 Grow big grape harvest - a huge work requiring a gardener of certain theoretical and practical knowledge and skills. An important point of agricultural technology is the formation of a bush, the duration and abundance of fruiting of grapes depends on it.
Grow big grape harvest - a huge work requiring a gardener of certain theoretical and practical knowledge and skills. An important point of agricultural technology is the formation of a bush, the duration and abundance of fruiting of grapes depends on it.
Content
- 1 What is the formation of a grape plant
- 2 The need to form vineyard bushes
- 3 The main conditions for choosing a formation scheme
- 4 Features of culture growth
- 5 The basic scheme of the formation of the bush
- 6 The accelerated formation of vine bushes
- 7 Formation methods using trellis
- 8 Arbor Formation
- 9 Dates & Rules
- 10 Reviews
- 11 Conclusion
What is the formation of a grape plant
 The life period of a grape bush is conditionally divided into three stages:
The life period of a grape bush is conditionally divided into three stages:
- growth, a set of vegetative power (lasts 5-6 years);
- active fruiting (25-50 years);
- weakened growth, decreased reproductive activity.
Fruiting and aging depend not only on the climatic conditions of the area, nutrition, care, but also pruning of bushes. On lianoid plants, shoots appear in the most unexpected places, and to increase the number of bunches it is necessary to form a bush.
Formation is pruning according to certain schemes, where the variety, the characteristics of the bush, and other factors are taken into account.
Clean:
- not particularly significant stepsons;
- diseased and deformed shoots;
- extra kidneys.
Thanks to the procedure, redistribution of nutrition takes place, providing the necessary elements of the main fruiting vines with the necessary elements.
The need to form vineyard bushes
 Pruning bushes - laborious, but important procedure to increase crop yields. In addition, due to the formation of:
Pruning bushes - laborious, but important procedure to increase crop yields. In addition, due to the formation of:
- simplified planting care;
- the risk of infections is reduced;
- the taste of berries improves.
Strong, strong bushes are able to withstand adverse loads, to avoid freezing even in severe climatic zones. Properly trimmed bushes give more berries, while there is no difficulty in collecting clusters.
In the absence of pruning, the berries gradually grow smaller, taste deteriorates every year, yield from the bush decreases. Plants do not tolerate the cold period, often get sick.
The main conditions for choosing a formation scheme
 Cut the shoots according to certain patterns. Several options for removing branches of grape bushes have been developed and put into practice. The choice is determined by:
Cut the shoots according to certain patterns. Several options for removing branches of grape bushes have been developed and put into practice. The choice is determined by:
- the climate of the territory where the grapes are grown;
- type of soil;
- the rate of shoot development;
- the main characteristics of a particular variety;
- the need for shelter for the winter.
Take into account the parameters of the accumulation of wood pulp bushes, soil fertility. On scarce soils, where there are problems with watering, bushes with a small number of sleeves are grown. For fertile soils with abundant watering, any form, including with many sleeves, is suitable.
In cold regions, grapes in winter requires shelter, therefore, choose the most suitable for prigibling shoots scheme. In central Russia, where winters are not snowy and strong winds often blow, the bushes are covered entirely. In the northern regions (Urals, Siberia, North-West) winters are colder and longer, therefore, there they practice their methods of pruning.
Features of culture growth
 When choosing a scheme take into account the general features of the culture:
When choosing a scheme take into account the general features of the culture:
- Grapes have no fruit branches.Each branch under certain conditions can produce a crop, and the result depends on pruning.
- There are shoots of the first year (summer), biennial (usually clusters of the main crop are formed on it), perennial.
- The vine can be of standard and non-standard type. The first is common in the southern regions, characterized by upward sleeves (fruiting vines). The second type - the bush grows with fan-type sleeves, for supports use stakes (bowl) or trellis.
- A stamp is a long-term part, a shoulder.
- A sleeve is a perennial shoot located on the shoulder.
- Arrows or fruiting vines - biennial branches.
The location of the shoulders or cordons is different, depending on the climate of the region. One common thing - they are located horizontally to the surface of the earth, while the height of the sleeve and shoulder is high, medium, low.
The basic scheme of the formation of the bush
 Cut the fruit plant in certain ways, providing ventilation, a sufficient level of lighting, the stability of the bush.
Cut the fruit plant in certain ways, providing ventilation, a sufficient level of lighting, the stability of the bush.
Sleeve scheme
Plants trimmed by the sleeve method have a short life span. But for small areas, this option will be convenient and most acceptable.
Suitable for regions with harsh climates, cold winters, strong winds. Parts of the plant are cut annually, otherwise there is a nutritional deficiency and, as a result, planting death. In the first season, all branches are removed, leaving only the strongest and heap-growing (long and short). The number of kidneys on the long - 7-9, on the short - 2-3 pieces. In the fall of the second year, a long branch is cut. The short one leaves only strong arrows.
Fan shape
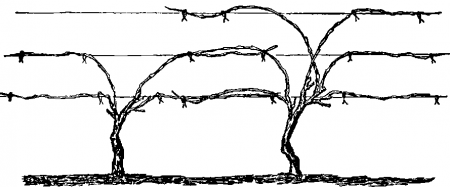 The scheme is similar to a sleeve, but the gardener has to grow at least 5-6 sleeves. The name is given due to the similarity of the resulting form with a fan, since there are more branches on the plant. Location - on either side of the root.
The scheme is similar to a sleeve, but the gardener has to grow at least 5-6 sleeves. The name is given due to the similarity of the resulting form with a fan, since there are more branches on the plant. Location - on either side of the root.
For two seasons, you need to grow two strong powerful vines. The garter is vertical. On the support, the arrangement is a fan, for lengthening, a pair of processes are left. Large, medium and small vines are distinguished along the length.
The fan pattern is popular with winegrowers, as it is suitable for many varieties of culture. Use faith when growing plants on trellises, stakes.
Cordon form
 The time for creating the shape of the bush is about four years. To begin with, growing branches thin out, leaving a distance of 30 to 42 cm between them. Leave long sleeves, use all the vines.
The time for creating the shape of the bush is about four years. To begin with, growing branches thin out, leaving a distance of 30 to 42 cm between them. Leave long sleeves, use all the vines.
It is necessary in the first two years to grow a strong powerful stalk, then cut it at a certain distance, tie it up arbitrarily to the support (trellis, trellis).
In the third year, they begin to grow arrows on the sleeve, thinning them, removing weak and sick specimens. In the 4th year they begin to work with the fruit link.
Using Guyot's Scheme
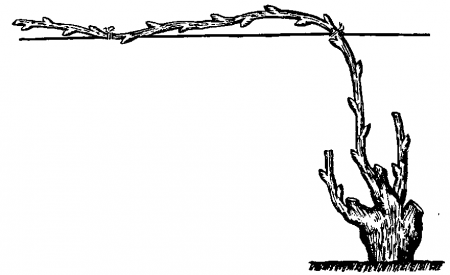 A relatively simple scheme for pruning a vineyard using the Guillot method. Using it, get juicy, large grones, while increasing the overall productivity.
A relatively simple scheme for pruning a vineyard using the Guillot method. Using it, get juicy, large grones, while increasing the overall productivity.
Forming options - with one or two shoulders. In the first case, they form the only small shoot with a well-developed fruit bud. When leaving two shoulders, two sleeves with stepsons grow.
Guyo with two shoulders fits when growing vineyards on poor soils when the bushes are weak. One-shoulder planting is practiced with tight schemes where the distance between plants is 1-1.2 meters.
Moser Formation
 The scheme was named after the famous Austrian winegrower Lorenz Moser. Basically, the growing method is used in industrial viticulture, noting the intensity of the technology. In amateur gardening, the method was modified, taking into account specific climatic conditions.
The scheme was named after the famous Austrian winegrower Lorenz Moser. Basically, the growing method is used in industrial viticulture, noting the intensity of the technology. In amateur gardening, the method was modified, taking into account specific climatic conditions.
The essence of the Moser formation: the use of boles, height 1.2-1.3 meters. The system for maintaining green vines has been changed; instead of a vertical arrangement, free overhang is used.This gives a moderate vine growth, simplifies the care of the crop. Binding is done only for some branches, in order to avoid twisting of branches and falling bunches.
Bowl Shaping
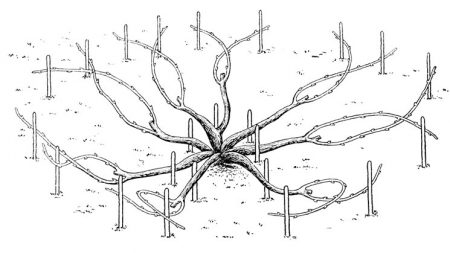 The scheme is used in the vineyards of the southern regions. The location of the sleeves, as well as the quantity, varies. The number depends on the power of the plant, the type and fertility of the soil. Most often, 3-6 pieces are left.
The scheme is used in the vineyards of the southern regions. The location of the sleeves, as well as the quantity, varies. The number depends on the power of the plant, the type and fertility of the soil. Most often, 3-6 pieces are left.
Form for 5-6 years. The scheme for the main stages is similar to fans, but the branches of all plants leave for growth.
Formation of VNIFS-1
 The name of the scheme was obtained in honor of the research anti-phylloxera station, whose employees proposed their own version of pruning the vine.
The name of the scheme was obtained in honor of the research anti-phylloxera station, whose employees proposed their own version of pruning the vine.
Short arrows are left on the sleeves that do not carry knots of substitution. The distance between plants during planting is 2-2.5 meters. Make intermediate anchors, on which the trellis wire is pulled. In the second season, all branches longer than a meter are tied to supports. Weak shoots are left until the next season. Cut the vine to 3-4 eyes, and then proceed to the creation of fruit links.
Hammerless Fan
 In the group of covering schemes, a promising method developed by the gardener D. Tokarev is popular. It is used in areas of small area when it is important to save space.
In the group of covering schemes, a promising method developed by the gardener D. Tokarev is popular. It is used in areas of small area when it is important to save space.
Plants are planted at a distance of 0.8-1 meters, spacing in the aisles up to two meters. Shelter provides protection; grapes quickly resume.
Stub formation
 The method is relevant for southern territories, where the risk of freezing of the vineyard is excluded. It takes 5-6 years to fully form, then it is necessary to maintain the created form of the plant.
The method is relevant for southern territories, where the risk of freezing of the vineyard is excluded. It takes 5-6 years to fully form, then it is necessary to maintain the created form of the plant.
The stamp option allows you to solve many problems in the cultivation of plants. For example, with this method, vineyards are less likely to be affected by infections and pests.
Molding work in the first year
They grow the only strong shoot, defining strong branches on it. One branch is left for growth, the others are cut. In winter, grapes are wrapped up, otherwise the whip will freeze.
Second year molding
The sturdy pillar of last season is becoming like a standard. Carry out a control pruning, leaving the branch of the desired size and adding a distance of 2-4 eyes.
After minting, two stepson remain, growing by about 30 cm during the summer.
Third year molding
Cut off stepsons formed on the second level. Only the upper kidneys are left, then the arrows grown from them thin out and tie up.
Fourth year molding
The shoot closest to the ground is cut off, leaving no more than three eyes. This will be the stem (knot) of substitution. From above the growing vine form a fruit arrow, cut into 6-10 eyes.
The accelerated formation of vine bushes
 Schemes are used for the rapid entry of young vineyards into the fruiting stage. Kinds:
Schemes are used for the rapid entry of young vineyards into the fruiting stage. Kinds:
- method N.I. Sklyar;
- scheme stepsons (author F. Bashirov);
- Method of Research Institute "Magarach" (bending of the vine).
Green Formation
It is recommended on fertile soils and subject to the rules of agricultural technology. In young plants, pinch the tops, then leave a couple of stepsons that appeared. In the second year, from these stepsons create knots of substitution, fruit arrows. For 4 years receive a full crop.
Vine bending
 Strong shoots grown in the first year are cut in the spring of the second year by 2-3 eyes. Over the summer, stepsons will appear from them.
Strong shoots grown in the first year are cut in the spring of the second year by 2-3 eyes. Over the summer, stepsons will appear from them.
In the third year in the spring, stepsons are cut:
- a pair of pieces for 12-15 eyes;
- the rest is cut into 2 eyes.
Long tied to a support with the creation of a bend of the vine.The following year, those parts of the stems that gave the crop are cut. Shoots from a part of a curved vine are used to create a fruit link.
Formation methods using trellis
 In the south, vineyards are often grown on trellises. Equip two-plane structures, so that the yield increases by 20-40%.
In the south, vineyards are often grown on trellises. Equip two-plane structures, so that the yield increases by 20-40%.
It is required to follow the rules of planting plants, placing the seedling in the pit so that the lower bud is 10-12 cm higher than the ground. A popular scheme is a fan-shaped one with fanless sleeves.
Between the rows leave a distance of 2-3 meters.
First Year Formation
Get four sturdy shoots, removing all the rest. In the fall, stepsons are cut, length - 70-80 cm. For the winter, the vines are covered with shields, non-woven materials. If the shoots are weak, they leave buds on them, which next year will give the necessary branches.
Second Year Formation
The number of stepsons is increased to six pieces. A shoot is left, which will then play the role of a stem located horizontally. Attach it to the trellis, cut to 8 kidneys.
If it is necessary to form a stem from two sides, a strong stepson is chosen, all the stems below are used for substitution.
The entire upper part of the plant is cut. In spring, two strong shoots are cut into 3 eyes. The total number of sleeves leave up to 5-6 pieces.
Arbor Formation
 Scheme:
Scheme:
- multi-sleeve with the formation of the stem;
- multi-sleeve without a stem;
- vertical cordon.
Used only for varieties that tolerate low temperatures well. Grapes are planted near arches, sheds, arbors.
The length of the main stem is at least three meters. All side shoots are trimmed to 6 eyes. In autumn, the main stem is cut to 2/3, the lateral - up to two buds.
Dates & Rules
 Plant pruning is carried out throughout the life of the vineyard. At the same time, the first years form bushes, and then maintain a given shape. Of all the techniques of agricultural technology, this one is considered the most difficult.
Plant pruning is carried out throughout the life of the vineyard. At the same time, the first years form bushes, and then maintain a given shape. Of all the techniques of agricultural technology, this one is considered the most difficult.
Crop Dates:
- Spring. Form a bush to increase productivity, ease of care for planting.
- Autumn. Plants are prepared for wintering, sheltering in the cold period. Also, by removing excess, diseased shoots, plant health is ensured.
Reviews
Konstantin, Pyatigorsk
I use my own method on my site, I call it cordon. I clean the thin shoot, and tied the strong one to the trellis. I’ll leave shoots on it after about 28-30 cm. Then there will be cordon horns from them. All other stems are harvested.
For the season we get a cordon with several horns on it. The length is about two meters. A strong vine in the current season is left for fruiting. Usually I make 5-6 shoots, one cluster grows on each. Only one cordon remains for next year.
Ivan, Voronezh
I use the fan method. I leave the distance between the bushes no more than 1.2 meters. In the spring with a garter, we make sure that the first eyes on the fruiting vine are higher. They will receive good nutrition, and then in the fall it is easy to select from them a vine for fruiting. All others delete. Then you do not need to grow a knot of substitution.
Conclusion
The rules for forming a vineyard bush are versatile. It is enough to know the fundamentals of the theory, the existing schemes, and then try them out in practice. This is the only way to get the most suitable option for a specific region and site.



 Non-covering winter-hardy grape varieties for Moscow region
Non-covering winter-hardy grape varieties for Moscow region How to keep the vine in winter
How to keep the vine in winter When can I transfer grapes to another place in the fall
When can I transfer grapes to another place in the fall How to cover and prepare grapes for the winter in the suburbs
How to cover and prepare grapes for the winter in the suburbs