material is placed. The substrate should have the following characteristics:
- high breathability;
- high moisture capacity;
- good friability.
First, prepare a nutritious soil mixture consisting of peat and sand, which are taken in equal proportions. To increase the moisture capacity and breathability of the substrate, a small amount of perlite and charcoal are added.
Rooting stimulation
Gardeners can use the drug for better and faster rooting of cuttings. The range of such compounds is significant:
- Kornevin - the drug is based on indolylbutyric acid. The solution is made at the rate of 1 g of product per 1 liter of water.
- Epin - improves immunity and stimulates the formation of the root system.A solution for use is prepared from 0.5 ml of the drug per 1 liter of water.
- Heteroauxin is a phytohormonal drug. The base is β-indolylacetic acid. 1 tablet requires 1 liter of water.
- Zircon is a complex multidisciplinary tool. Based on hydroxycinnamic acids. The solution for use is made up of 1 ml of the product and 1 l of water.
It is forbidden to violate the dosages indicated by the manufacturer, since the opposite process will begin - inhibition of root formation and planting material in general.
But, it is possible to use folk remedies:
- weak honey solution;
- composition based on potato tubers;
- willow water;
- yeast based product.
The cuttings are immersed by a third in a solution of a purchased or folk remedy to accelerate the rooting process, and the remaining part is used for adding to water, for irrigation in the future.
Planting the cuttings in the ground
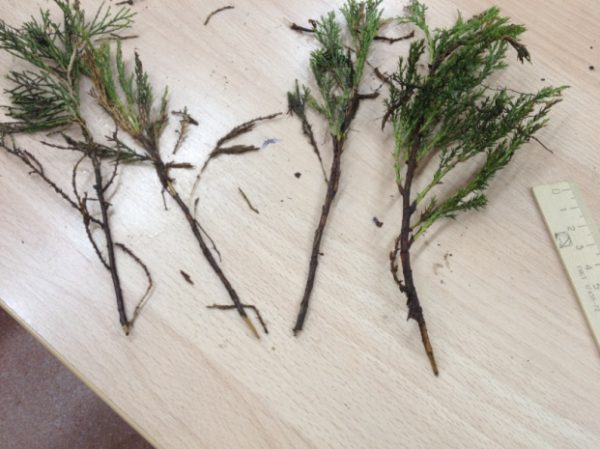 The process of planting the cuttings in the soil mixture is as follows:
The process of planting the cuttings in the soil mixture is as follows:
- A 3-4 cm hole is formed, a circumference of 1 cm. The stalk is placed in a hole, the soil around is slightly tamped and watered. When there are several cuttings in 1 container, there should be a gap of 6-8 cm.
- The temperature in the room is maintained at the level of 18-23 ° C. If the level of the thermometer is lower, the cuttings decay, and at higher temperatures, the soil dries and the roots dry.
- It is required to create the effect of a greenhouse - for this, the containers with cuttings are covered with cling film or transparent glass.
In the future, care involves maintaining normal lighting and periodic watering. The light should be scattered, direct contact with the sun's rays should preferably be avoided. Regular ventilation is required so that condensation does not collect under the shelter, otherwise the planting material will die.
Propagation by layering
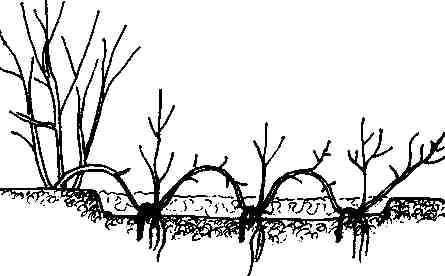 Juniper is easy to propagate by layering. This option for obtaining young instances of conifers is most often practiced in the case of creeping varieties of culture. Juniper branches bend to the ground and gently fix them to it. Often this is done using specialized studs or staples.
Juniper is easy to propagate by layering. This option for obtaining young instances of conifers is most often practiced in the case of creeping varieties of culture. Juniper branches bend to the ground and gently fix them to it. Often this is done using specialized studs or staples.
In places of juniper shoot fixation with soil, the earth needs to be periodically earthed up and moistened. To root successfully, exclusively young shoots are used for layering, which have not yet had time to lignify.
 You may be interested in:
You may be interested in:To accelerate the formation of the root system on the juniper layer, it is required to prepare the soil in advance. To prepare the soil, the following manipulations are required:
- they dig up the earth;
- excavated soil is loosened;
- peat and coarse sand are added to the soil.
Layering root for six months to a year. Cutting off cuttings from the mother conifer is permissible only after the juniper has developed and is actively growing. The separated layers along with the roots are transplanted to a separate, prepared for him, place of constant growth.
Care
 Active rooting of cuttings begins only 2-4 months after planting in the ground. These time frames are rather arbitrary, as they depend on the variety of juniper. At the same time, it is required to accept that in the summer season the formation of the root system can slow down before the onset of autumn coolness. The root system for such periods is not able to gain enough strength for open space, so it is recommended to leave the stalk in the greenhouse until the next warming.
Active rooting of cuttings begins only 2-4 months after planting in the ground. These time frames are rather arbitrary, as they depend on the variety of juniper. At the same time, it is required to accept that in the summer season the formation of the root system can slow down before the onset of autumn coolness. The root system for such periods is not able to gain enough strength for open space, so it is recommended to leave the stalk in the greenhouse until the next warming.
In order to prevent stagnation of water near the root system of the juniper, the conifer is required to be watered with the arrangement, allowing the ground to dry under the plant. For irrigation, they use settled water, which at its own temperature corresponds to the environment. To prevent fungal diseases during watering, several times a year, fugicidal formulations are added.
When the main part of the root system has already been formed on the cuttings and growths begin to develop, hardening is carried out. To do this, the greenhouse needs to be opened for short periods and fully ventilated. In the winter season, it is recommended to cover young plants with burlap, synthetic covering materials or leaf litter.
In spring, young juniper needs to be transplanted to a constant place of growth, for which plants are moved to prepared holes with an earthen lump, taking into account each of the points in the process.
Permanent landing
 One should not hurry with the planting of young juniper plants. This issue needs to be considered taking into account the full list of factors and rules:
One should not hurry with the planting of young juniper plants. This issue needs to be considered taking into account the full list of factors and rules:
- The planting period of rooted plants is selected taking into account the time for adaptation. If cuttings were harvested at the end of winter, the beginning of spring, then planting material can be planted immediately - the optimal period is 70 days from placement in greenhouse conditions. In the case of late harvesting, juniper hibernates indoors, subject to each of the conventions, until next spring.
- In the variant of a separate potted rooting of the cuttings, planting in autumn is possible. But, in this case, the plant is moved together with the soil and additional insulation is used. Prior to full adaptation in the open ground, juniper is highly susceptible to freezing risks, which is highly likely to lead to death.
- Preservation of a coma on the root system plays a major role - the roots of a young plant are easily damaged. The approximate dimensions of the landing hole 1 m2, relative to the earthen coma, they should be 2-3 times large. A drainage layer is placed at the bottom of the pit - this is taken into account in the question of depth with the condition of immersion of the cuttings to the root neck.
- Choosing a place for juniper planting requires bright diffused lighting. The only tolerance is the presence of light shading on one side. The exact terms of the procedure are also determined by this characteristic - if the length of the day has already increased, then there are risks of burnout of coniferous landscaping.
- While the plant is still small, the conifer is required to be protected from direct sunlight and winter frosts. The option of such protection is selected depending on the general conditions - for the winter, it is possible to cover the juniper or completely cover it with warming materials, and in the summer just arrange temporary shading on excessively sunny days.
Immediately after planting, the juniper needs to be watered - 1 bucket of water without auxiliary impurities is enough. In the future, the conifers are watered no more than 1 time per month. Juniper fertilizer in the spring requires the use of mineral fertilizers, for example, nitroammophos. With this composition, it is better to limit it to 45 g per m2. In the summer season, organics are used - compost or rotted manure. Also, top dressing is introduced in the case when the plant develops excessively slowly.
Watering
The duration of rooting of the juniper cuttings, subject to general conditions, is 60-80 days. This period requires constant maintenance of soil moisture. Watering is carried out through agrofibre at least 3-4 times a day.
In fact, the stalk should not dry out.However, rooting conifers in clean water should not be done, as this can cause the death of a new plant.
Advice
The main rule when choosing a shank for cutting and propagating juniper is size. Due to the dense structure of this coniferous plant, a stalk is selected not shorter than 25 cm.
It is also necessary to focus on the variety - in the case of creeping and shrubby species, a plant is planted at an angle of 45 °, and for upright (column-shaped) variants, the vertical is maintained.
Conclusion
The best option for propagation of juniper is cuttings. With full compliance with the rules, reproduction does not take much time. The result of the process is fully viable seedlings for growing on your own site.



 Aralia Manchurian - medicinal properties and contraindications, the use of tinctures in bodybuilding
Aralia Manchurian - medicinal properties and contraindications, the use of tinctures in bodybuilding Seedless pomegranate - cutaway appearance, benefits and harms
Seedless pomegranate - cutaway appearance, benefits and harms Dates - the benefits and harm to the body, how much you need to eat, properties and calorie content
Dates - the benefits and harm to the body, how much you need to eat, properties and calorie content The benefits and harms of mango for the body of women and men - how to eat it?
The benefits and harms of mango for the body of women and men - how to eat it?