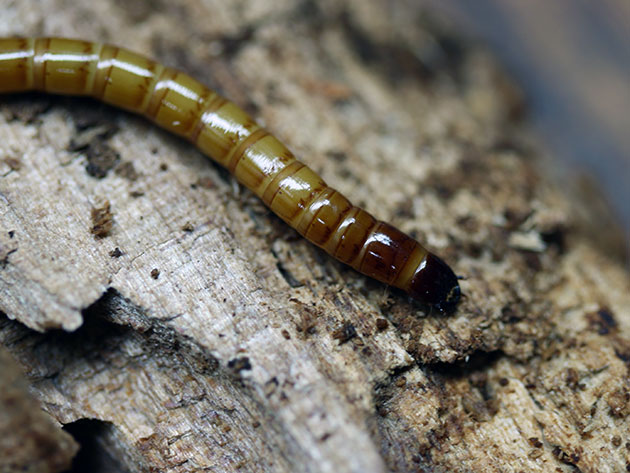
 Nutcrackers or wireworms are a whole family of beetles. A rather large insect, with a maximum length of approximately five centimeters (usually 2 cm). The family has a large number of species - ten thousand inhabit America and Europe, are found in Asia, several hundred species live in Russia, and are distributed almost everywhere.
Nutcrackers or wireworms are a whole family of beetles. A rather large insect, with a maximum length of approximately five centimeters (usually 2 cm). The family has a large number of species - ten thousand inhabit America and Europe, are found in Asia, several hundred species live in Russia, and are distributed almost everywhere.
The name “nutcracker”, in English “click beetle”, the bugs got for their peculiarity. If they turn them on their back, then the bug will jump with a characteristic sound, similar to a click. The sound will continue until the insect returns to its normal position.
Beetle larvae are called wireworms. They eat most often the underground parts of most plants. They owe their name to the unusual body structure and behavior. They have a fairly dense cover, consisting of chitin and a worm-like body, which makes them look like a piece of wire. The thoracic section of the insect can be divided into several parts - the front and middle parts. On the lower side on the front of the chest there is a finger-shaped outgrowth, facing back, and on the middle part of the chest there is a fossa. The beetle, tipped over on its back, bends, pulls out the outgrowth from the fossa and rests it on the edge of its wall, after which the click returns to its original position with a click. This action allows the bug to bounce. He will jump until he rolls over onto his abdomen and legs.
Content
Life cycle
The developmental cycle of the nutcracker beetle occurs within five years. During spring, female beetles after hibernation (from April to July - depending on the region of habitat) lay their eggs in the upper fertile soil layer. Especially makes it easier for them to have cracks, weeds, lumps and other irregularities. The masonry process occurs in groups (3-5 pieces). At one time, the female can lay a maximum of about 200 white eggs. Further, depending on the habitat and species of the beetle itself, after about 20-40 days, larvae emerge from the eggs, which develop over four years. Wireworms are in the ground. All their first year they feed on plant roots, but practically do not bring harm to the economy. By next year, the larvae grow and become usually yellow or light brown in color. They become mobile. The body covers the chitinous cover, so it is almost impossible to crush them. From this year, the larvae become dangerous and cause great damage. By the fourth year, pupation of an adult larva in the earth occurs, and in the spring new bugs appear from them. The cycle repeats. Before pupation occurs, the larva must eat a lot - “gain stock”, so they are very voracious.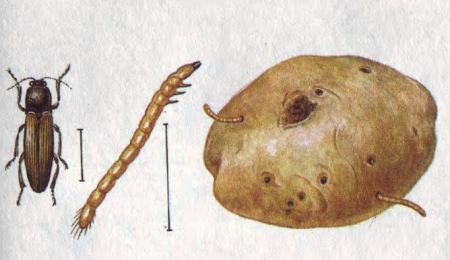
The rules struggle folk means
Chemicals also cause harm to beneficial organisms, so many prefer to use substances of plant nature - for example, celandine infusion. They are advised to water the land before planting.
Between the rows of plants you can sprinkle earth with wood ash. This leads to the death of the wireworm.
Also a good effect is the introduction of nitrogen-containing fertilizers into the ground, pouring with ammonia water. It also allows fertilizing plants.
One of the relatively cheap, but working methods is crushed egg shells, which are scattered throughout the site;
For wireworms, baits are laid out, slices of beets, carrots or oilcake are used in their quality, in pits to a depth of 7-15 cm, which are then covered with a layer of plywood or iron. After a few days, the lid is removed from the pits, the larvae accumulated in them are burned. This procedure begins to be carried out two weeks before planting crops and continues throughout the summer.
Decline acid the soil
The optimal conditions for the life of the wireworm is acidic and moist soil. In contrast, many food crops need neutral or alkaline earth. Therefore, another method of control is liming the earth or reducing its acidity.
This procedure is recommended to be carried out every three years. You can determine your soil type using litmus paper.
If your site has a large number of larvae of the nutcracker beetle, then watering the plants should be carried out after the soil becomes very dry. The depth of the dry layer should be at least 15 centimeters. This will create disastrous conditions for wireworms.
Agrotechnical methods of controlling beetle
These methods are lengthy in their implementation, a single application is not effective.
- In autumn, a deep digging of the site is carried out. Dig the soil as deep as possible before the start of frost. At the same time, the larvae do not have time to hide back into the ground and freeze out;
- Hygiene of the earth. This is achieved by the most complete harvest of weeds, their roots, branches, debris. In the first year, the rhizome of wheatgrass and other weeds are excellent food for larvae. Therefore, during the first stage (digging) you need to carefully remove the wheatgrass roots;

- The sun's rays adversely affect the eggs of beetles, until death. Therefore, in late spring or summer, surface loosening of the soil is carried out;
- Two-or three-field crop rotation is carried out. That is, after harvesting the potato field, the field is planted with legumes. It also helps to enrich the soil with nitrogen, to fight many pests, including wireworms. It is also a good way to control weeds.
Chemical way
This method consists in treating the soil with various anti-wireworm preparations. It has its drawbacks - poisons cost a lot of money, they also hit useful animals and bacteria that are in the ground. Therefore, it is not always resorted to, especially in small areas.
However, in cases when the nutcracker beetle has already greatly bred, you can use the tool "Aktara". They are watered the land in which they will be planting, you can also soak in the solution the tubers that you are going to plant.
Prevention
- Each year in the spring and autumn it is recommended to dig the land on its site to the maximum depth. In the raised lumps weed roots, sticks are removed, wireworms also fall to the surface and die in sunlight and heat (in summer) or frost (in winter);
- You must regularly weed the site to clean it of weeds and their roots. Especially loved by nutcrackers and their wheat grass larvae. If this does not help and the herbs are too much, you can use chemicals (such as Roundup) to destroy it;
- You can grow plants with a strong smell, such as marigolds. Its aroma attracts pests, but the juice is poisonous to the larvae. You can also alternate the cultivation of crops, for example, after potatoes, plant legumes, soy. On their roots live special bacteria that release nitrogen into the soil. This leads to alkalization of the soil (reduces acidity) and adversely affects pest larvae.
Reviews
Alyona:
And the neighbors advised sprinkling mustard or rye seeds from the wireworm, they say it effectively, but we have not tried it yet.
Anna:
I have been sowing mustard after harvesting potatoes for a year now.The wireworm was long gone. I also heard that there are varieties and plants that pests do not attack so much. I was advised the Laton variety. Only I have been growing it for three years now, and this potato has become worse in fruiting, the tubers are smaller in size. Nutcracker larvae bite literally on a bit of potatoes.




 Where does moss come from in the garden and is it necessary to get rid of it?
Where does moss come from in the garden and is it necessary to get rid of it? The most effective ways to deal with ants in the area
The most effective ways to deal with ants in the area Cockchafer and Bear: An Easy Way to Save Plant Roots
Cockchafer and Bear: An Easy Way to Save Plant Roots Get rid of the aspen nest quickly and safely.
Get rid of the aspen nest quickly and safely.