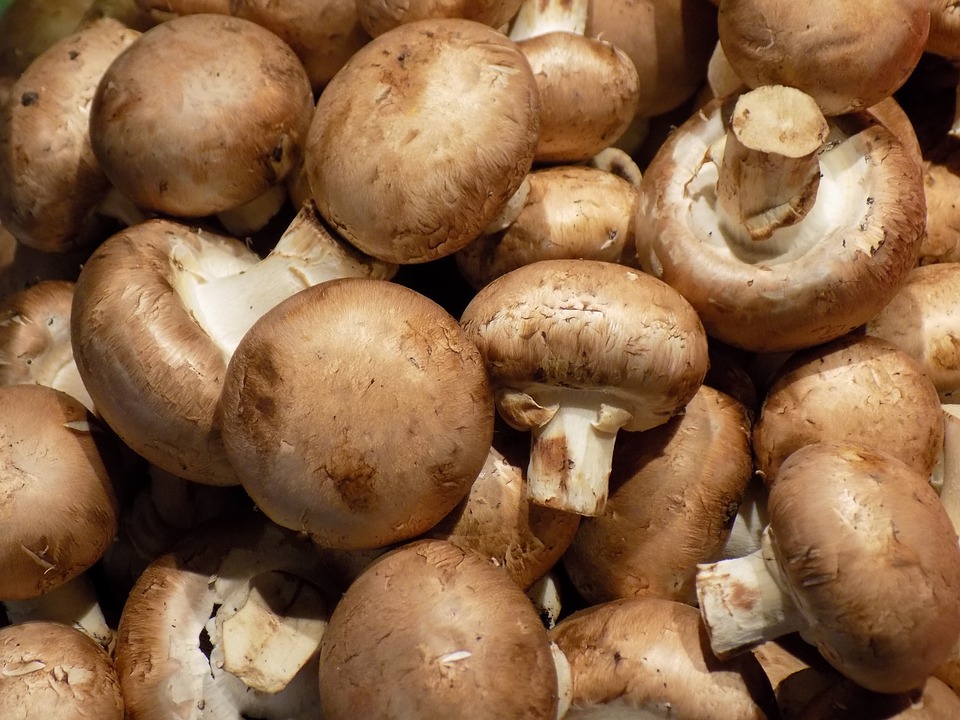
Most fans of mushroom dishes find champignons only in stores. But experienced mushroom pickers know that there are many places where these delicacies grow in natural conditions, which makes them even more rich in taste. On the eve of a quiet hunt, a beginner mushroom picker should get acquainted with a photo and a detailed description of champignon mushroom, because it is sometimes difficult to distinguish an edible mushroom from a poisonous double.
Content
Characteristic features of the variety
Champignon belongs to the family of Champignon. Also, the fruit is known as the pechitsa.
Appearance, description and photo
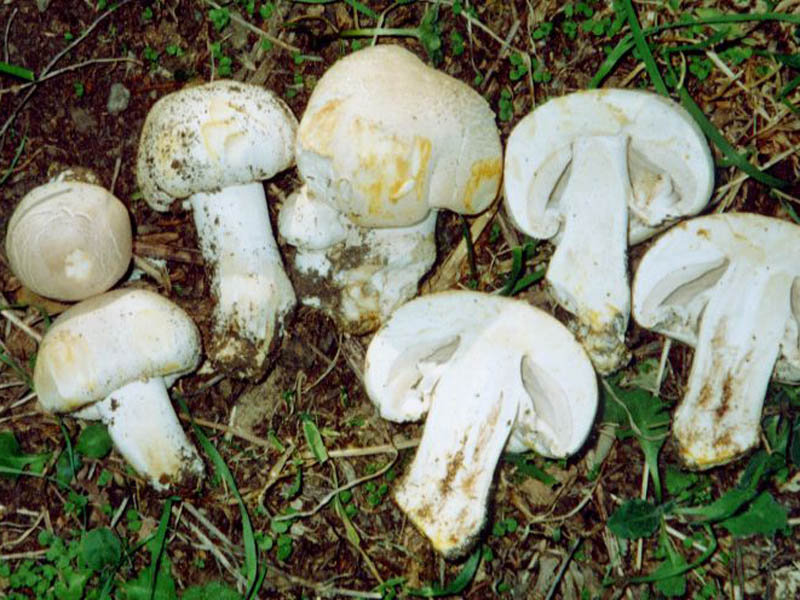
Now there is no person who does not know what mushrooms look like - as this is the most common mushroom sold in stores. However, it should be understood that it is not so easy to recognize his forest counterpart.
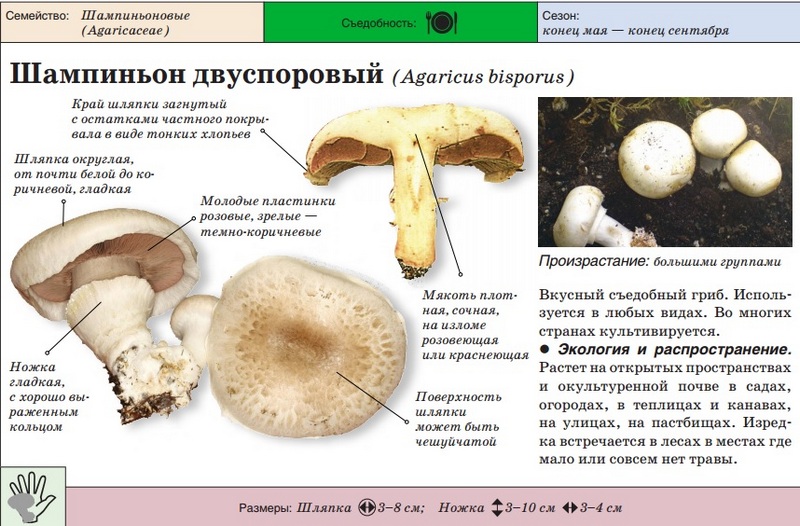
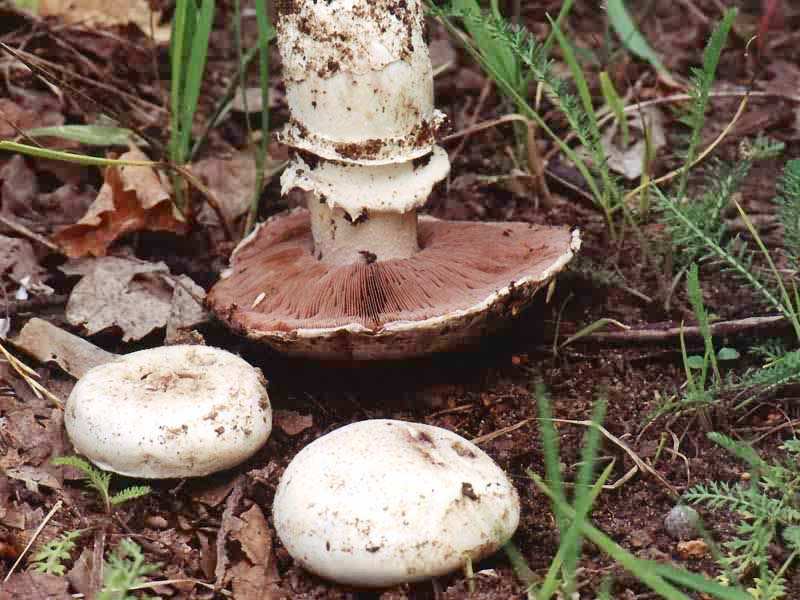
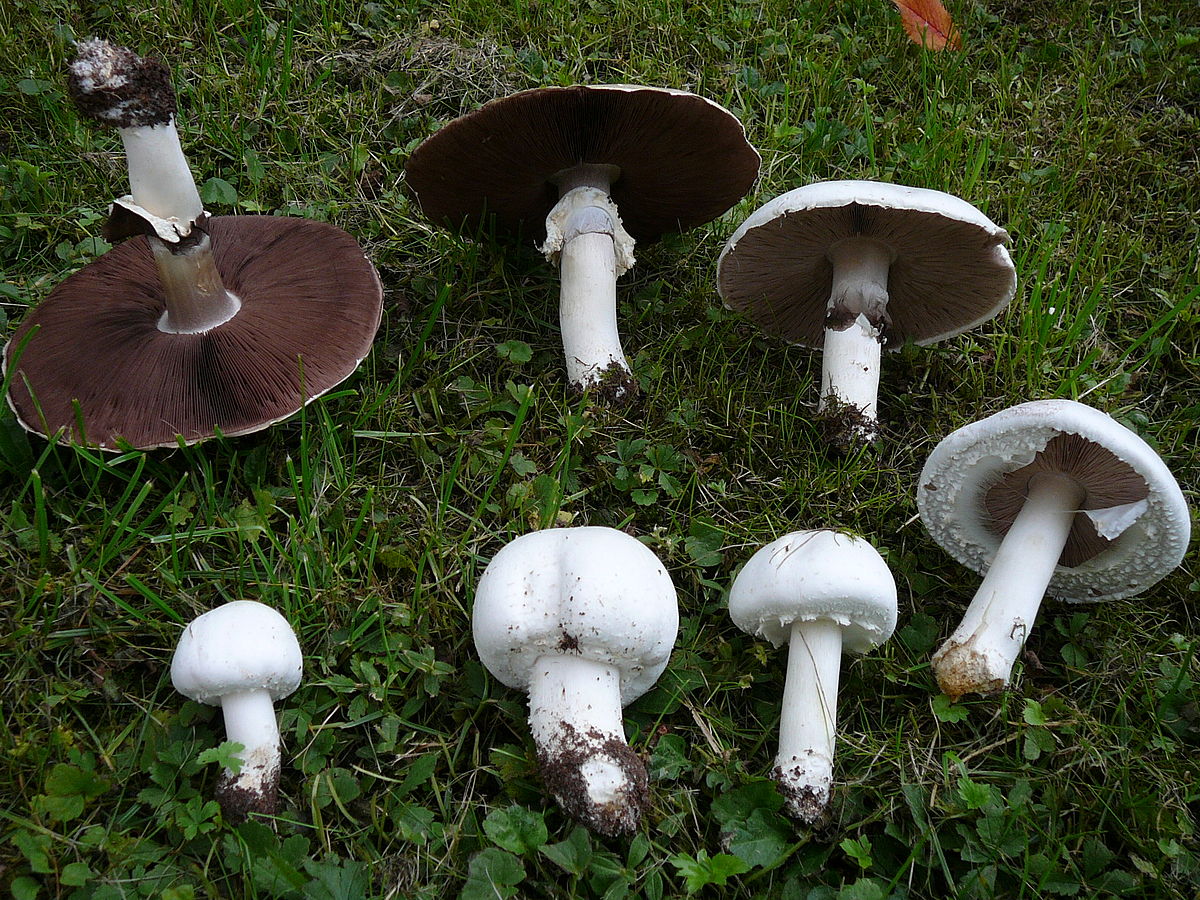
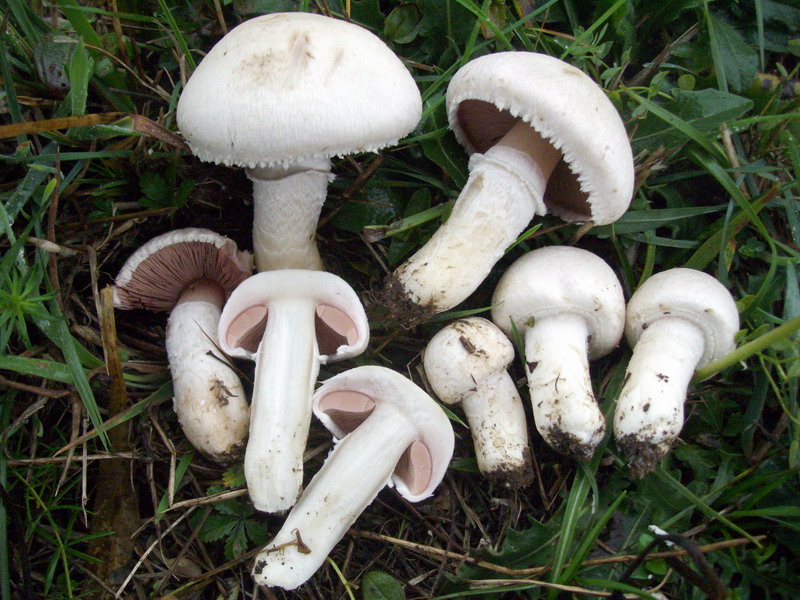
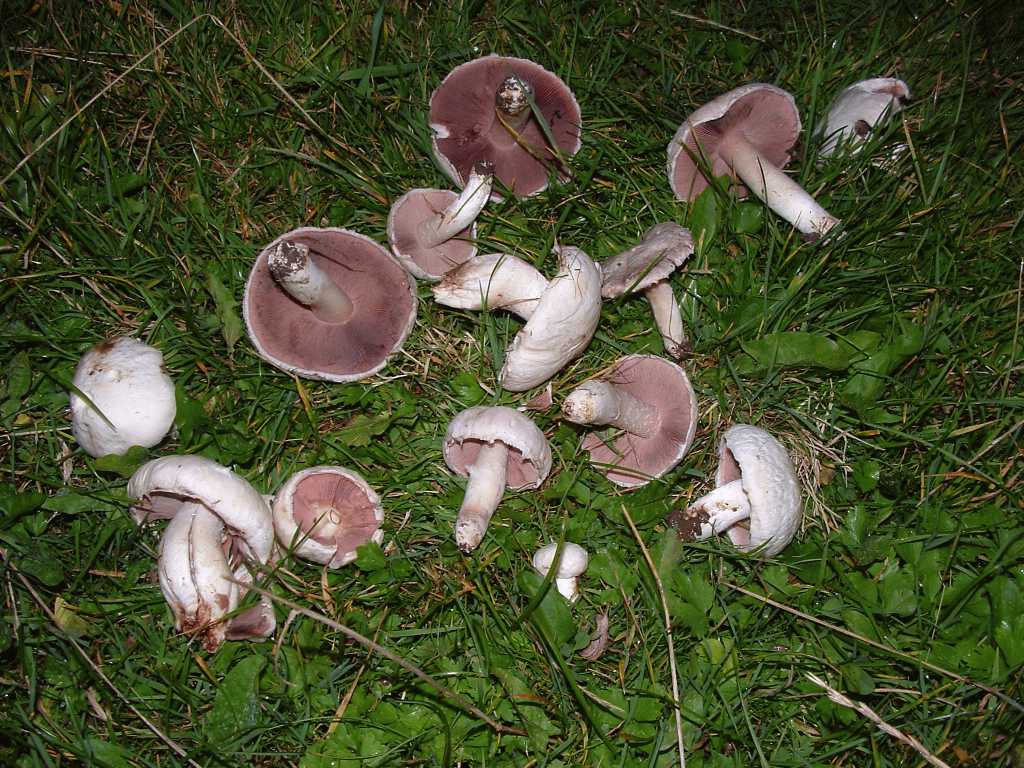
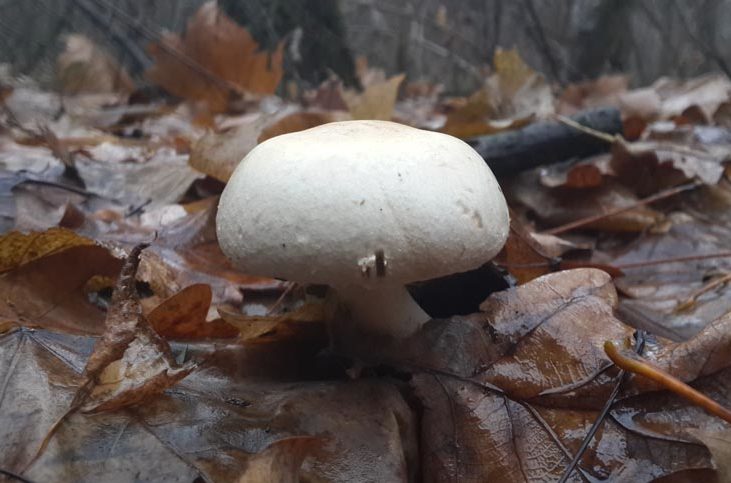
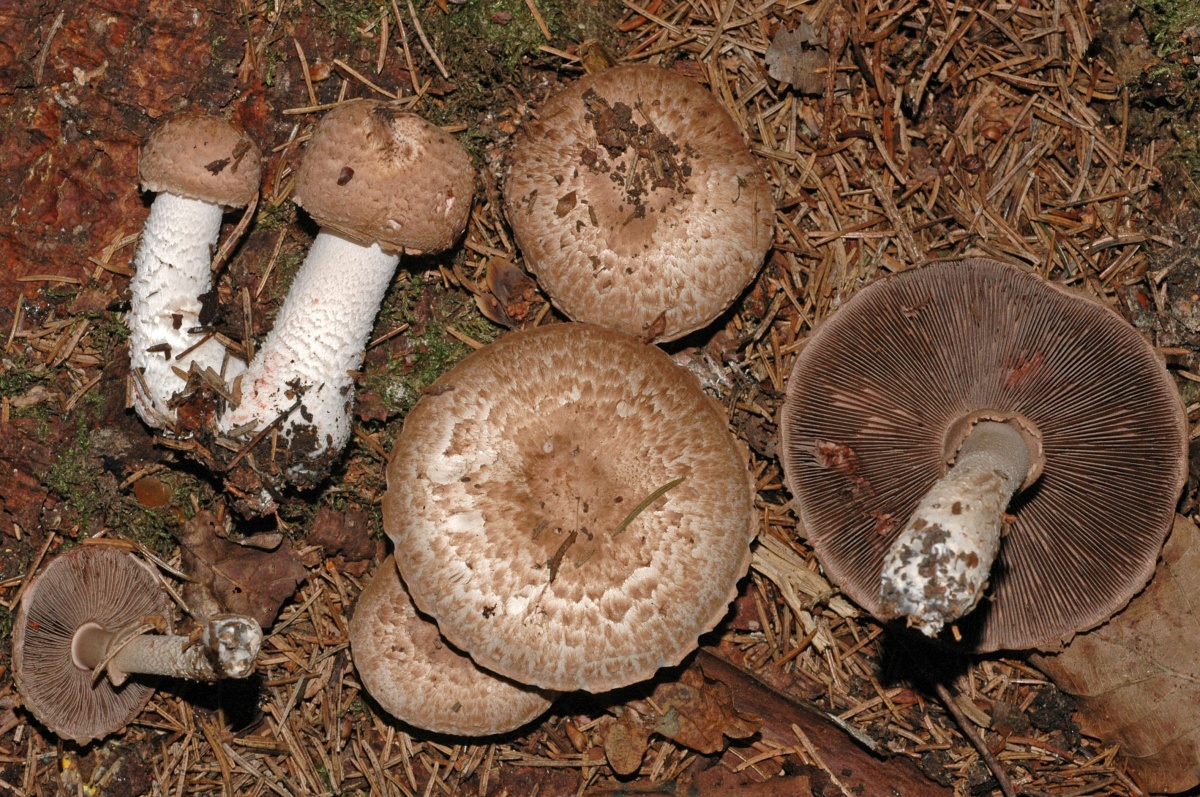
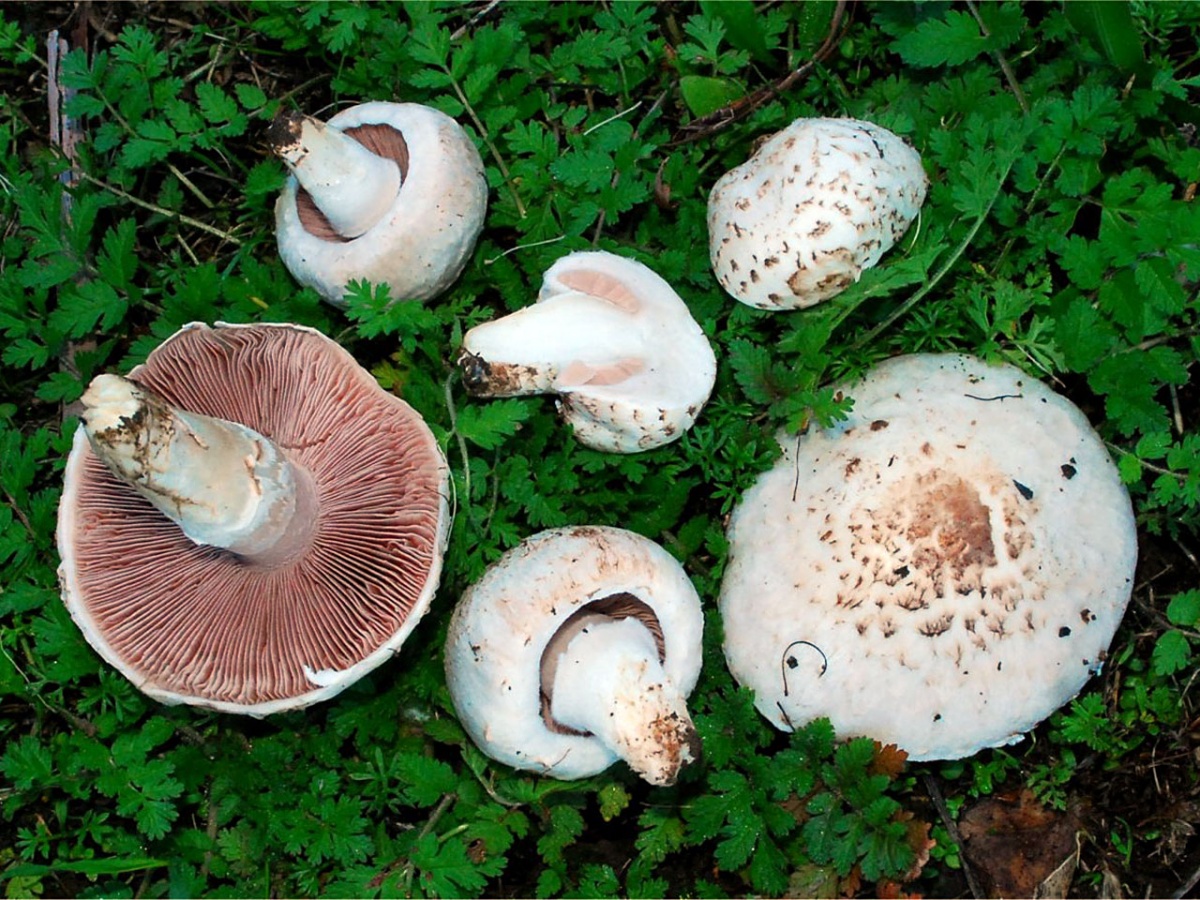
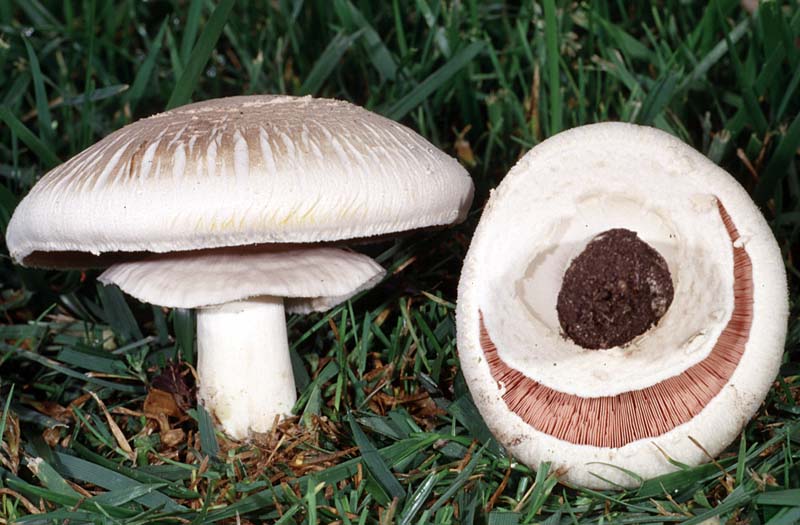
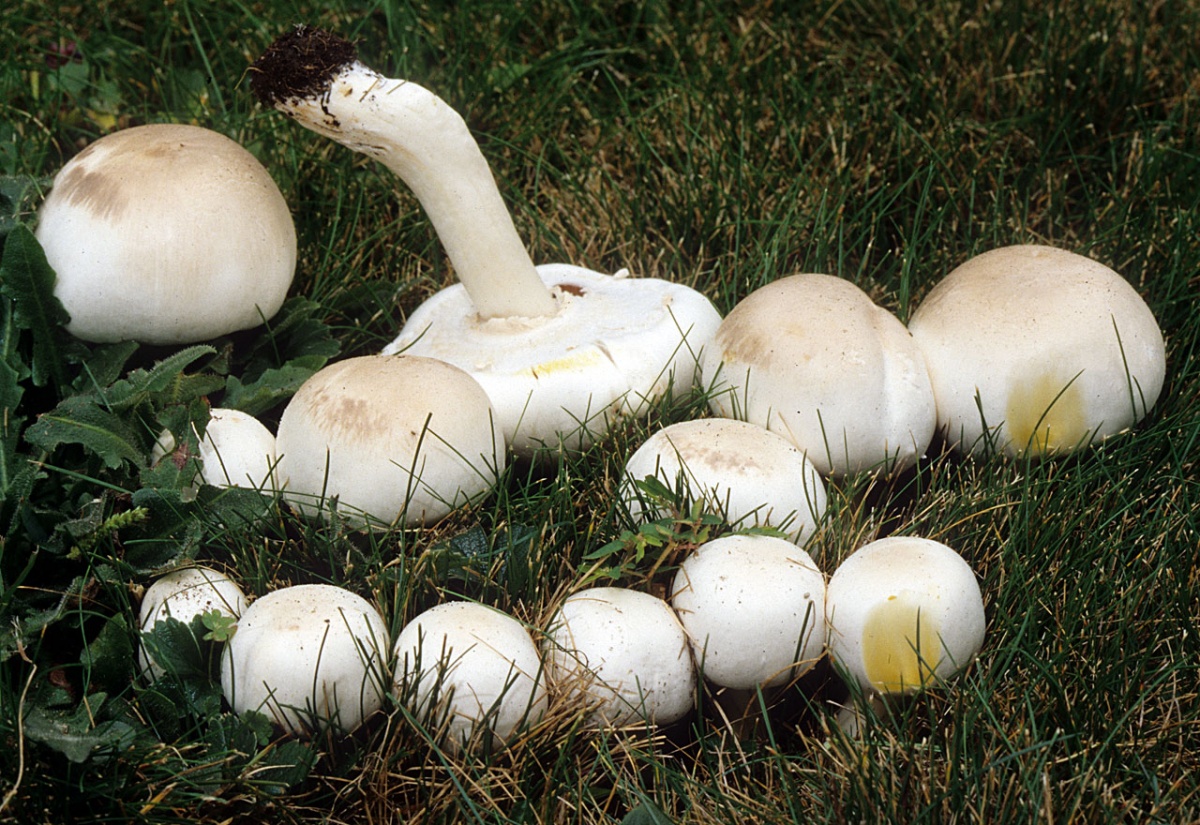
Depending on the species, the surface of the fungus may be brownish or white. Young individuals form small smooth hats that are hemispherical in shape.
 You may be interested in:
You may be interested in:As the hats of young individuals grow, they straighten and can take on an open form. In the center of the cap you can often see a small convex tubercle. The skin is smooth, velvety and dry, often covered with small scales. All varieties are compact in size. For example, the diameter of a hat of a real champignon varies between 8-15 cm.
A distinctive feature of the species is the presence on the leg of a wide ring, which has a dirty white or white color. Common champignon has a cylindrical leg. It is flat, but expands to the bottom. The diameter of the legs is 1-2 cm, and the color coincides with the color of the hat or a tone lighter.
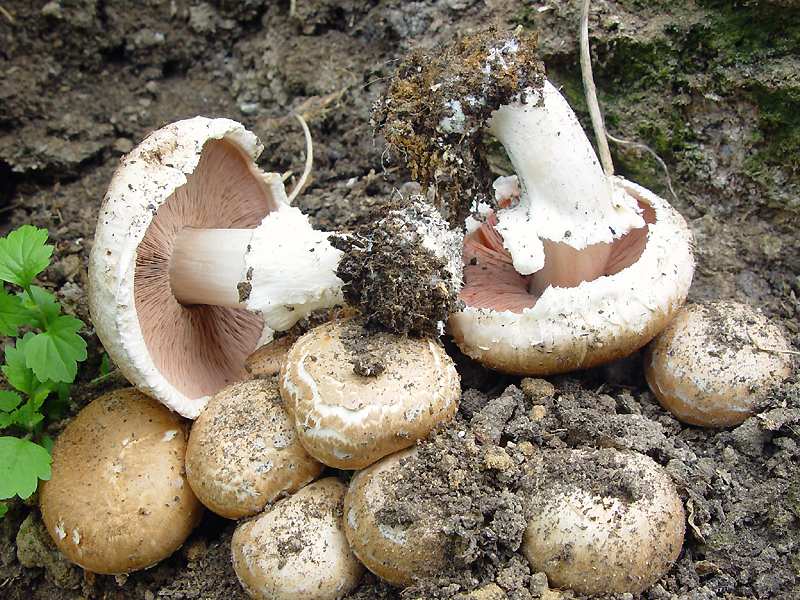
The white flesh at the break becomes reddish over time. It is fleshy and has a pleasant aroma. The color of the pulp should be paid special attention, because edible species have doubles.
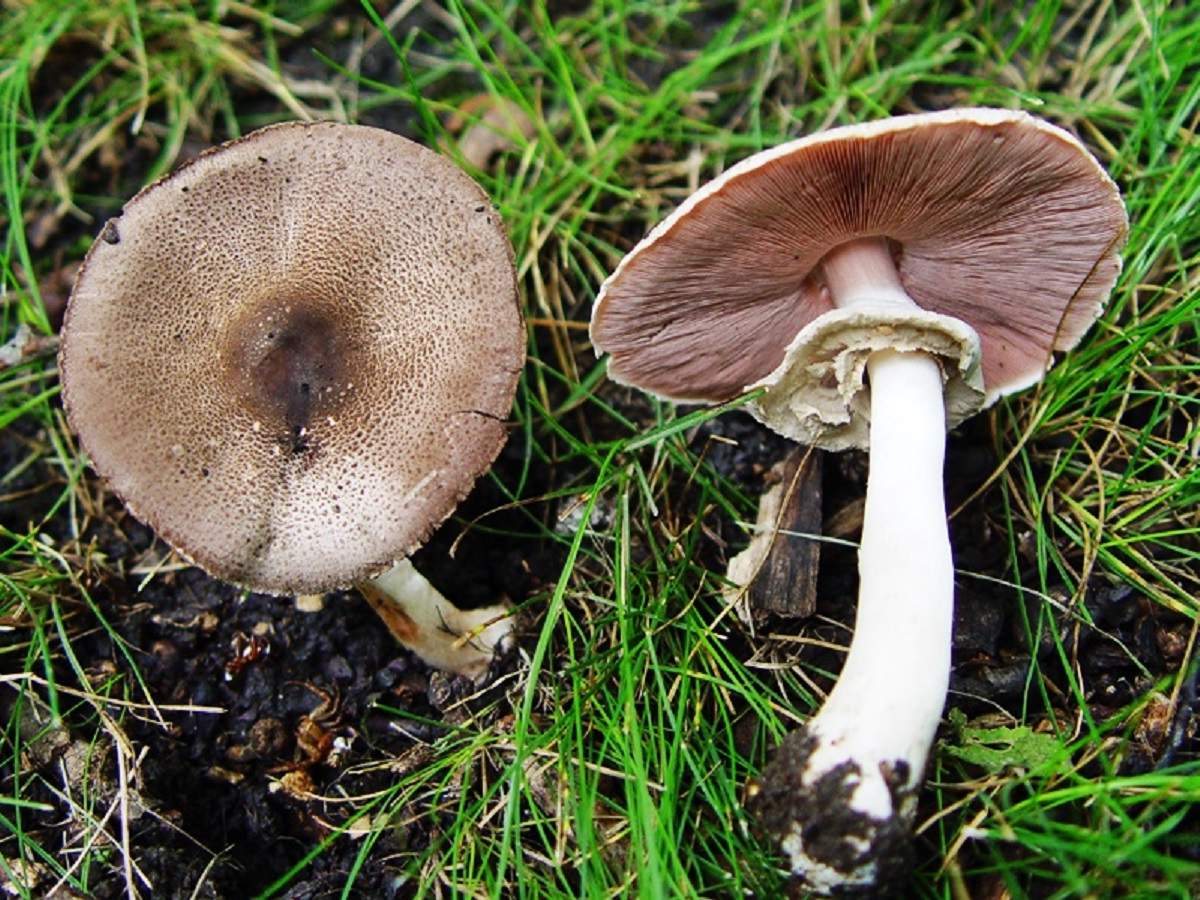
The plates of the young mushroom are painted white, but as they grow, they first acquire a pinkish, and then a light brown hue. The records are rare, thin and not too long.
Place of distribution of champignons
This fruit is most common in the steppe and forest-steppe zone of Eurasia. The most diverse species of this fungus are found in open areas, meadows and prairies of Africa and Australia. In Russia, they should be sought on moist soils, which consist of a large number of natural fertilizers and compost.
Mushrooms generously bear fruit in the Volgograd region. The most mushroom places are the following areas:
- Olkhovsky;
- Rudnyansky;
- Zhirnovsky;
- Novoaninsky.
You can collect them already at the end of June. They are found near fir trees, in oak forests, on pastures and meadow places.
 You may be interested in:
You may be interested in:Eating
The product can be safely consumed even raw. This is the most common mushroom in Russia.Culinary specialists have come up with many cooking methods. In addition, pregnant women and children can use the product.
It is very appreciated by vegetarians and people who want to lose weight. The calorie content of the pulp is very small, while amino acids, vitamins and minerals are contained in large quantities in the mushroom.
Types and their description with photos
Champignons grow in forests, fields and meadows, depending on this, experts identify several types of mushrooms that have certain differences.
Forest
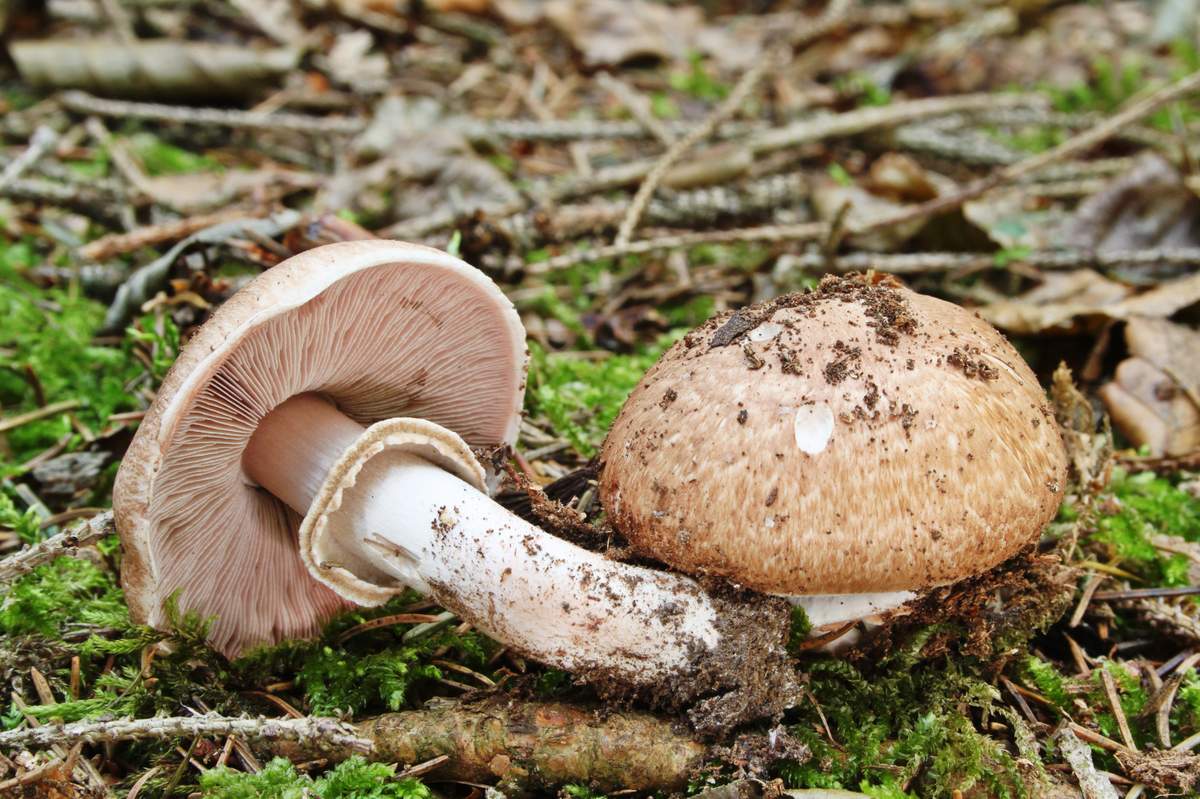
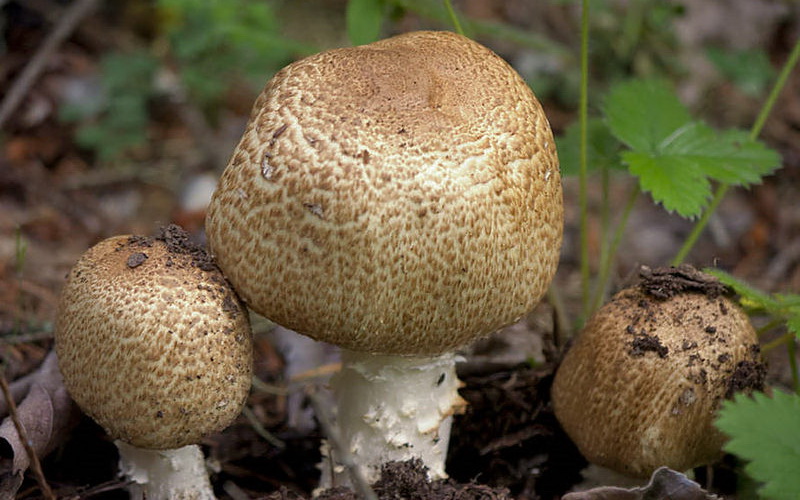
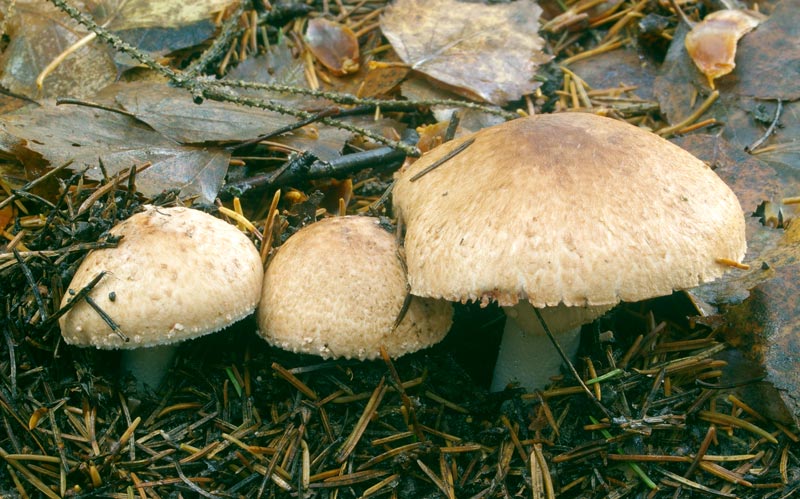
Champignon forest can often be found under another name - sweetheart. The hat reaches 5-10 cm in diameter. The color is brownish pink, and the surface is covered with large scales of brown color. Due to the scales, the mushroom acquires a purple or purple hue. If you press on the pulp, then it first turns red, and then becomes a brown hue. The taste and smell of pulp is pleasant, mushroom. The light flesh at the cut site turns red.
The length of the legs is 5-10 cm, and the thickness is about 1.5 cm. The fruit forms a cylindrical leg, which often becomes curved. Younger specimens have a single leg, while in more mature ones it becomes hollow. Leg whitish shade with small scales. The dangling ring is located closer to the hat.
 You may be interested in:
You may be interested in:Meadow
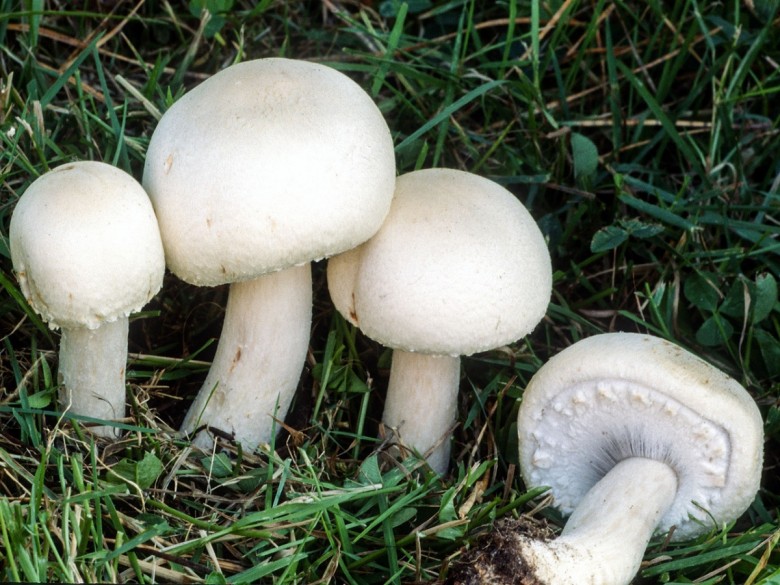
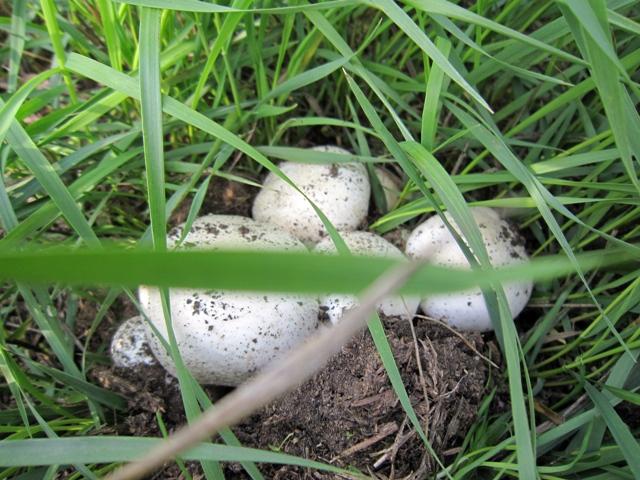
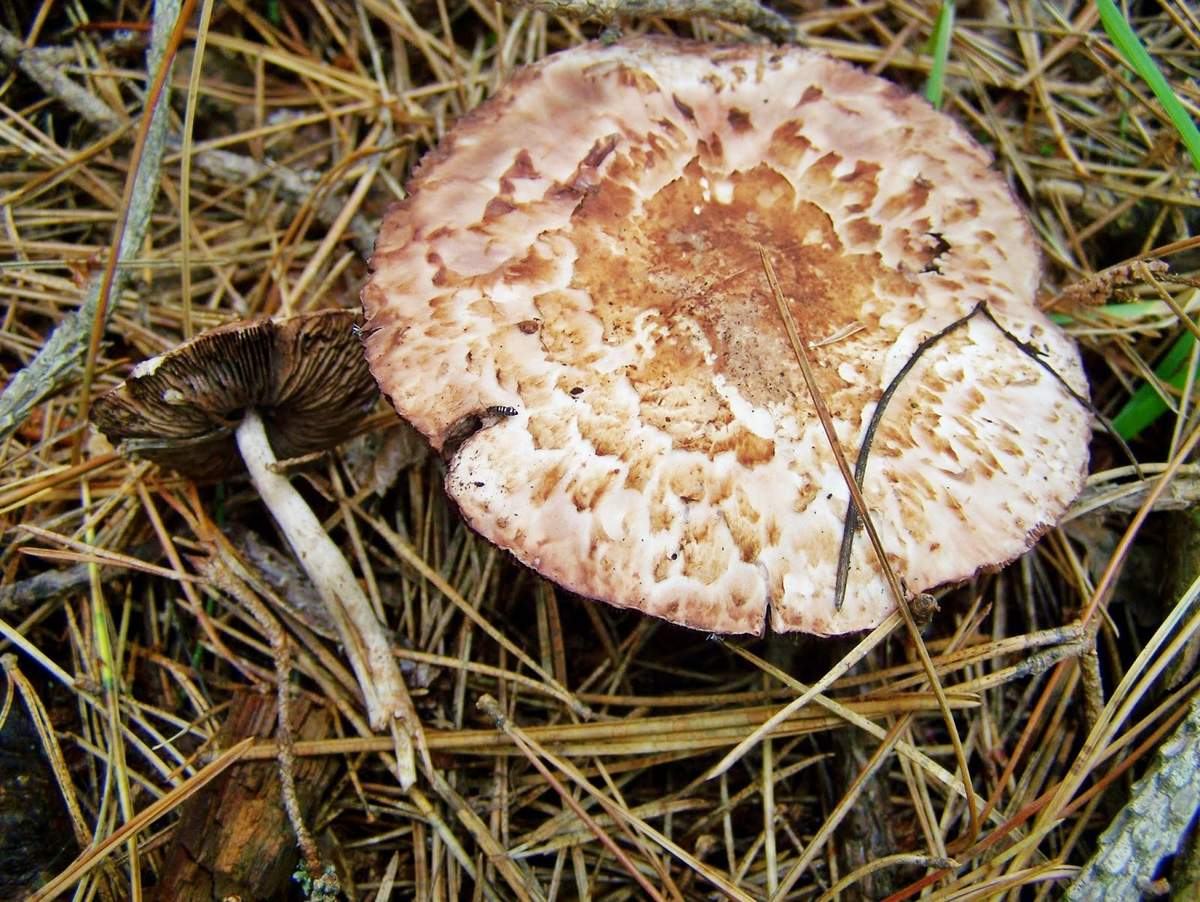
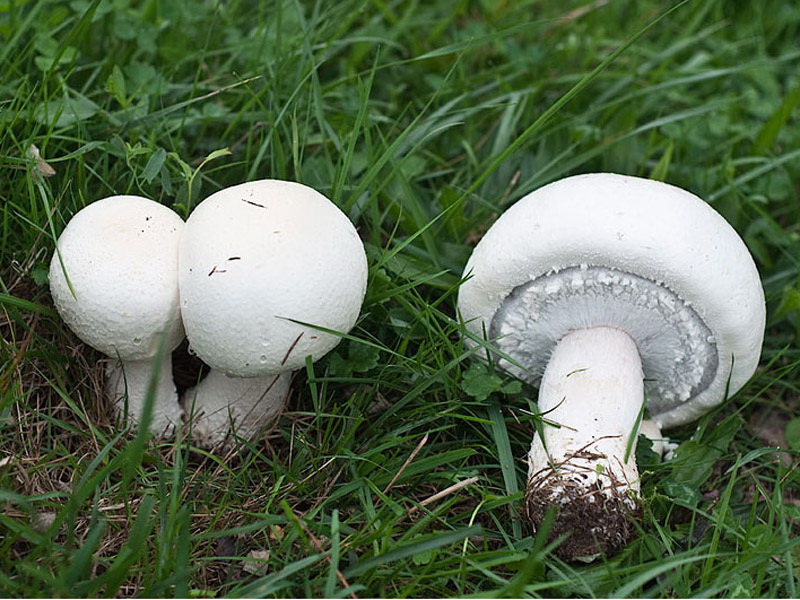
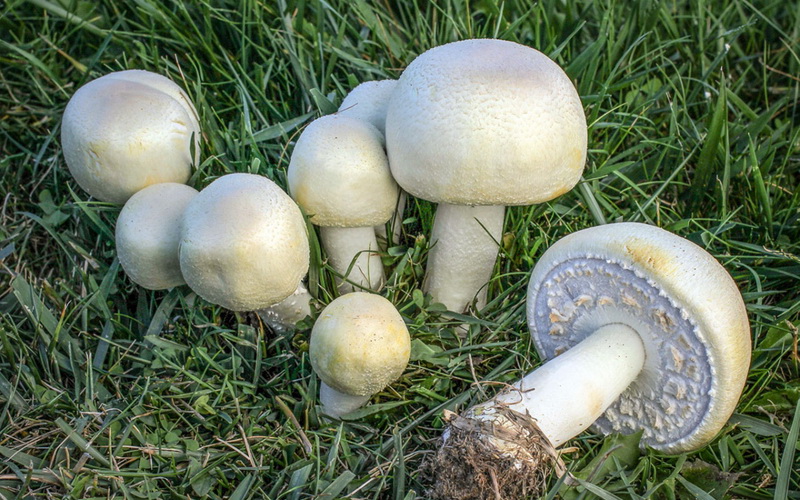
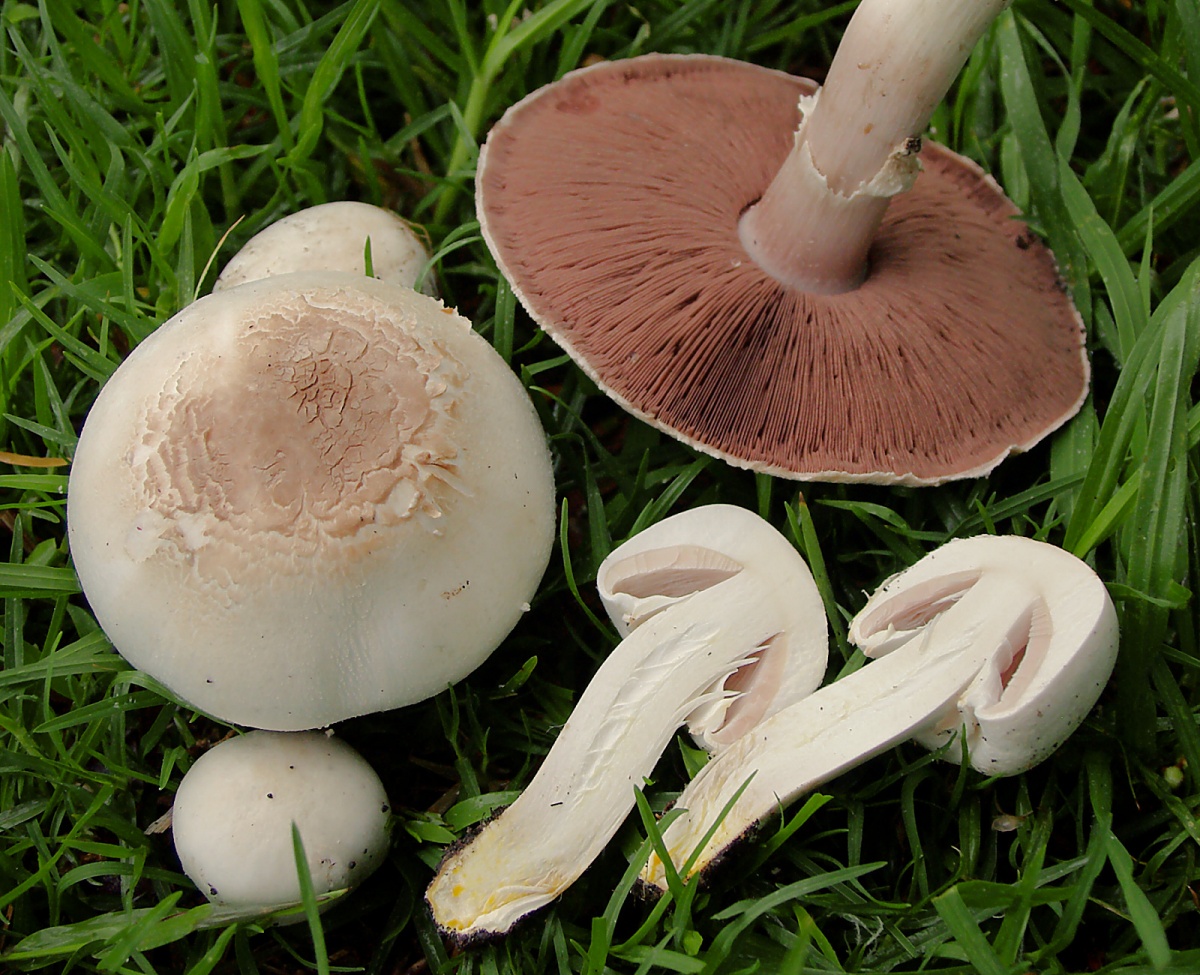
Meadow champignons are often called peppers or ordinary mushrooms. The hat grows in diameter up to 15 cm. Young mushrooms form a spherical, then hemispherical hat. When ripe, the hat becomes outstretched and silky to the touch. The dry hat of old fruits is sometimes covered with small scales and acquires a brownish tint in the center.
The leg length is 3-10 cm. The cylindrical leg is solid and painted in the same color as the hat. Its base is often brownish in color. A thin ring is located closer to the middle of the leg. Often in mature fruiting bodies, the ring disappears. The pulp is white, in places of the slice acquires a pink hue.
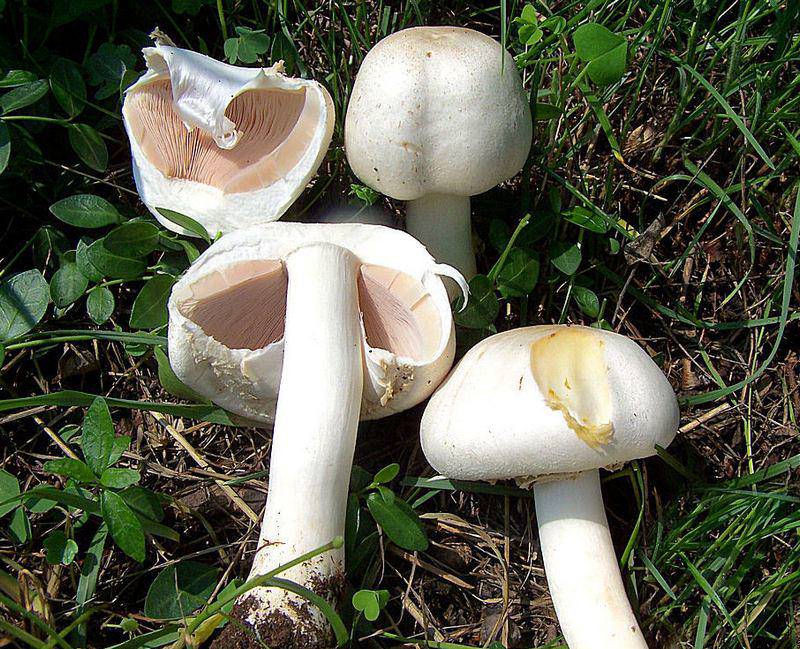
Field
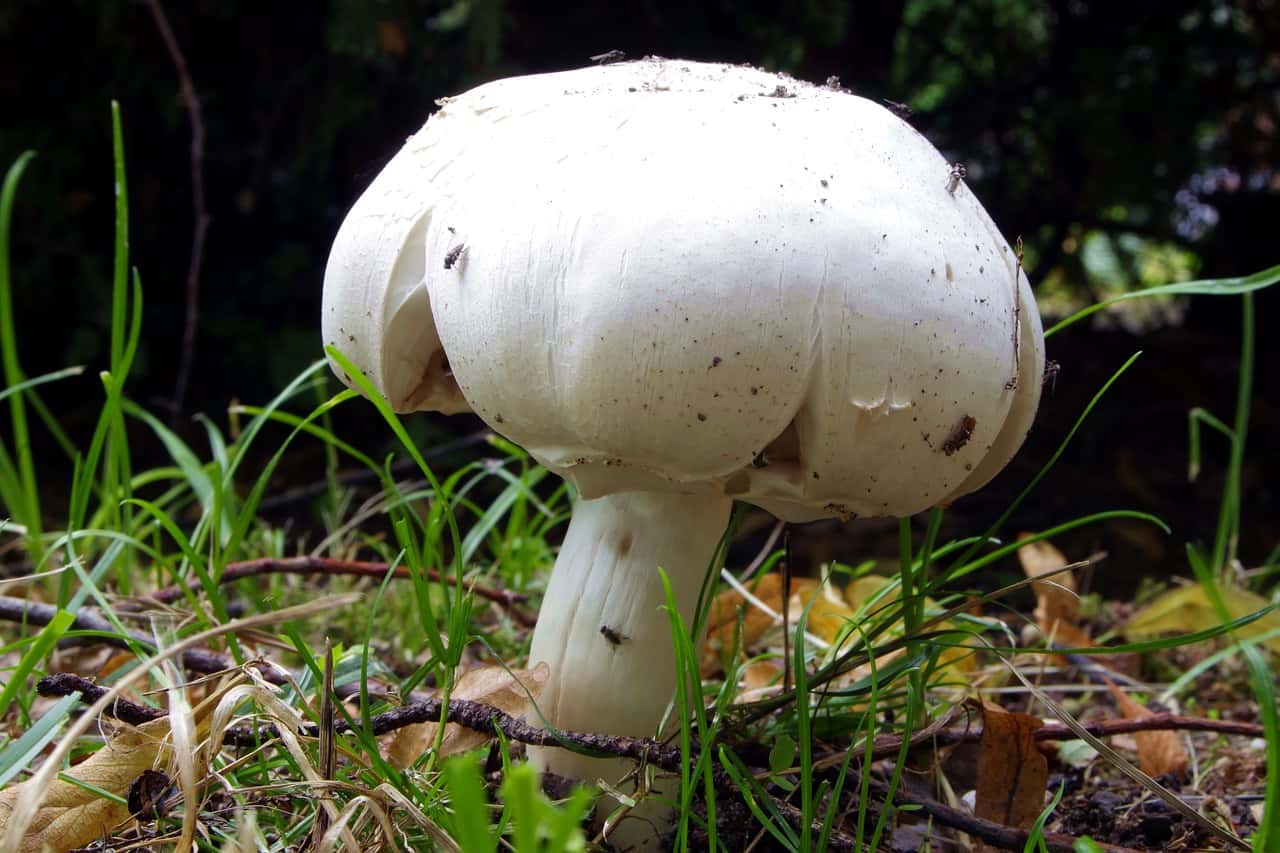
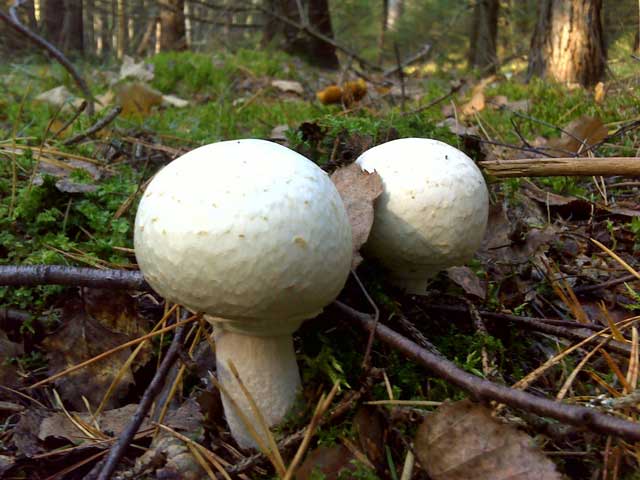
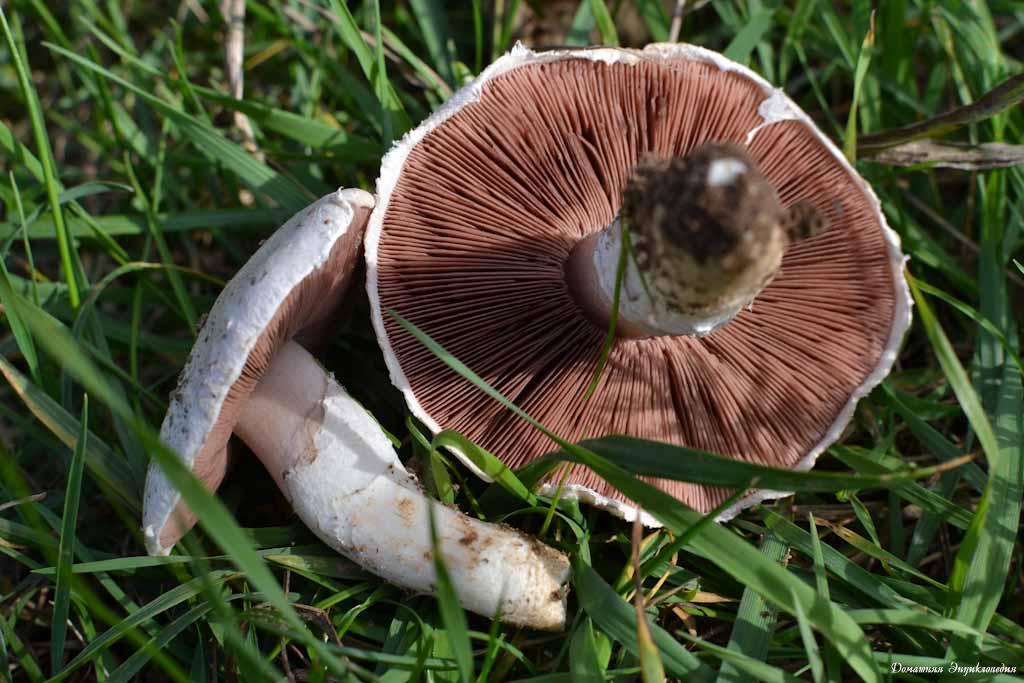
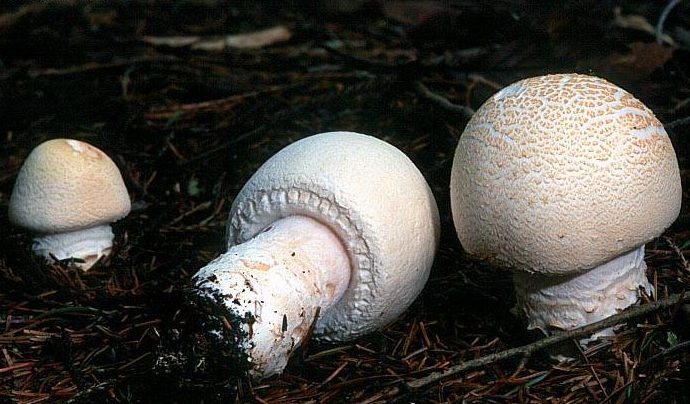
Field champignon is characterized by a silky white hat, the diameter of which varies between 5-15 cm. For a long period of time, the hat is closed and hemispherical. Ripe fruits have an open hat that wilts in old age. The strong leg is quite thick and painted white. A two-layer ring is formed on it, the lower part of which is radially torn.
The curved plates at the beginning of the growth are off-white in color, and in mature mushrooms they become brown and free. The white flesh on the break turns yellow and smells of anise.
Rules and gathering places
It is better not to cut the mushroom, but to twist it from the soil. The place of cut can begin to rot, which is fraught with the death of the entire mycelium.
You can find meadow champignons in open areas, the soil of which is rich in humus. After rains they are found near farms, in meadows, pastures, in gardens, parks and kitchen gardens. Sometimes mushrooms are found in forest edges, where they usually grow in groups. It happens that fruiting bodies form “witch rings”. Field champignon can live in mountainous areas, near firs and thickets of nettles. Forest champignon most often forms mycorrhiza with spruce. He is also found near anthills.
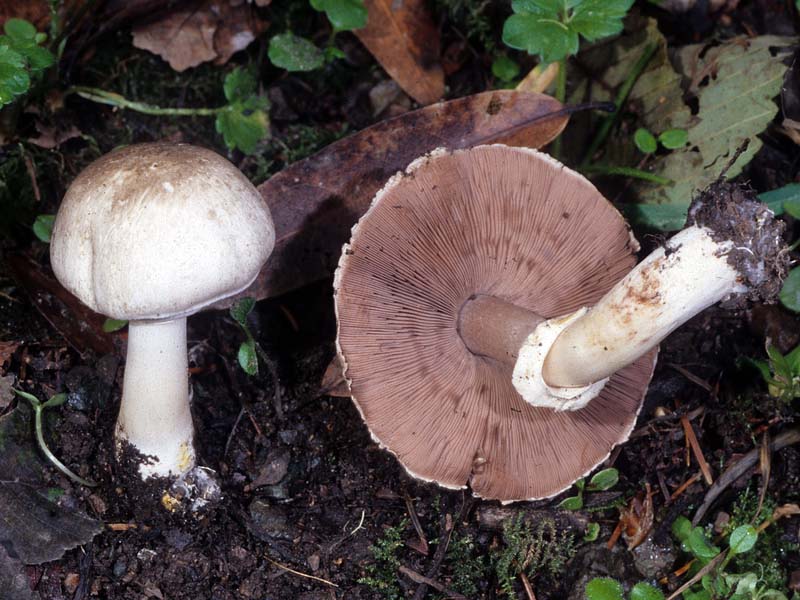
Difference from other species
Inexperienced mushroom pickers are advised to go on a quiet hunt with a more experienced companion, because there are many dangerous doubles that look very much like mushrooms.
False, inedible champignons
Most often, inedible species live in forest areas, but can be found in gardens, parks and meadows. Outwardly inedible fruits are very similar to champignons, but have distinctive features.When pressed on the fruit body, the twins immediately turn yellow, and the cut at the base acquires a bright yellow color, which gradually turns into orange or brown. Edible smells pleasantly of anise, and their counterparts have a “pharmacy” smell of iodine or carbolic acid.
The following types are of great danger to human health:
- redhead (A. xanthoderma);
- yellow skin (A. xanthodermus);
- ploskoshlyapkovy (A. placomyces).
The most accurate way to determine the unsuitability of the fungus is heat treatment. Mushrooms placed in boiling water are painted for a few seconds in a bright yellow color along with water. When boiling, the unpleasant odor of the medicine increases, but only for a couple of seconds. These fruiting bodies should not be eaten, because toxic substances do not disappear after boiling.
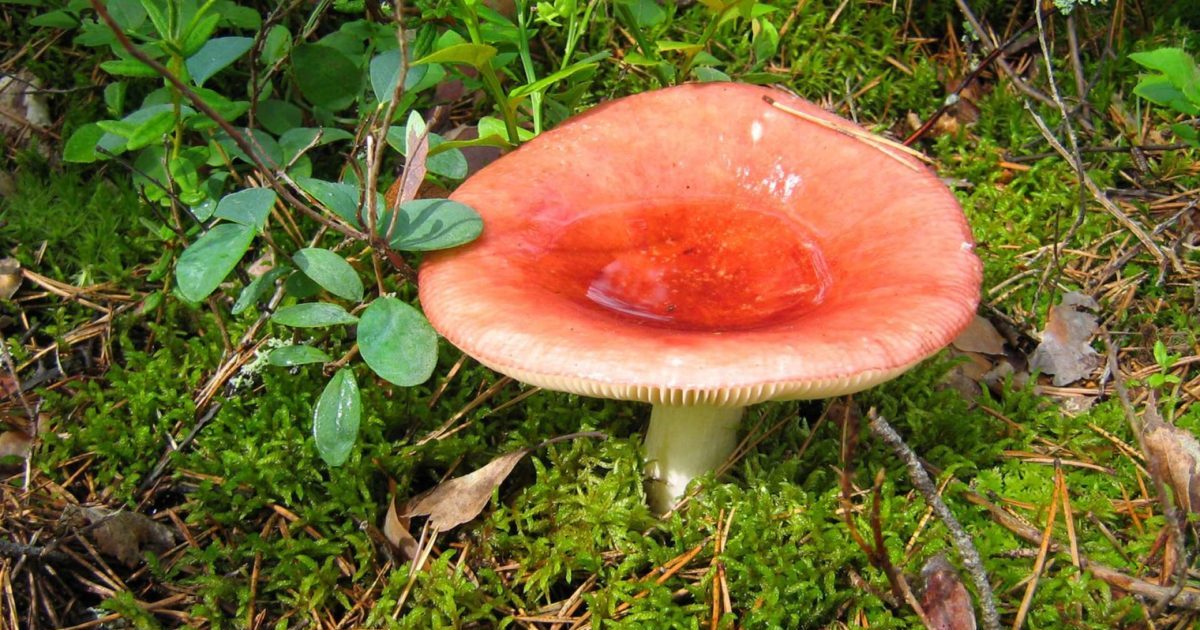 You may be interested in:
You may be interested in:White mushroom-like mushrooms
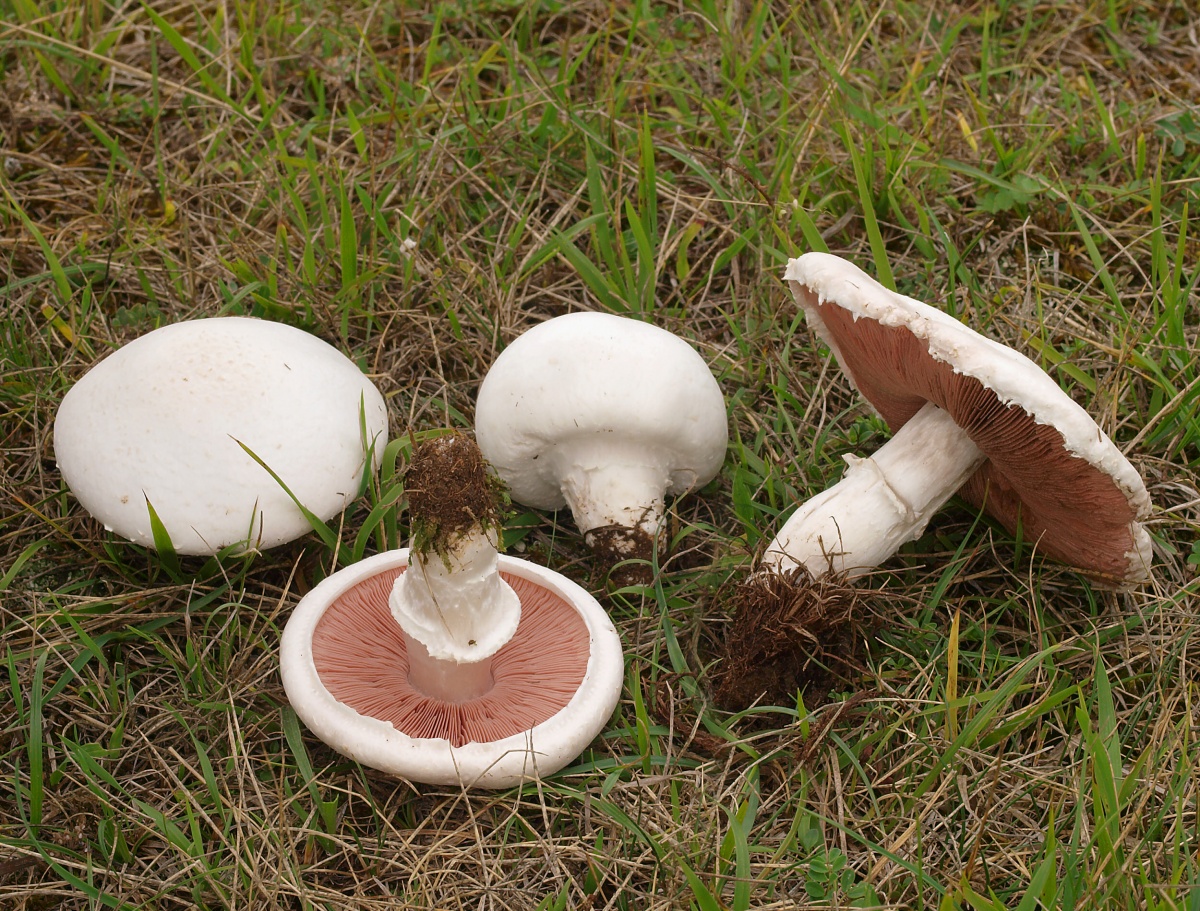
In addition to close relatives, you can confuse the mushroom with other similar mushrooms. Young edible fruits are very similar to a pale toadstool and light species of fly agaric.
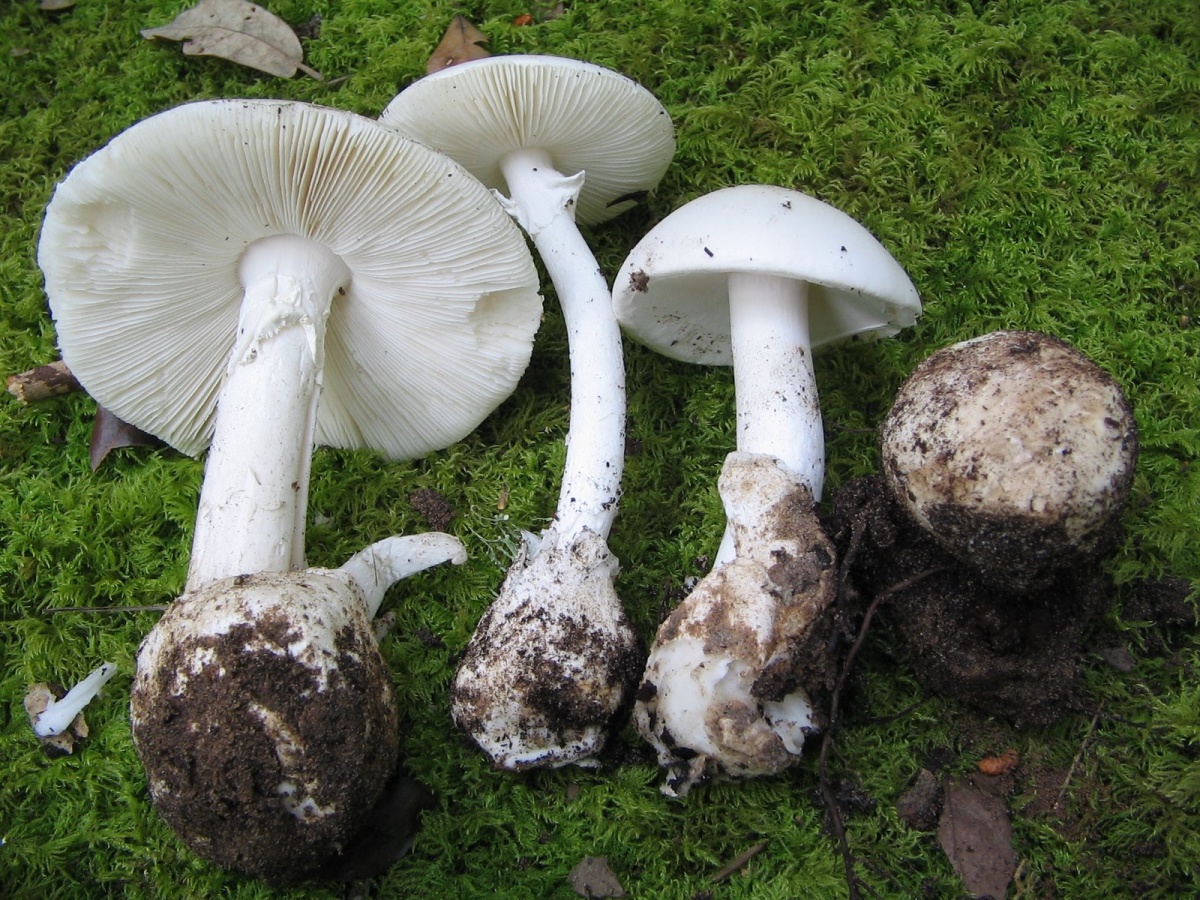

These poisonous species with white plates live in coniferous and mixed forests, so they can be mistaken for coppice champignon. Its appearance practically does not differ from poisonous mushrooms: on the surface of the hat there are scales, the shape of the caps is the same, the white color of the plates and the presence of a ring on the leg.
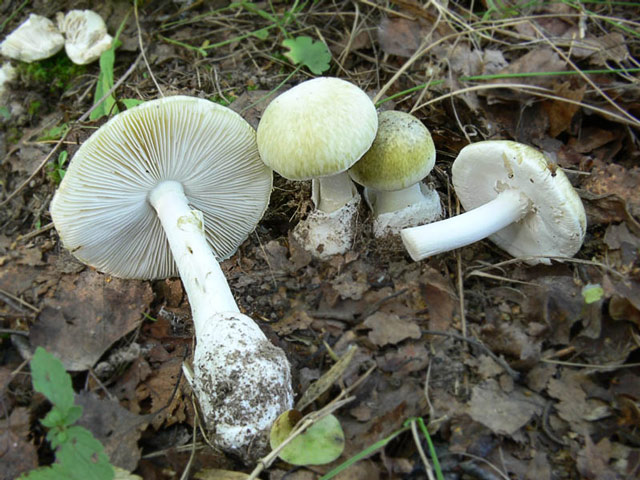

As you know, with age, champignon changes the color of the plates, and the plates of grebes and fly agarics remain snow-white all the time. When pressed, the poisonous fruit does not turn yellow, and its leg always grows from a Volvo, which is not always clearly visible.
The benefits and harms of champignons
If the fruits grew in good conditions and did not have time to absorb environmental toxins, then they can be consumed even by pregnant and lactating mothers.
The mushroom contains a lot of substances useful for humans:
- Minerals: manganese, magnesium, calcium, zinc, sodium, iron.
- Vitamins of group B, E, C, PP, D.
- They contain protein that is easily digested. Minerals along with protein accelerate metabolism, so this product is often included in various diet foods.
In addition, the product is also consumed raw - in appetizers and salads. When cooking, part of the nutrients disappears, but excellent taste qualities are revealed.
Recipes and cooking rules
Champignon is so common mushroom that there are many recipes with its addition. Consider the most universal.
Treatment
After collecting or buying mushrooms, they should be processed before cooking. For this:
- washed under running water;
- wipe with a damp cloth;
- remove the top layer of the skin from the cap;
- if the cut on the leg is old, then it should be updated;
- skirts and dark plates are removed;
- places of damage are cut off.
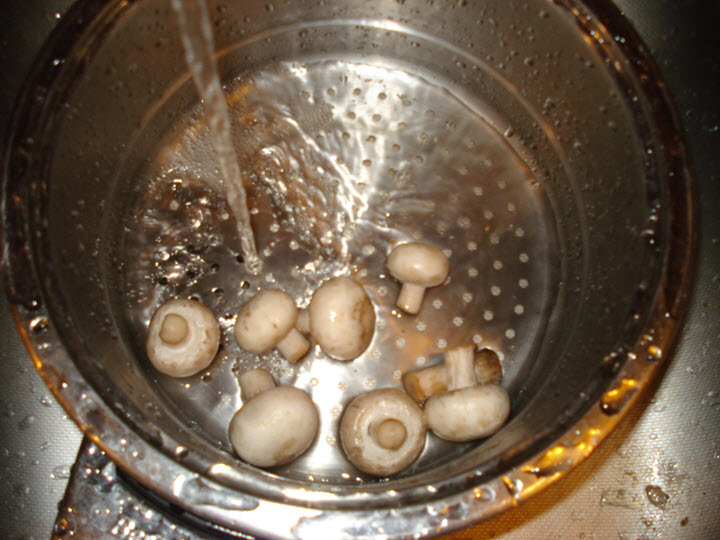

It is not necessary to clean the hats. This procedure is done only for large mushrooms, because their skin becomes rough. If the skin is easy to move with your fingers, then the top layer is better to remove.
 You may be interested in:
You may be interested in:Cooking time and methods
Store champignons should be cooked for only five minutes, but it is better to boil wild ones for 10 minutes. If there is a slow cooker, you can cook them without adding water by setting the “Extinguishing” program for 40 minutes.The frozen product is thawed and then boiled for 10 minutes.
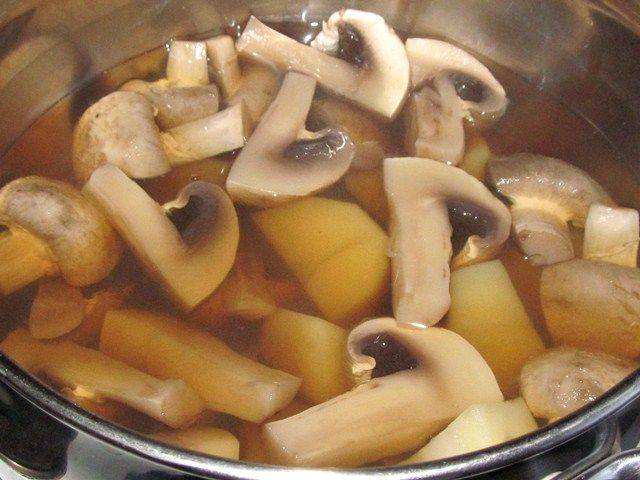

For salad, you need to cook them for 5 minutes with the addition of salt, black allspice, bay leaf and citric acid. If the fruits will be used to make soup, then boil them in slightly salted water for the same time.
How to fry champignons
For frying, fruiting bodies do not need to be boiled beforehand. To properly fry them, you should:
- it is good to heat the pan over medium heat;
- pour a little vegetable or butter;
- put the chopped mushrooms into a container in small portions and fry, stirring regularly;
- salt and pepper to taste at the end of frying.
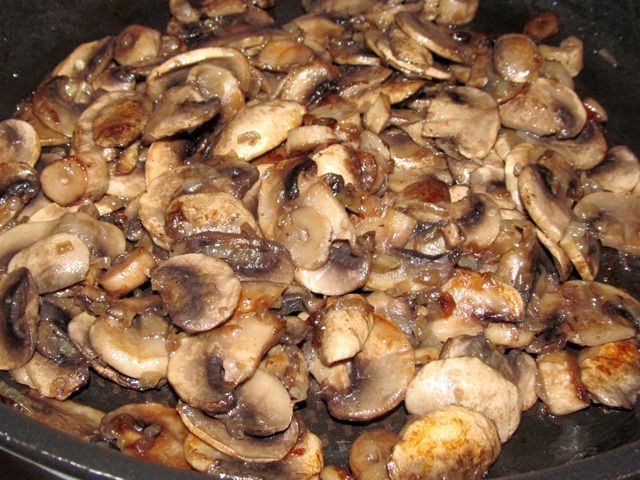

Frying time should not exceed 7 minutes. You can use mushroom mass as an independent snack or include it in the composition of a wide variety of dishes.
Answers to Common Questions
 You may be interested in:
You may be interested in:To date, champignons are the most popular mushrooms. They can be found not only on any supermarket shelves, but also have a great time hunting for them in the forest.































 Care and use of Kombucha at home (+22 photo)
Care and use of Kombucha at home (+22 photo) Edibility of the fungus of the motley umbrella and its description (+19 photo)
Edibility of the fungus of the motley umbrella and its description (+19 photo) Description of edible and inedible oils, their poisonous counterparts (+40 photos)
Description of edible and inedible oils, their poisonous counterparts (+40 photos) Useful properties of milk mushroom and its contraindications (+17 photos)
Useful properties of milk mushroom and its contraindications (+17 photos)