Does a greenhouse need a foundation?

The foundation is the underground part of the structure, which transfers the loads to the ground, created by the weight of the structure and the movement of water, transport, and wind. When choosing it, you need to pay attention to the method of manufacture, options for reliance on the soil and form.
With proper design, the foundation transfers all loads to the ground, which prevents shrinkage, distortion or destruction of the object.
Why do we need a foundation

In warm, dry climates and in mountainous areas, you can do without a strong base, but in areas with snowy winters, with the construction of buildings, you can not do without a foundation. When freezing the ground swells and rises to the top, sometimes up to 10-15 cm, which would entail a violation of the integrity of the object. The foundation for greenhouses has a number of functions, it is:
- does not allow wind, rain to damage or move the greenhouse;
- protects against contact with the earth, prolonging its service life;
- increases the temperature in the shelter by 10%;
- prevents penetration of rodents;
- limits the penetration of cold air and fog.
In cases where gardeners want to grow greens and vegetables in a heated greenhouse in winter, a foundation is vital.
Types of foundations

Many gardeners, when buying a greenhouse, are wondering: “Does a greenhouse need a foundation?”. You can put it directly on the ground, but this will significantly reduce the service life of the covering device.
Before installing a polycarbonate greenhouse, you should think about what type of foundation for it to choose, depending on:
- the height of groundwater and freezing of land;
- terrain relief;
- the size of the greenhouse;
- financial capacity of the owner;
- features of landscape design.
Distinguish the foundations:
- tape
- slab;
- Pile
- columnar.
Tape

Refers to the most sought-after view among supports for buildings. There are several types of the type of construction:
- Not buried For this species, only the upper fertile layer is removed. Lay it on a dense ground.
- The shallow-depth is laid on a special pillow in a trench at a depth of 70-80 cm. It is not used in areas with high groundwater.
- Recessed, which is dug below the level of freezing of the earth by 20-40 cm.
Strip foundations vary in the use of materials. They are:
- monolithic concrete, in which the frame of the reinforcing mesh is filled with cement mortar;
- from concrete blocks connected by reinforcement;
- rubble - from clay and bricks;
- from foam blocks;
- from scrap materials (logs, bottles).
- timber.
We collect odnoskatny greenhouse
In conditions of lack of free space on the site erect sloping greenhouses with their own hands within 1-2 hours ....
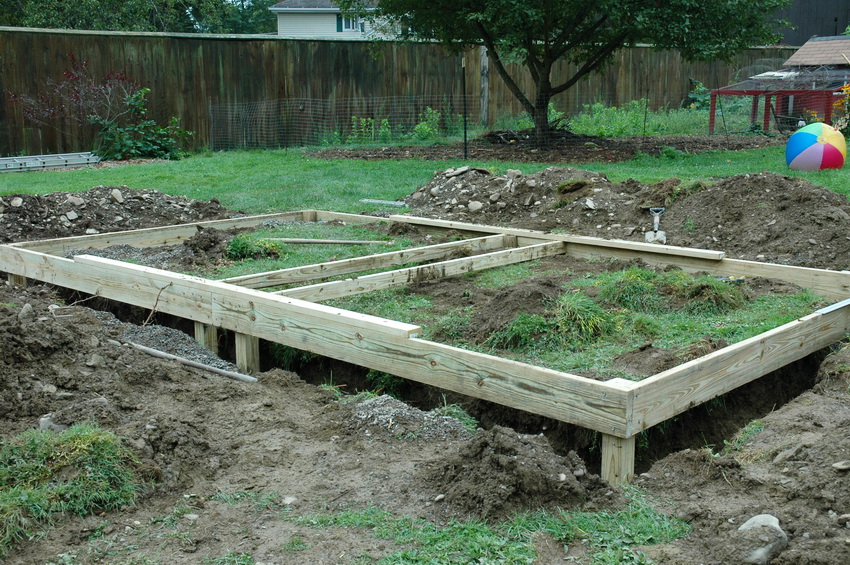
Strip foundations are constructed for large and heavy greenhouses. The procedure is as follows:
- Determine the size of the greenhouse and make the layout of the foundation.
- To avoid bias, pegs are driven into the corners and the thread is pulled.
- Focusing on the thread, dig a trench around the perimeter about 25-30 cm wide.
- Sand is covered with gravel on the bottom and tamped down.
- Install the formwork of the boards.
- Ruberoid is laid on the bottom.
- Inside the trench make the frame of the armature.
- Pour cement mixture.
- Waiting for complete drying and establish a greenhouse.
The advantages of such a foundation:
- withstands heavy loads;
- has a long service life;
- cheaper than monolith.
The disadvantages include the fact that this structure must be filled with concrete in one go, which is quite laborious. Therefore, each owner himself decides to put a greenhouse on the foundation or directly into the ground.
Unusual bottle foundation

Economical summer resident can not only build improvised greenhouse, but also to make the foundation for the greenhouse of unnecessary glass bottles. To reduce waste on concrete and increase the heat retention inside the greenhouse, they use bottles in the construction of the foundation. Operating procedure:
- They dig a trench around the perimeter of the future greenhouse to a depth of 10-20 cm more than the soil freezing.
- Install the formwork.
- Pour a pillow of gravel and sand, tamped.
- Pour a small layer of concrete.
- Tightly place the bottle in one row in a fresh, not frozen solution.
So, alternate the solution with the bottles to the top formwork. The last layer of bottles line pouring a thick layer of cement mortar.
Benefits:
- low cost;
- moisture resistance;
- long service life;
- corrosion resistance;
- no shrinkage.
Disadvantages:
- fragility of glass containers;
- unsuitable for use in heaving soil and high groundwater.
The foundation of the timber

The selected timber should be clean, with no signs of decay, treated with antiseptic.
For work choose bars with dimensions of 10 by 10 or 15 by 15 cm.
- With the help of a rope and a peg they make markings for the future foundation, observing an angle of 90 degrees.
- Dig a trench, more than height and width of a bar on 5-8 cm.
- Consolidate the bottom.
- Wrap the bars with ruberoid.
- The corners of the structure are connected in the paw way. Additionally fasten with staples.
- Minor horizontal deviations are eliminated by pouring rubble or sand.
How to make a greenhouse from plastic pipes with their own hands
In stores for gardeners, you can find any ready-made greenhouse, but it does not always correspond to the wishes of people. By this…
To make the wooden timber better preserved in the ground, not rotten and not covered with fungus, hardwoods such as larch are used, and before laying it is impregnated with protective agents, for example, with machine oil.
Slab

Most suitable for areas with high groundwater and unstable ground. Scientists have found that the pyramids in the desert are exactly on this foundation.
There are:
- floating where the concrete slab lies almost on the surface;
- combined construction, where the plate is laid on stiffeners.
For the construction of this type of foundation they dig a ditch with a depth of 30 to 70 cm, depending on the purpose of the future greenhouse. If vegetables are grown only in the summer period, then 10 cm of the basement thickness is sufficient. If the stationary heated greenhouse will function year-round, then 20-25 cm will be the best option.
Initially:
- A gravel-sand pillow is laid at the bottom of the pit, it is closed with either geotextile or roofing material to avoid moisture penetration.
- Install a timbering around the perimeter of wooden planks. Lay the armature and drainage pipe. The space between the walls of the formwork and the ground is filled with gravel.
- Fill the space with concrete along the edge of the formwork, trying to prevent the occurrence of voids. Insert fasteners for the greenhouse.
- For 7 days, wet the concrete with water to avoid cracking.
- They allow the foundation to dry for about 1 month depending on the region and weather conditions.
- Clean the screed, cover the space between the ground and the foundation with gravel.
Pile

Ideal if the plot is located on uneven wetlands. Piles are set at a level below the soil freezing by 20-30 cm. There are:
- zabivny;
- screw;
- Pour into drilled holes.
The sleepers include sleepers and pipes, and the screw ones - poles with special blades that are screwed into the surface of the earth with a drill or other special equipment. The procedure for pouring:
- Mark up the location of the greenhouse.
- Make markings for future pillars around the perimeter at a distance of about 1 m from each other.
- With the help of a drill, wells are made about 1.5 m deep.
- Install the formwork of roofing material or asbestos.
- At the bottom poured a layer of rubble and sand, rammed.
- Insert a pre-welded structure of reinforcement.
- Inside the formwork, high-quality concrete is poured in layers, allowing the previous layer to dry.
- Fill asbestos pipes completely and give the concrete some time to fully cure.
- Remove the formwork, install the grillage.
This design does not protect against rodents, drafts, does not have good thermal insulation. Use it only in the case when a different type of foundation is not suitable.
Benefits:
- does not require concrete work;
- less time is spent on installation;
- in violation of the geometry of the pile can be pulled out and reinstalled.
Disadvantages:
- complexity in vertical installation independently;
- the cost of calling specialists and technology.
After installation of the piles, they are leveled at the top points and are tied together with sleepers or timber.
Pillar foundation

Pillar foundations differ from each other in the materials used.
There are:
- reinforced concrete structures;
- brick;
- block.
For small greenhouses, 8 supports are sufficient. They are buried in the ground at 70-80 cm. The distance between the pillars is 1.5-2 m.
The disadvantages include the presence of a gap between the ground and the greenhouse, which is required to close
At installation of the greenhouse on the base it is not necessary to forget about an important point. To avoid the occurrence of drafts, ice formation, freezing, rubber gaskets are laid in the gaps in the joints and covered with special sealants. This is especially true of covering structures, where they plan to operate all year round.
Foundation selection
The choice of foundation depends on the goals. If the greenhouse will be in operation only spring and summer periods, you can stay on the foundation:
- columnar;
- from a bar.
If the tasks of the greenhouse include providing the family with vegetables and herbs all year round, then it will be necessary to spend money on a ribbon or tiled foundation.
If the groundwater is close and the site is on a slope, then pile, columnar and screw foundations will come to the rescue.