Mold fungi existed on planet Earth long before the advent of mankind. These are very resistant organisms necessary for the normal existence of the natural ecosystem. Mold fungi are unsafe for humans, as they can lead to their death. But at the same time, they are of great benefit to humanity. Some species are used in medicine for the manufacture of antibiotics and save people from disease.
Content
Types of molds and their description with photos
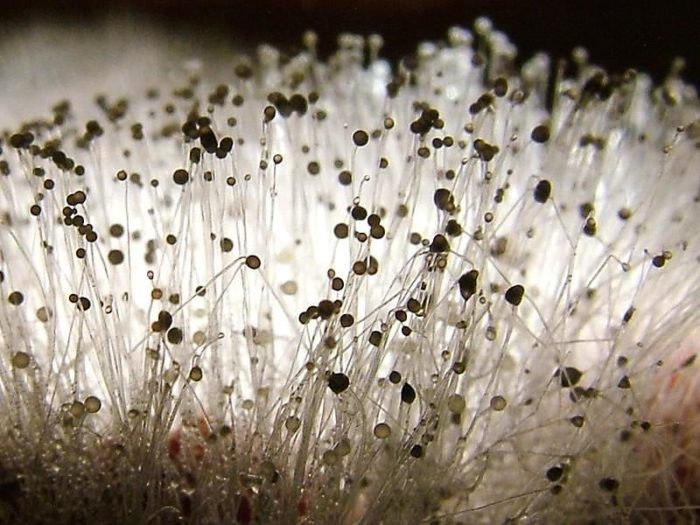
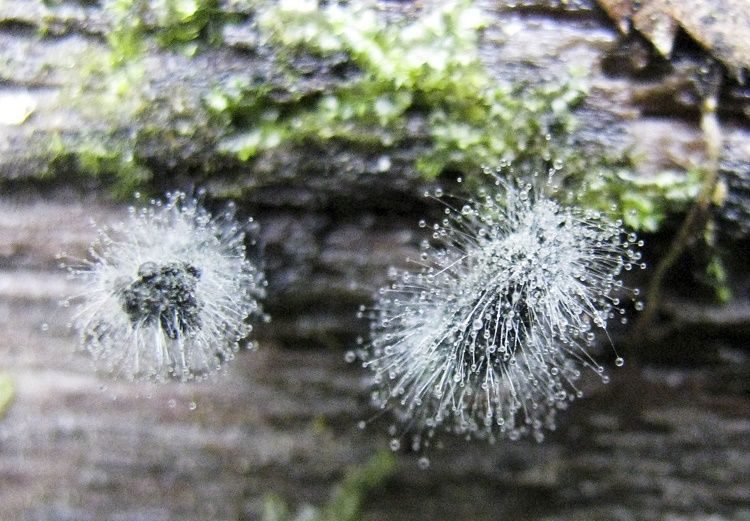
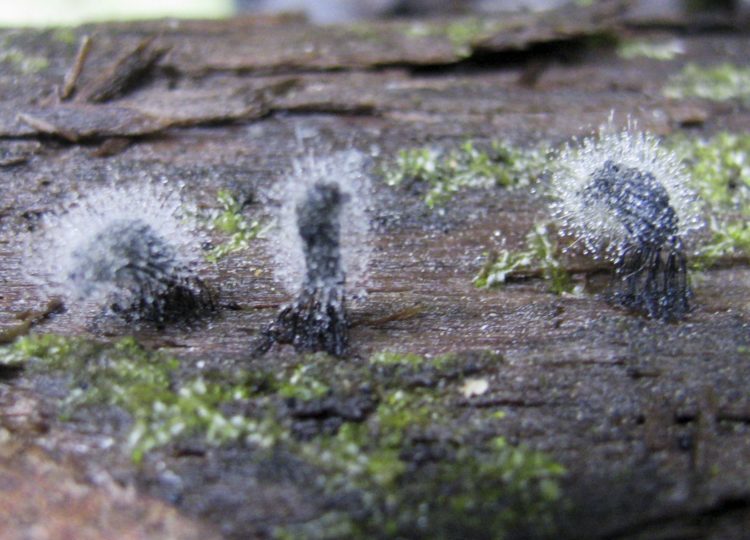
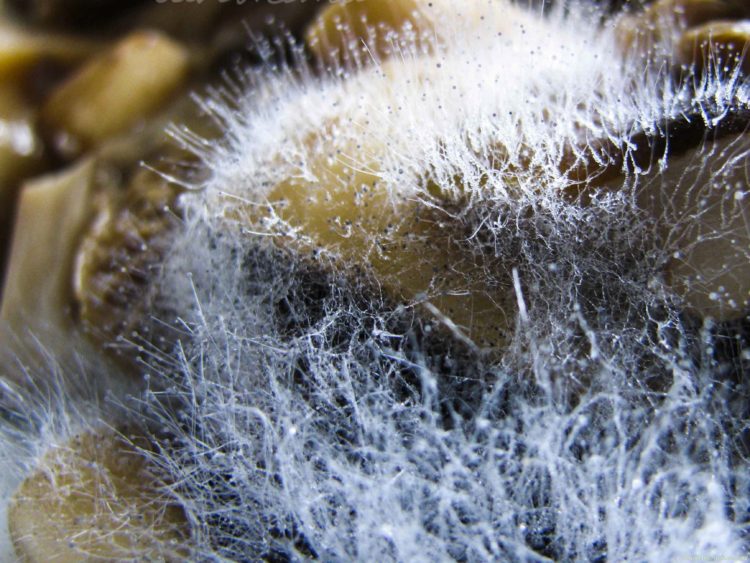
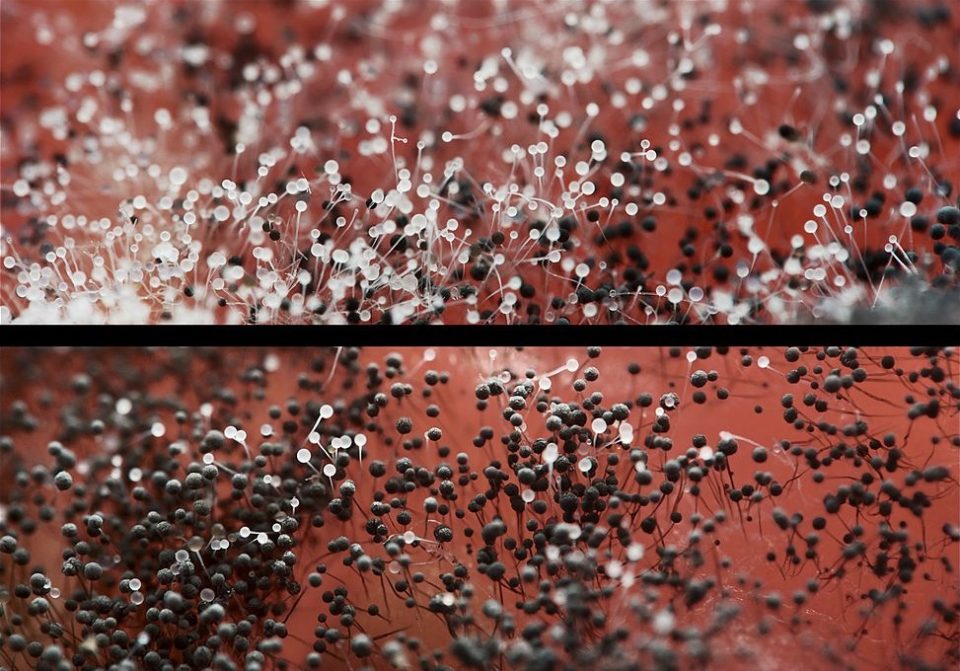
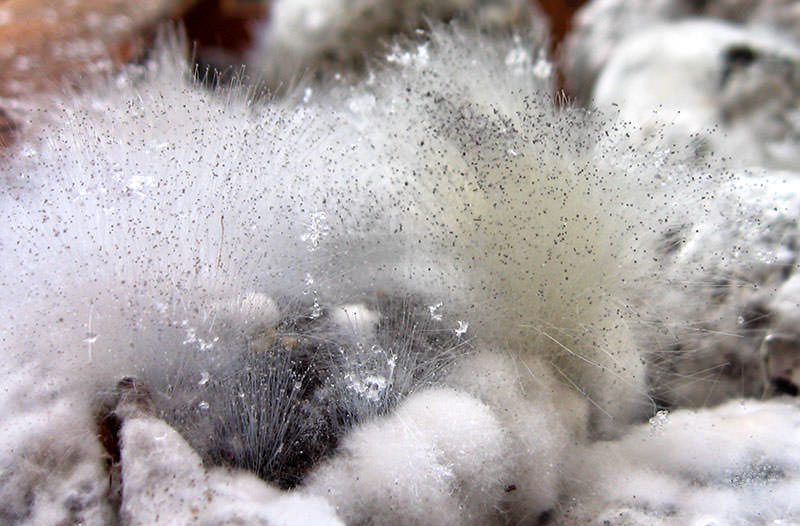
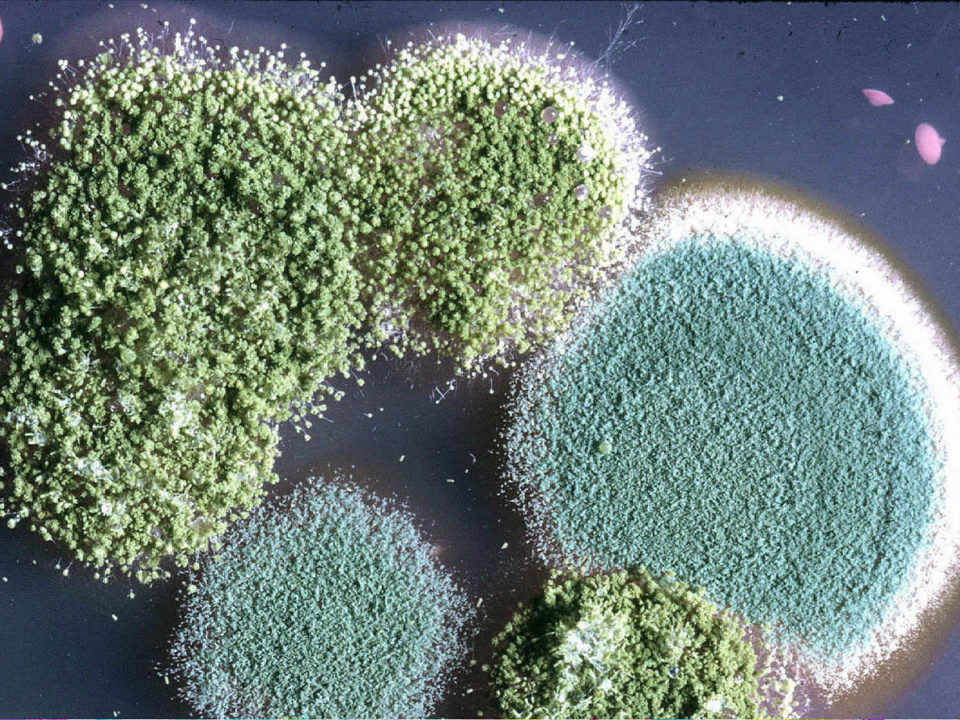
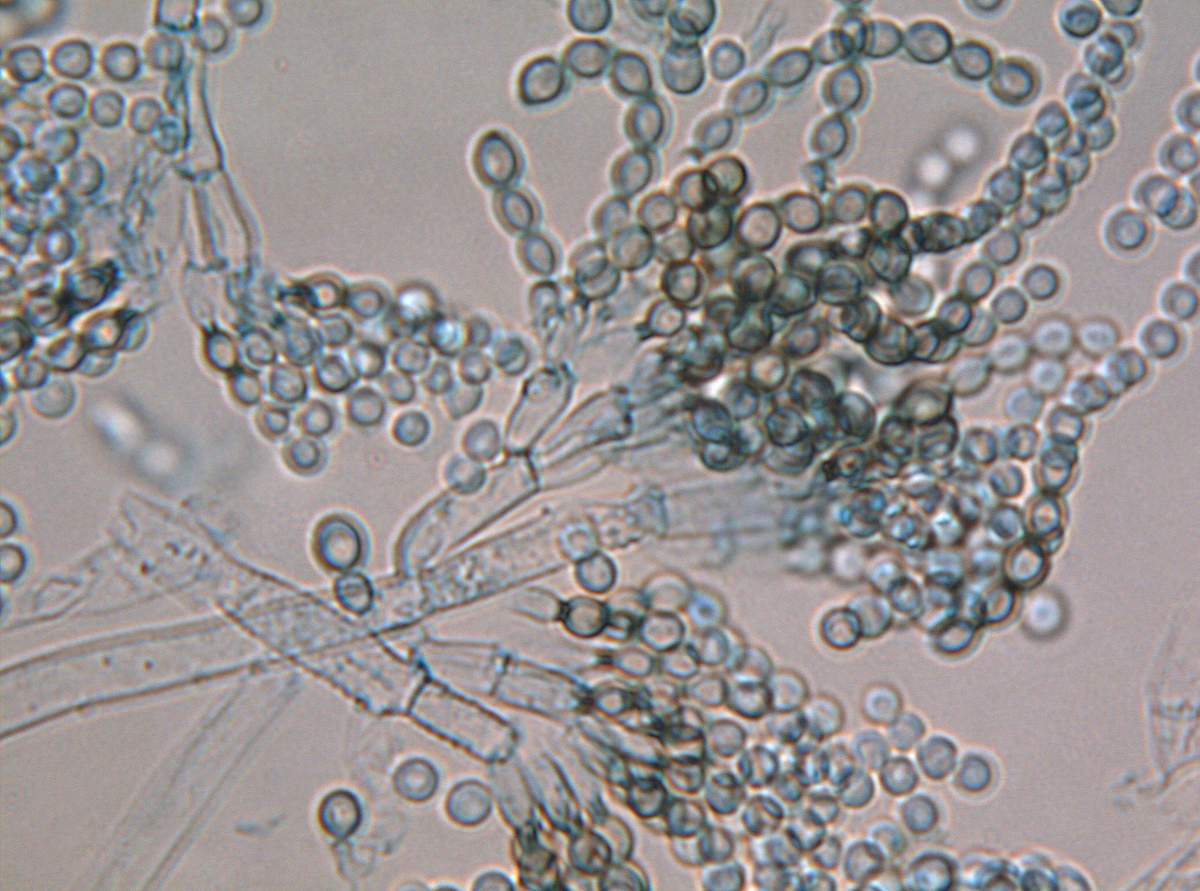
Mold fungi are called micromycetes. They have a microscopic structure, represented by a very thin multi-row body-mycelium. The body is branched, rarely contains partitions, is the base of a multinucleated mycelium. Details of the structure can be seen in the photo.
Characteristic features of the Mold are the following features:
- The mycelium is the basis of the vegetative body - filamentous branchy hyphae.
- Large size of mycelium.
- Mycelium, unlike yeast, is divided into cells.
- The possibility of reproduction in three ways: vegetative, asexual, sexual.
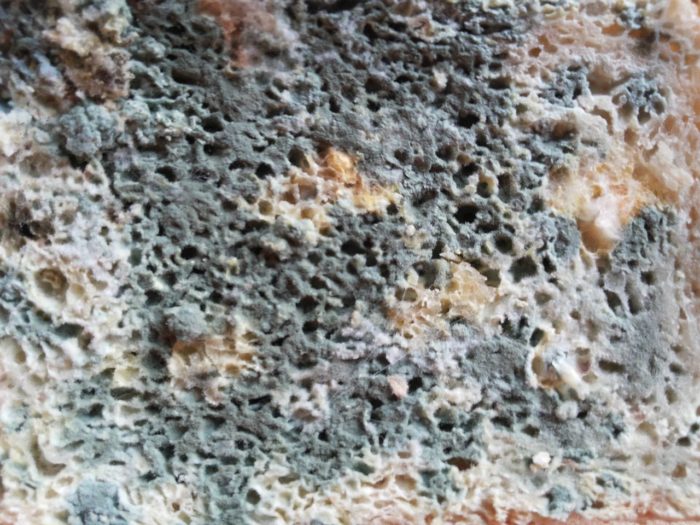
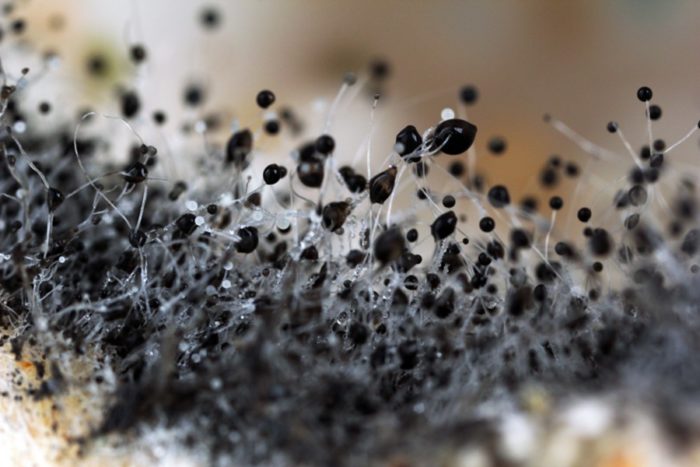
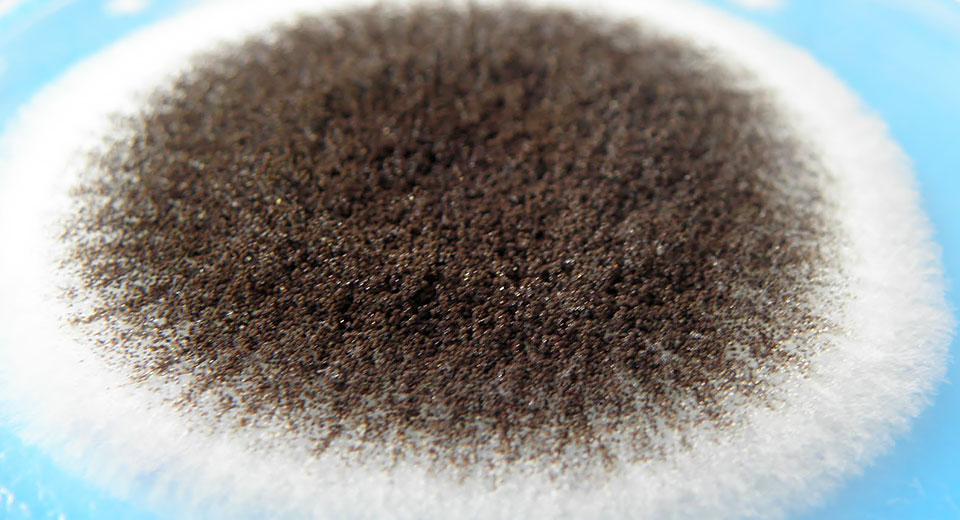
There are several classifications of mold. The most commonly used classification is by color (mushrooms are white, yellow, black, green, brown, red) and classification by the number of cells.
 You may be interested in:
You may be interested in:By the number of cells, mold is divided into 2 types: zygomycetes and ascomycetes. Zygomycetes are a small group of unicellular fungi. Ascomycetes are multicellular.
Mycologists distinguish 4 genera of the Moldy:
- Aspergillus.
- Botritis.
- Penicillium.
- Hypomyces.
The Aspergillus genus has several hundred species. Its mycelium has partitions characteristic of higher fungi. Initially, the mold has a white color, but as it grows older it acquires a wide variety of shades. The reproduction of Aspergillus species occurs in the traditional asexual way, but some higher species are capable of sexual reproduction.
Many species of Aspergillus are dangerous to human health. They can cause serious illness in people. Different types are actively used in the food industry and medicine.
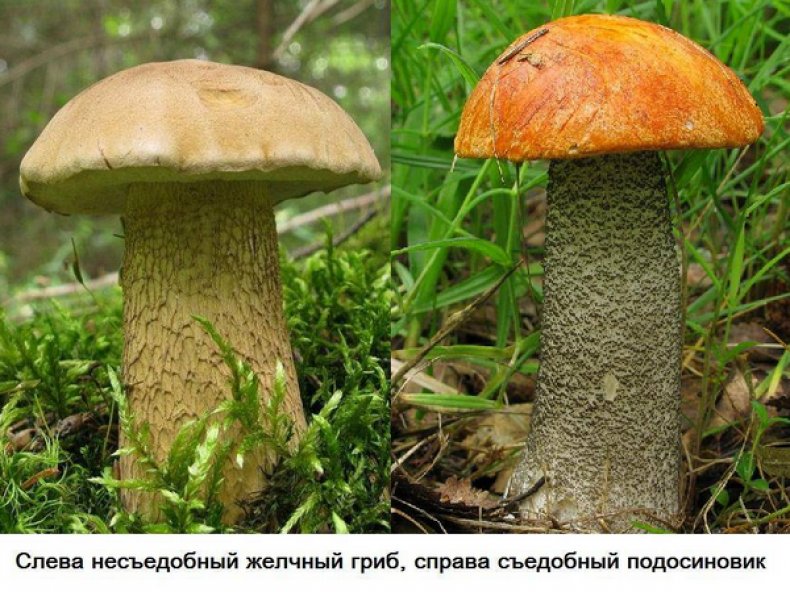 You may be interested in:
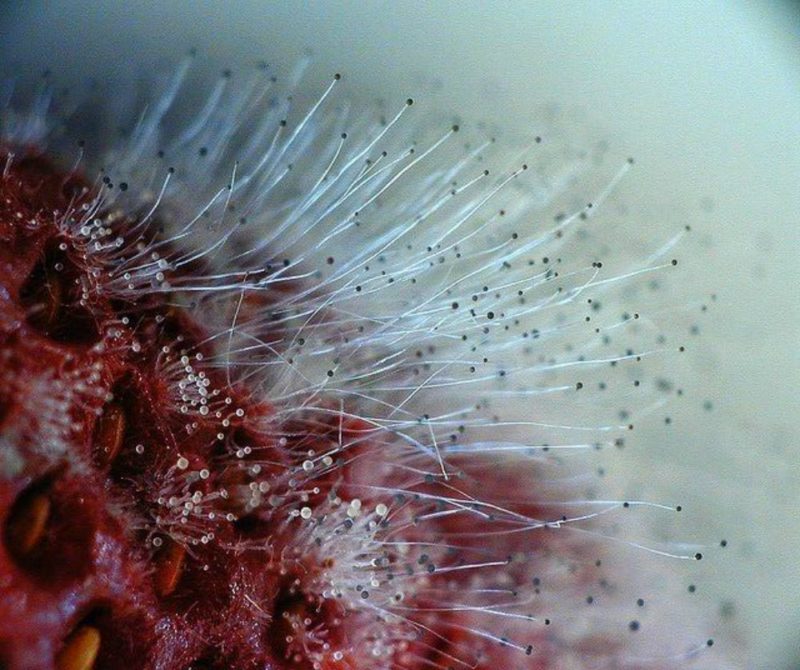
You may be interested in:Botritis is popularly called gray mold. Mushrooms form thick, colorless colonies, which, due to their density, acquire a gray smoky hue. Representatives of Botritis are unicellular fungi that settle in the soil and on plant remains.
Gyphs are visible to the naked eye. Species of this genus are very variable, so they can take a variety of forms. Representatives of Botritis are indispensable in winemaking. They do not carry a particular danger to humans. Species of Botritis can be affected by hyperparasitic fungi.
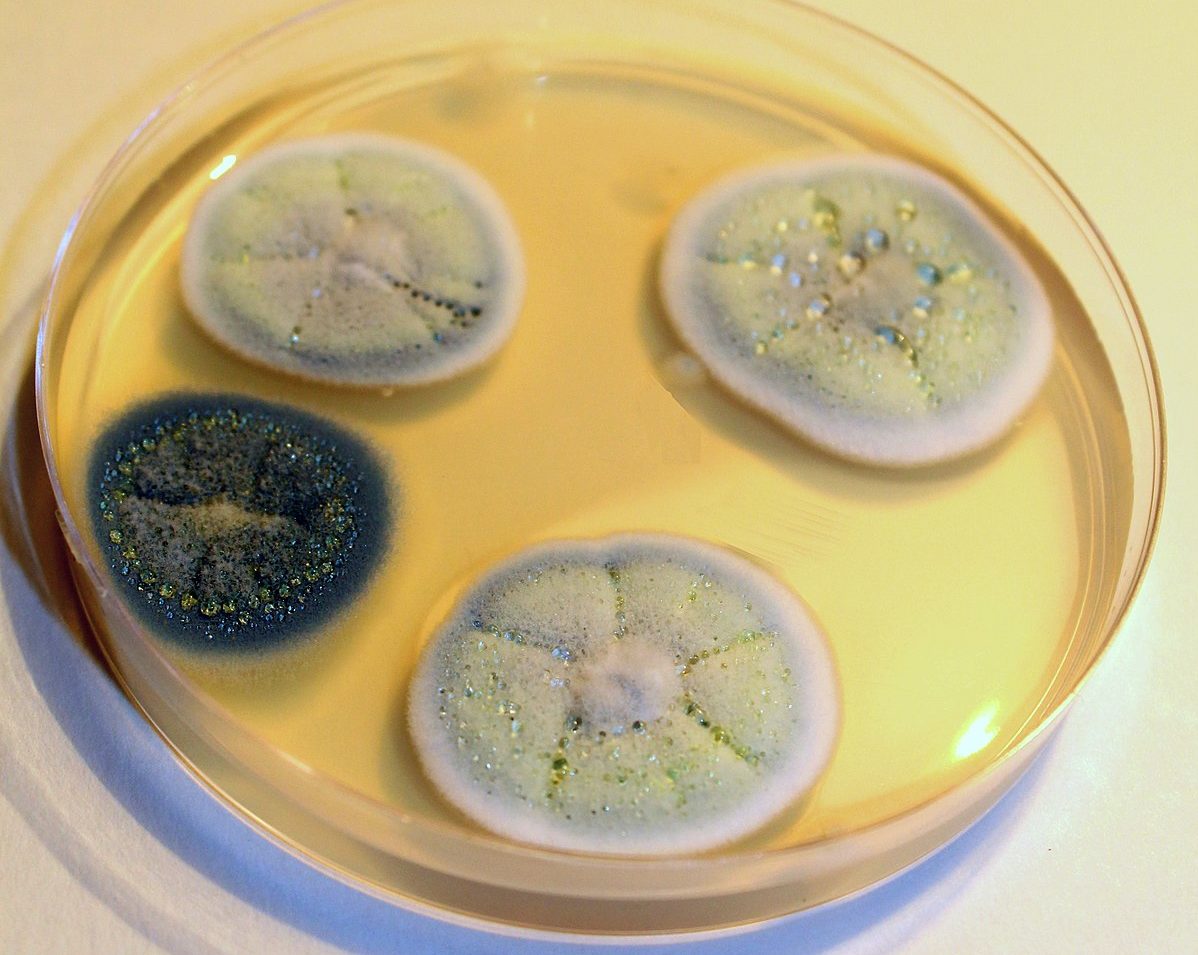
Penicillum is considered a noble mold. It is actively used in traditional medicine, as well as in cheese making and sausage production. There are 4 species groups of the Penicillus genus:
- velvety;
- felt;
- bundled;
- species with koremias.
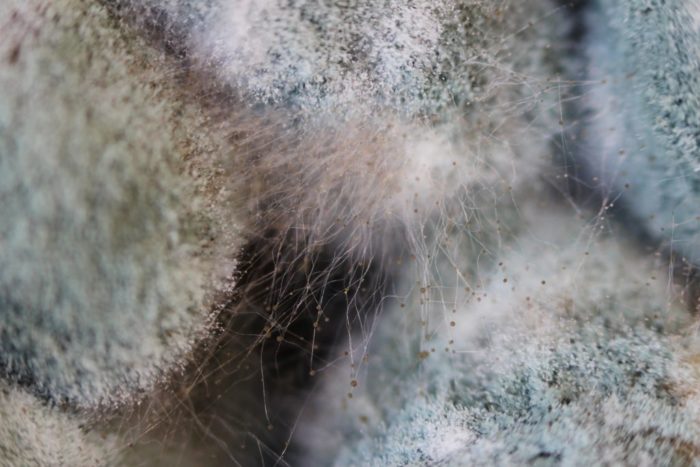
Species of the genus Penicill settle in soil, water, and air. Many of them prefer plants and foods.Depending on the species, the color of the mold changes. Most often it is white, yellow, orange or brown. Less common are instances of red and black.
Milky Hypomyces refers to edible mold. This genus of the Plesnevykh lives on edible mushrooms - russula and milkwort.
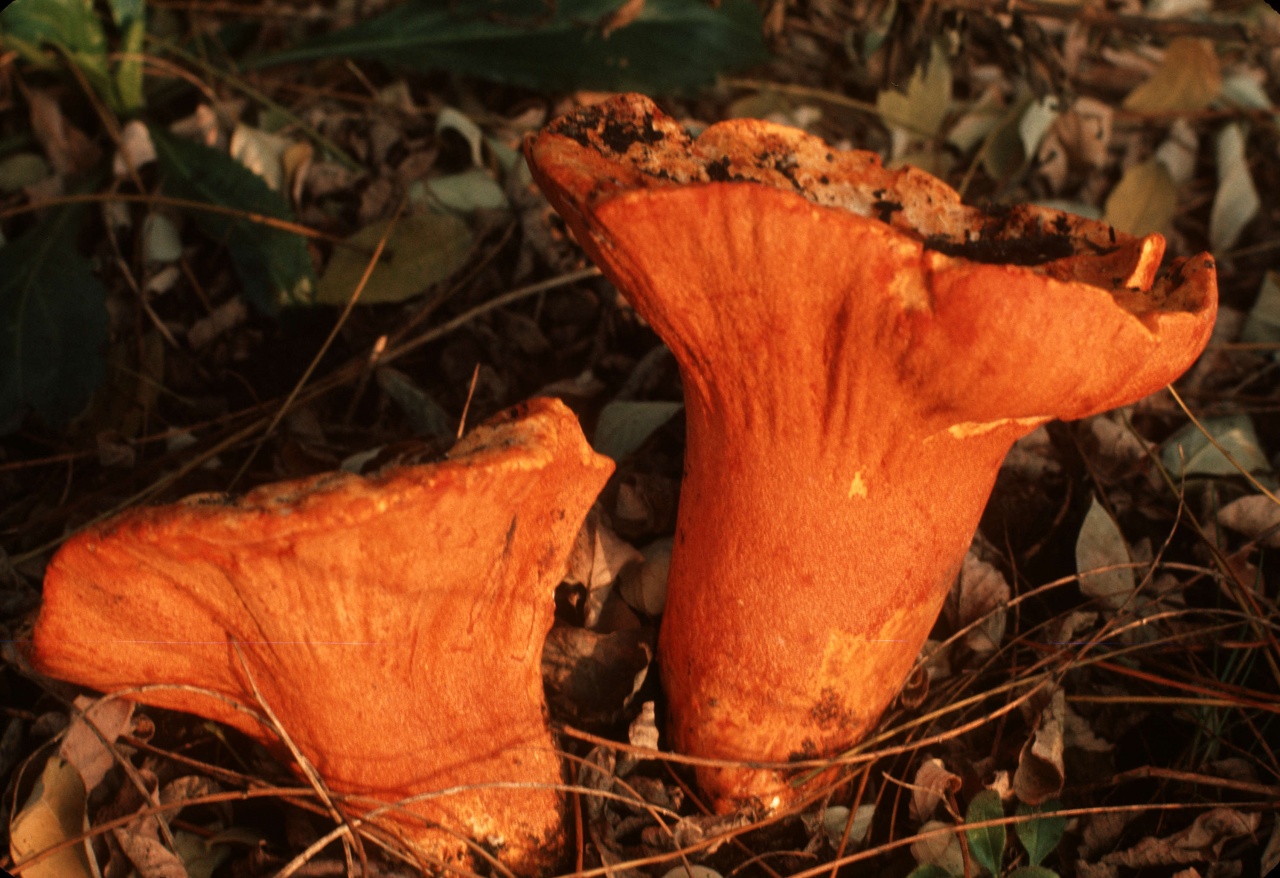

Initially, the mold is manifested by a thin coating of a bright red or bright orange hue. Then on it perithets begin to form - bulb-shaped bodies that can be viewed through a magnifying glass.
Milk hypomycosis is considered a delicacy. Mushroom pickers call it mushroom lobster for a color that resembles the color of a boiled lobster, smell and taste comparable to seafood. Mushroom lobster is not just eaten - it is a real hunt for him. This species poses absolutely no threat to human life and health.
The use of molds by humans
Mold fungi are actively used by humans in various fields of industry, starting with the production of food products and ending with the manufacture of medications. The most common use of these types of mold:
- Strains Aspergillus niger is used to produce citric acid.
- Strains of the genus Botritis are actively used in winemaking and the preparation of other alcoholic beverages.
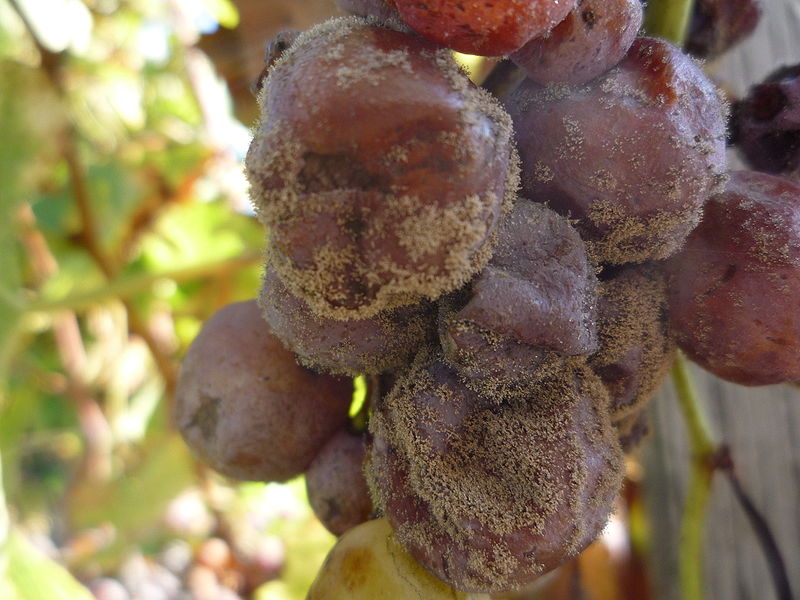

Botritis cinera on grape berries - Some noble types of mold are used to make special varieties of cheese (Roquefort, Camembert) and uncooked smoked sausages.
- Representatives of the genus Penicillus are the basic component of penicillin group drugs. Such drugs have antibiotic and bactericidal effects. Penicillin group drugs are widely used in traditional medicine.
Mold damage
Despite the benefits, molds can be very harmful. The most dangerous are representatives of the Aspergillus genus. They are able to infect humans and animals. The most common are skin lesions, infections of the outer ear, allergic reactions. A serious ailment called mycetoma also provokes mold of this kind.
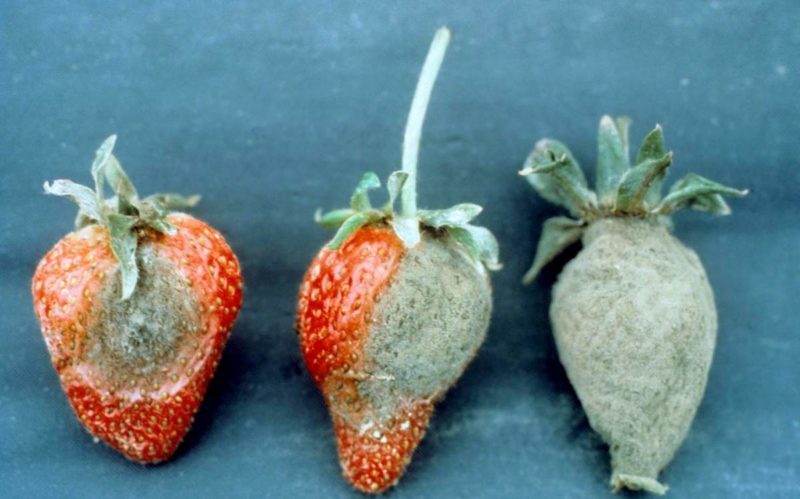
The genus Botritis can be safely called a garden pest.
Representatives of this genus cause a large number of fungal diseases in such plants:
- wild strawberries;
- grapes;
- onion;
- some root crops;
- citrus;
- nightshade;
- Beans
- linen;
- salad;
- peas.
In humans, botritis provokes an allergy. Sometimes fungal spores cause lung disease in people predisposed to respiratory diseases.
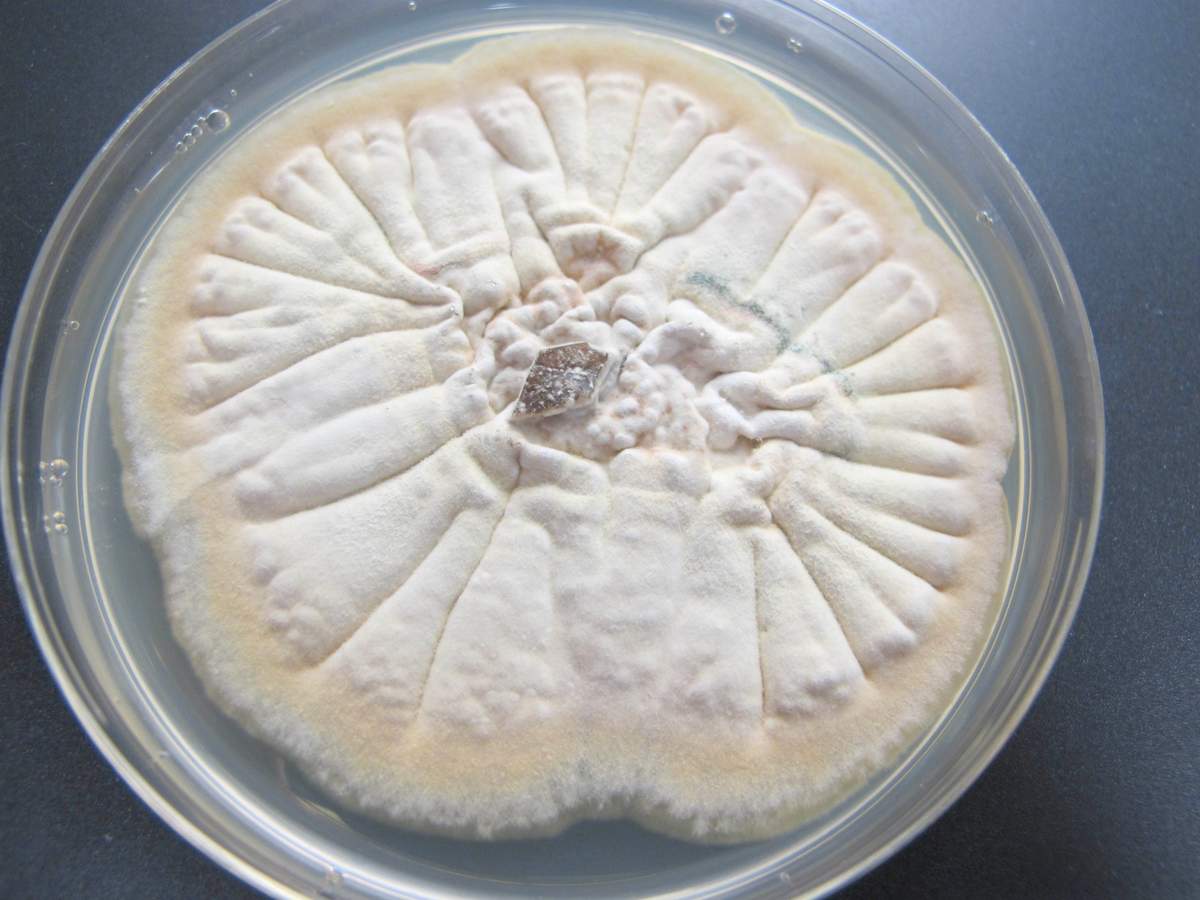
Cultivation conditions
Mold is very common. They grow on almost the entire surface of the globe, forming huge colonies. The mold habitat may be air, soil and water. They settle on food, plants.
The purpose of the colony is the absorption of all nutrients. After the depletion of the colony's power source, the active process of spore formation begins. Mature spores spread to new places rich in nutrients, and old mycelium remain at a dead source.
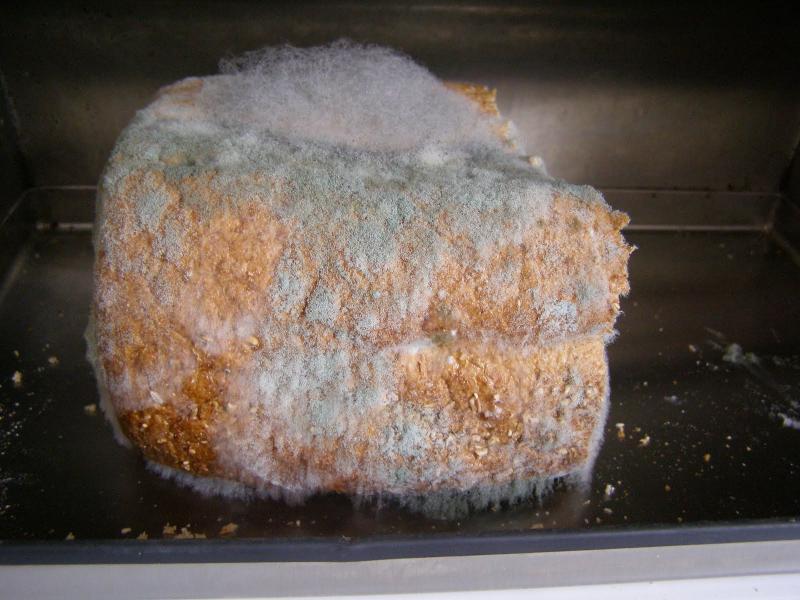

Mold is absolutely unpretentious to the external environment and develop regardless of its conditions. But the most favorable conditions necessary for the life and development of mushrooms are considered as follows:
- The abundance of carbohydrates.
- Heat.
- High humidity.
Molds love to settle on starch-rich substrates. Some scientists argue that molds are not cultivated in bright sunlight. This is not entirely true. They love the high level of humidity, and direct sunlight dries it. Therefore, mushrooms do not develop well under them. But bright light or partial shade accompany moisture - it does not play any role.
 You may be interested in:
You may be interested in:Answers to widespread questions
Such a mold familiar to everyone today is the subject of controversy among scientists. People are stubbornly looking for all the new possibilities and abilities of mold, blaming it for many diseases and endowing miraculous medicinal properties. The following are answers to the most common mold questions:
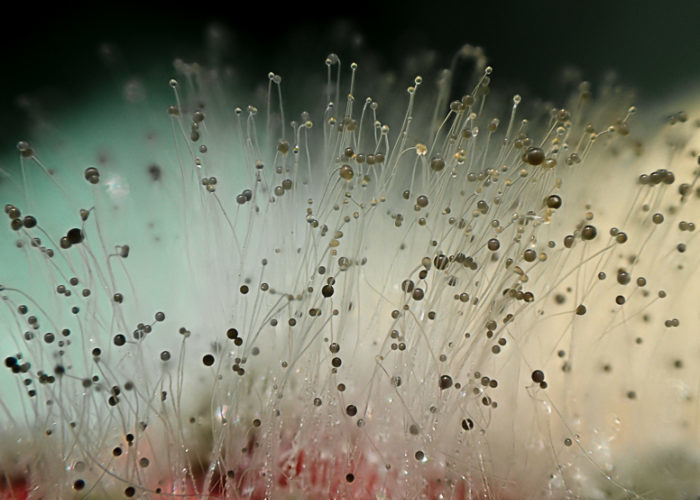
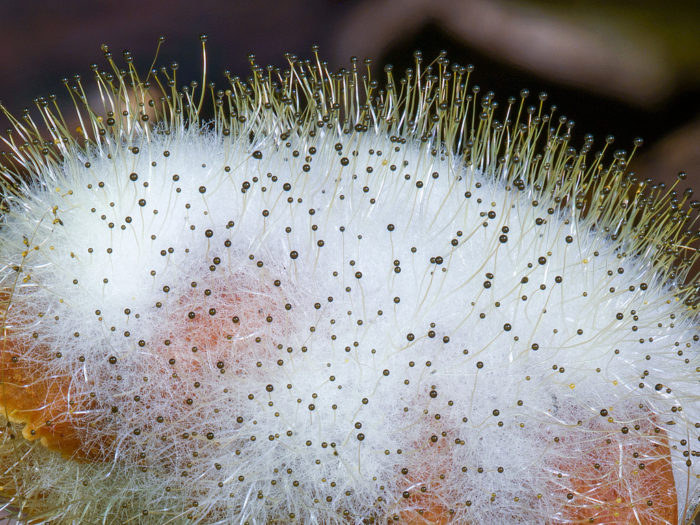
Mold species are very diverse. The benefits of these mushrooms to humanity are invaluable. But some species pose a serious danger to humans.

















 Care and use of Kombucha at home (+22 photo)
Care and use of Kombucha at home (+22 photo) Edibility of the fungus of the motley umbrella and its description (+19 photo)
Edibility of the fungus of the motley umbrella and its description (+19 photo) Description of edible and inedible oils, their poisonous counterparts (+40 photos)
Description of edible and inedible oils, their poisonous counterparts (+40 photos) Useful properties of milk mushroom and its contraindications (+17 photos)
Useful properties of milk mushroom and its contraindications (+17 photos)