In the forests of our country, tubular mushrooms are particularly common, in particular, a mushroom mushroom that looks like a sponge. The name of the fungus reveals one of the features that helps in its search - it grows in shady, moist places near moss. The flywheel is a genus of edible tubular mushrooms and is part of the Boletovy family.
Content
Characteristics
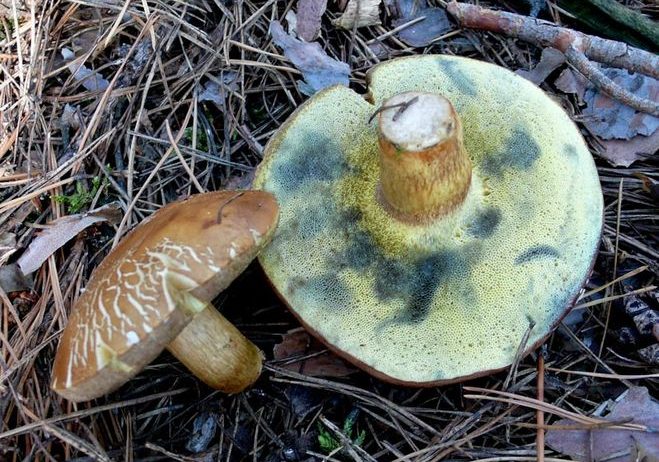
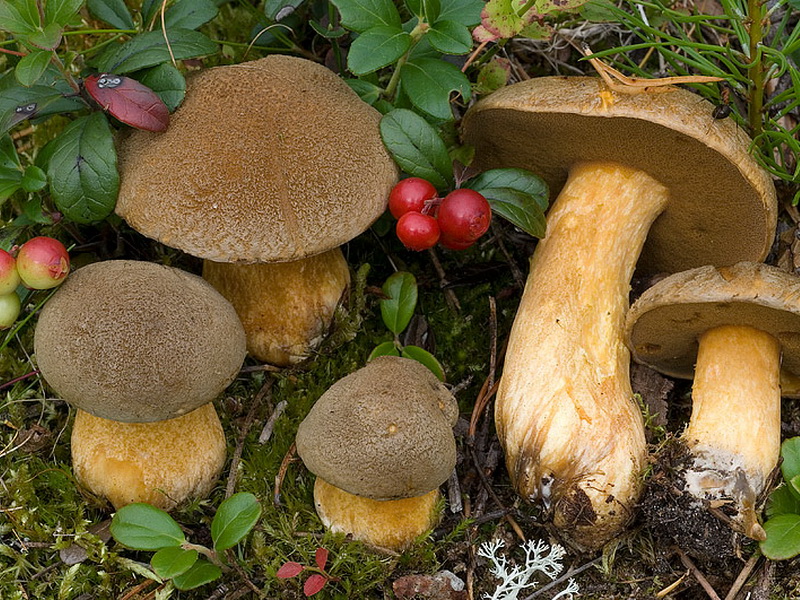
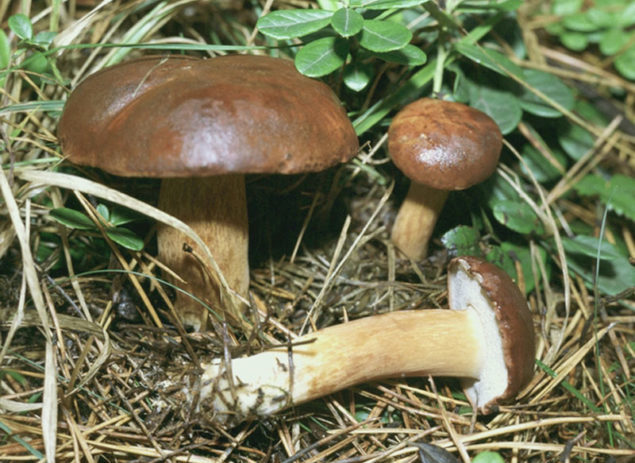
There are several types of mosses that differ in appearance. These mushrooms are widespread almost throughout the world, and they can be recognized by the spongy pulp and the reaction to shear and pressure.
Appearance and morphology of mossovics
The photo and writing of the mushroom of the flywheel make it possible to accurately recognize the fruit in the forest. Its main features:
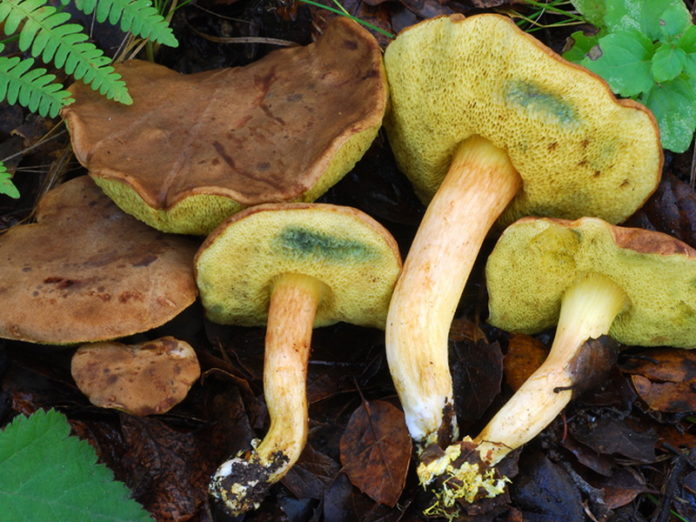
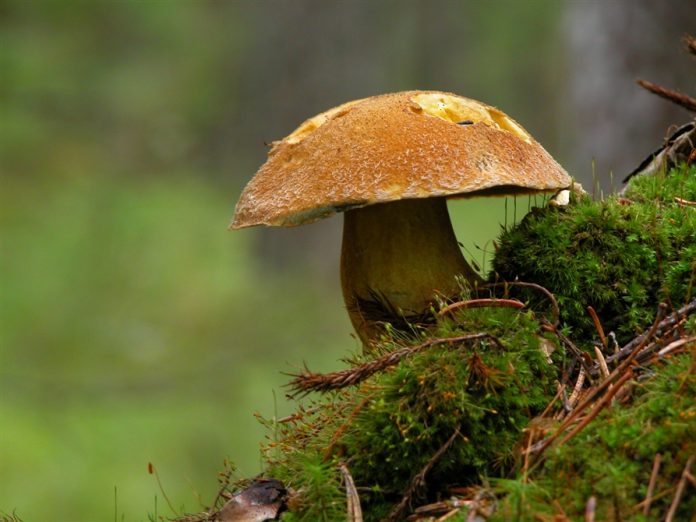
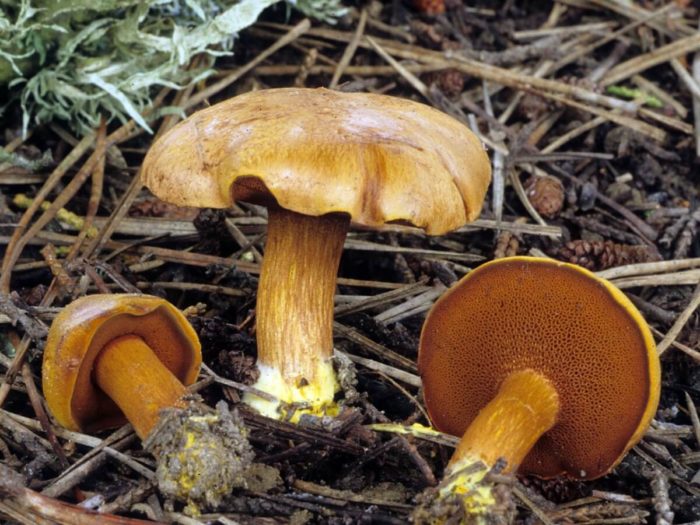
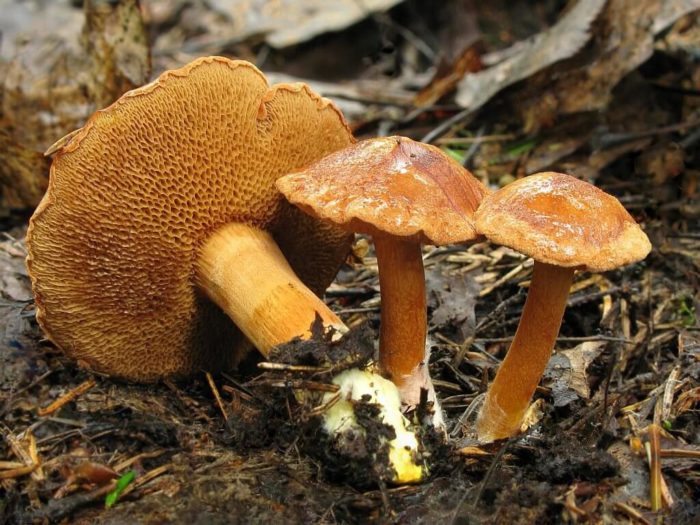
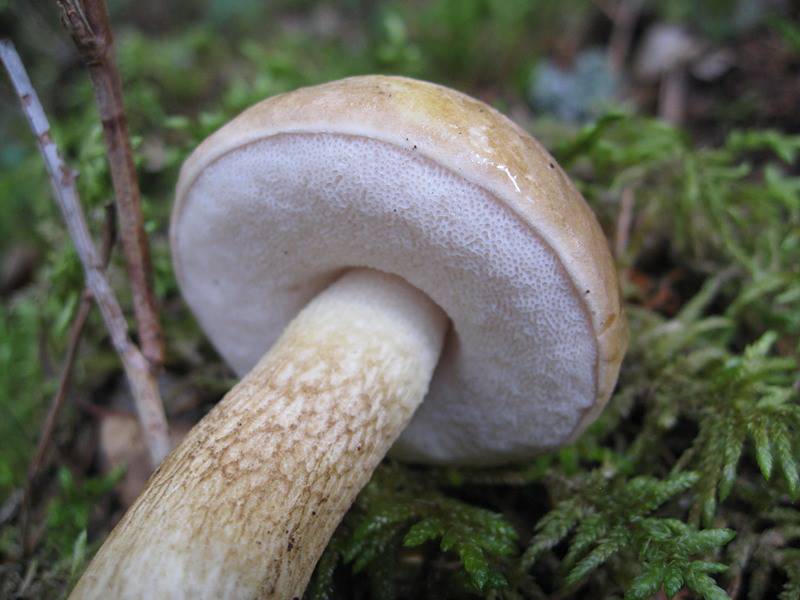
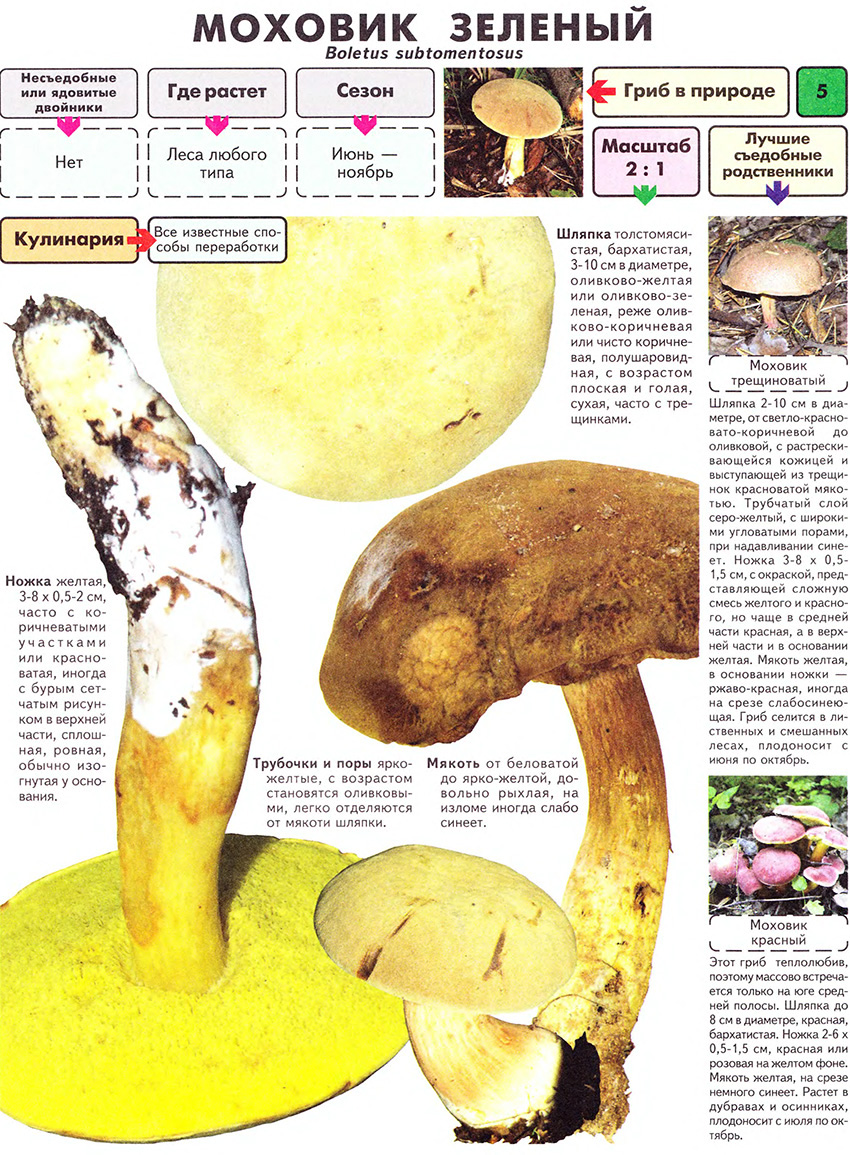
- The hat is slightly velvety and usually dry (in certain species it becomes sticky in conditions of high humidity); in young specimens - rounded; in adults - pillow-shaped or flat, cracks are possible.
- The hymenophore (the part of the fruiting body under the cap, which has a spore-bearing layer) is tubular, descends along the peduncle, and occasionally it has grown. At first it has a light chocolate-golden and slightly orange hue, but with age it gradually acquires brown-cherry, brown-green or yellow. Pore ducts are quite wide.
- Spore powder is colored in different brown shades.
- Leg is smooth or slightly wrinkled. There are no rings or any covers. The length of the leg often depends on the external environment: drier conditions are elongated, wet conditions are thickened and short.
 You may be interested in:
You may be interested in:Places of distribution
The natural range of this fungus is Eurasia, North Africa, North America and even Australia. Mostly he chose temperate latitudes, and even species of the subarctic and alpine zones are suitable for species such as green flywheel.
In coniferous, deciduous and mixed forests, together with woody roots, mossworms form mycorrhiza (symbiotic association). They are comfortable on sandy soils. Single specimens (sometimes small groups) grow in forest glades, in mosses and on anthills, some species adapt on stumps and tree trunks.
Edible or not
The flywheel has high taste and a lot of useful properties, therefore it is often used in diet food. Fruits are processed by any of the methods of heat treatment, without losing the taste and nutritional qualities.
Types and their description with photos
The genus Mokhovik combines 18 species. The most common varieties:
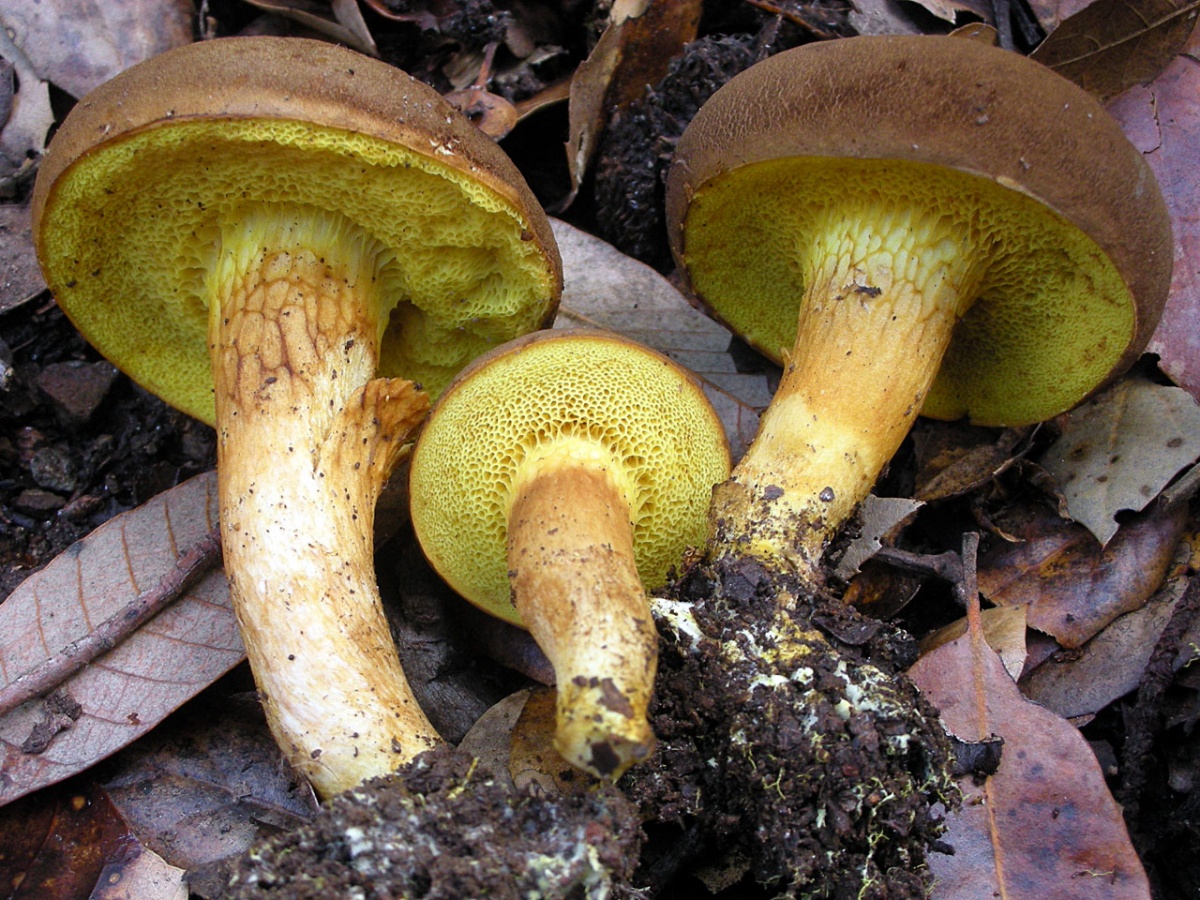
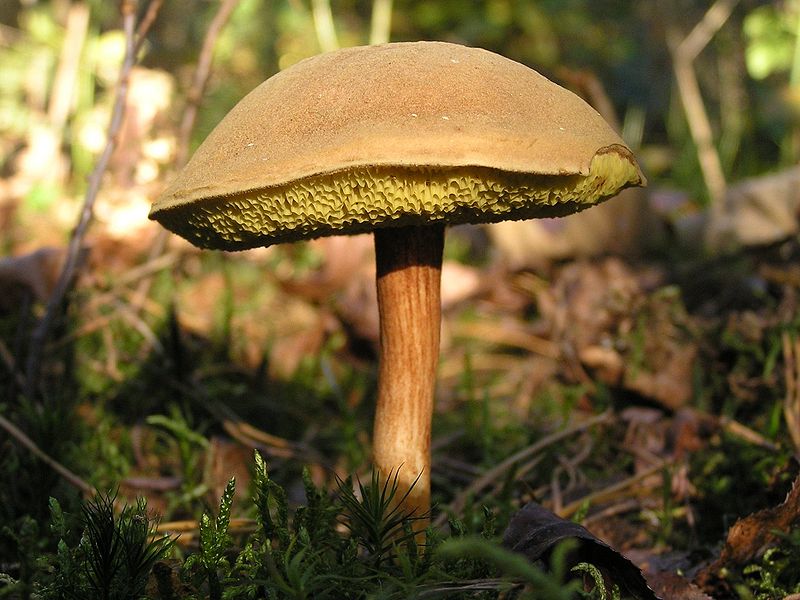
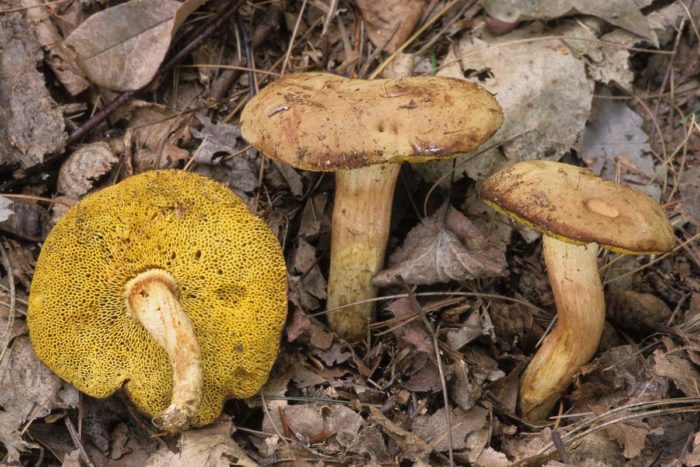
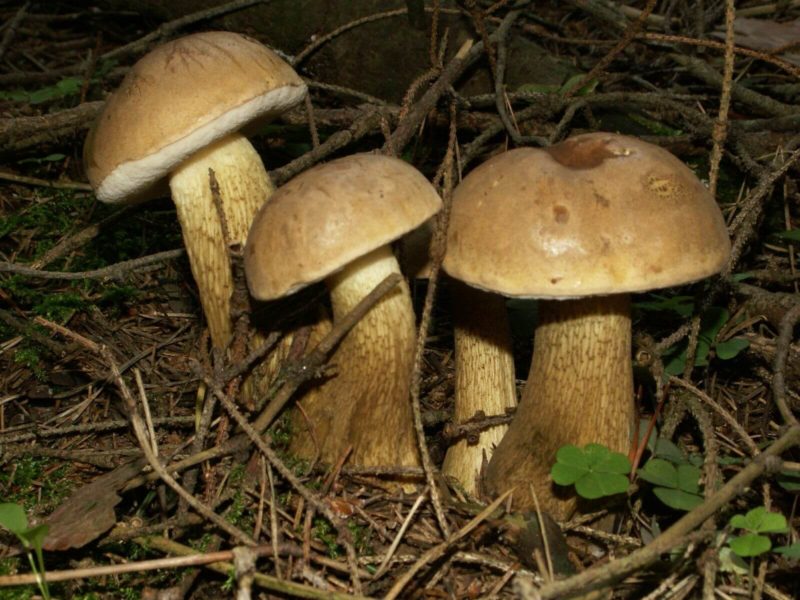
- The green flywheel stands out with its olive-brown or greenish-gray hat, slightly protruded and slightly velvety. It can be in section 12, or even 16 cm. The cylindrical shape of the leg is slightly thicker in the upper part, a brown mesh can be seen. The thickness of the legs is up to 2 cm, and the height is in the range of 4-11 cm. The flesh is snow-white, slightly bluer at the cut. Hymenophore is yellowish.
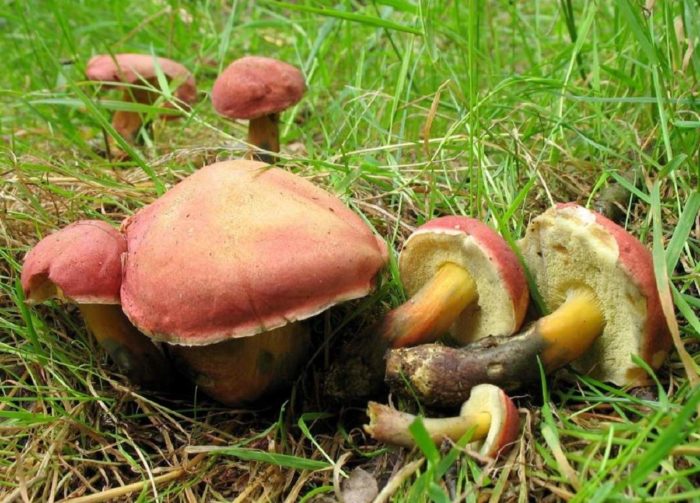
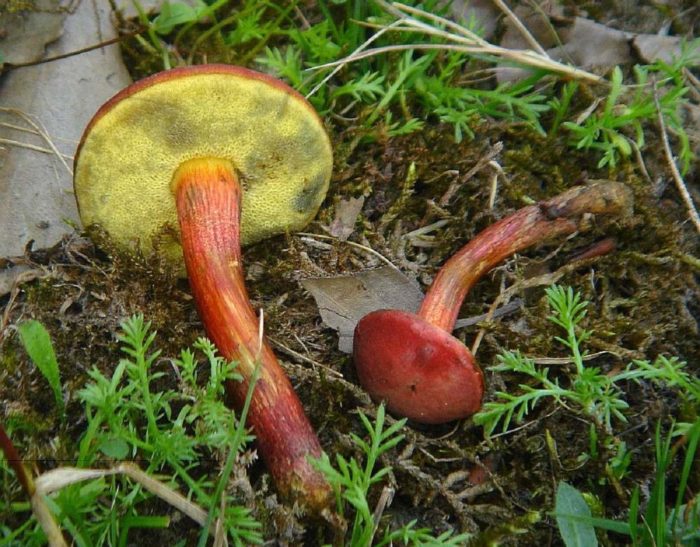
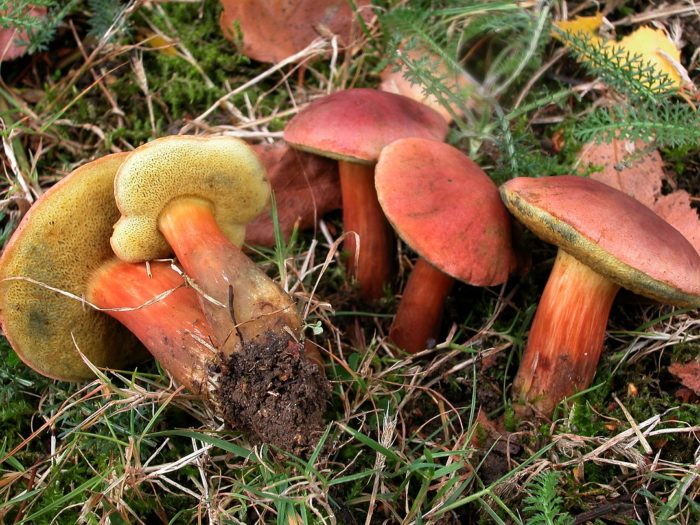
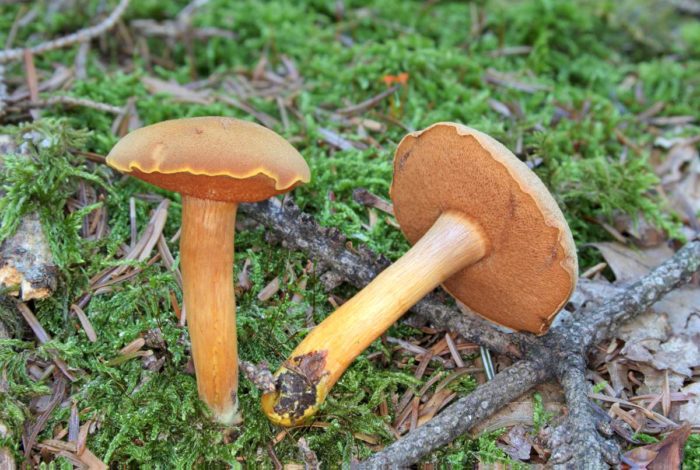
- The red flywheel is so called because of the red-brown hat with a diameter of 3-8 cm. ABOUTon convex at young copies, straightened - in age. AT gets dry weather small cracks. The thin leg has the color of the cap, but a little lighter, in the upper part it is yellow. The possible thickness is 1 cm and the height is 4-12. Gymenophore yellow, shades of olive or green. The pulp is dense, with yellowness. When pressed or cut, it intensely turns blue.
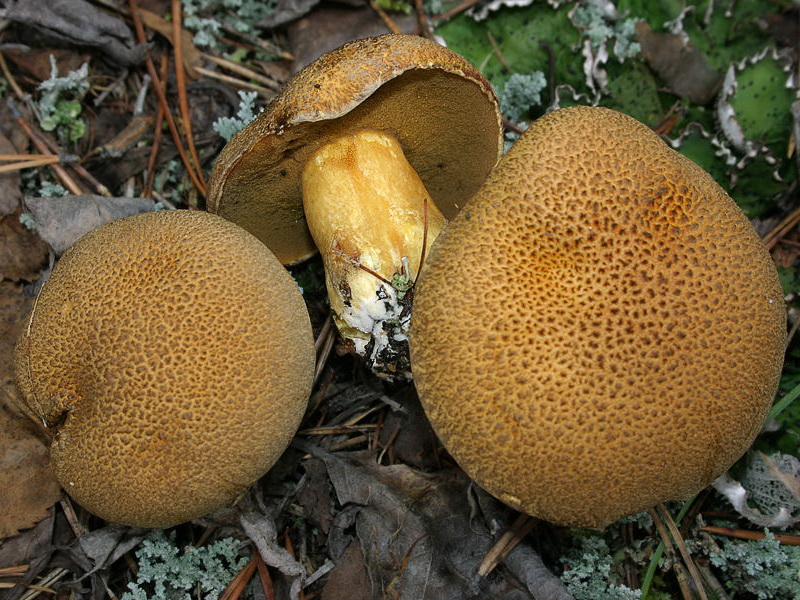
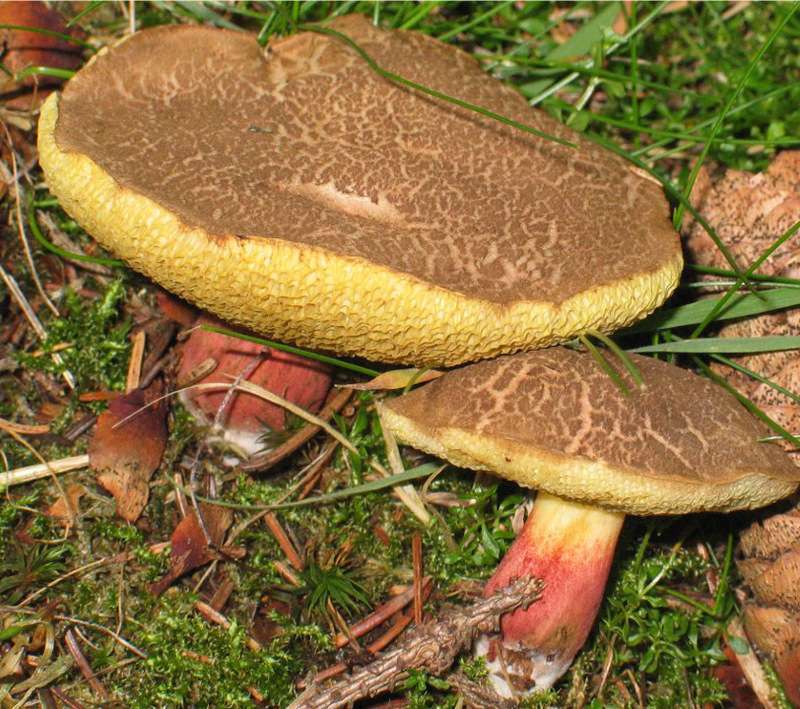
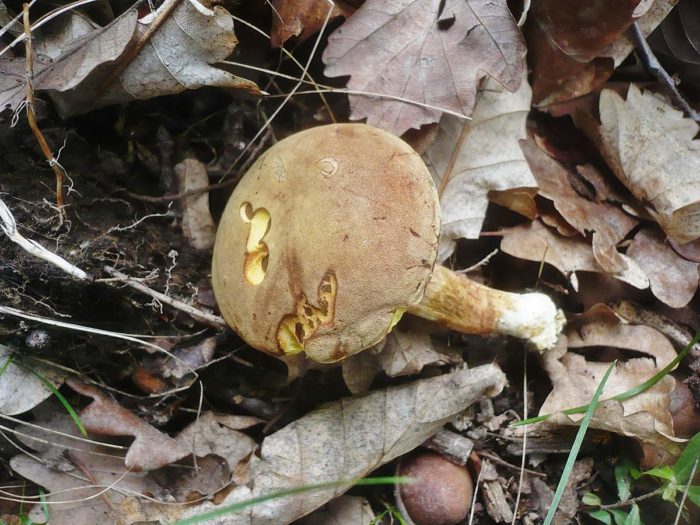
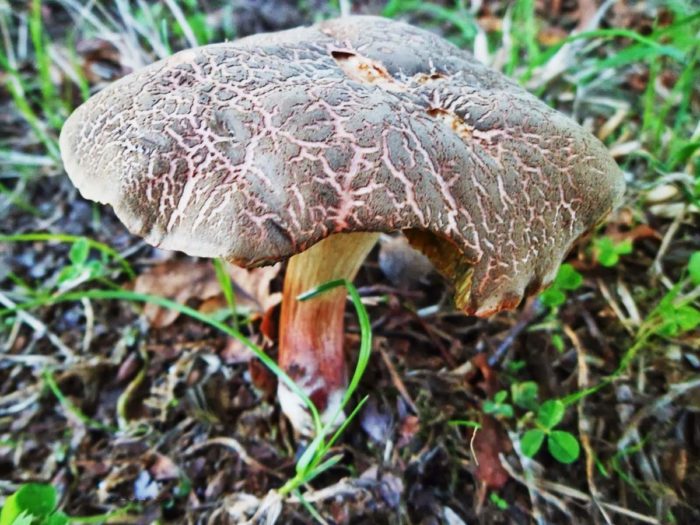
- A flywheel mottled or fissured can be recognized by a network of cracks (white or pink) on a small (8-10 cm) velvet hat. Meet burgundyolive chocolateeRed Terracottae and gray ochere shades of hats. Hat his form looks like a chubby pillow. Often this "pillow" is crushed in the central part.
FROMyellow-green or green-olive hymenophore large pores slightly descends on a leg 5-7 high and 1-2 cm thick. Leg club-shaped straight or slightly curved, reddish below, yellow above. The pulp is white or yellow, in the lower part of the leg and under the skin of the hat is red. When cut or pressed, this mushroom quickly turns blue.
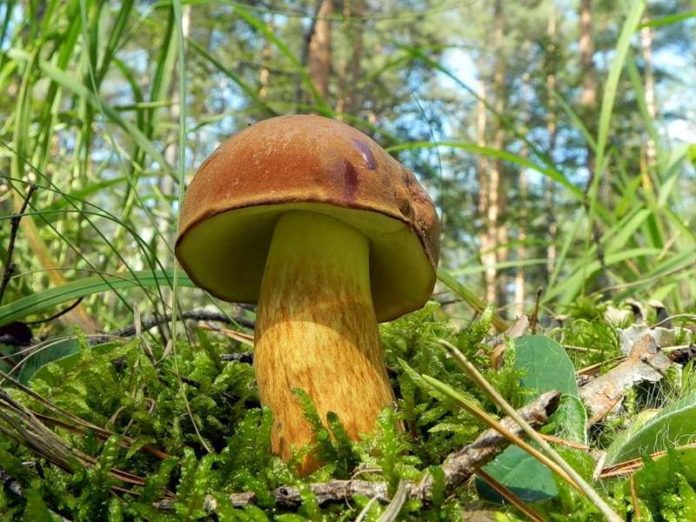
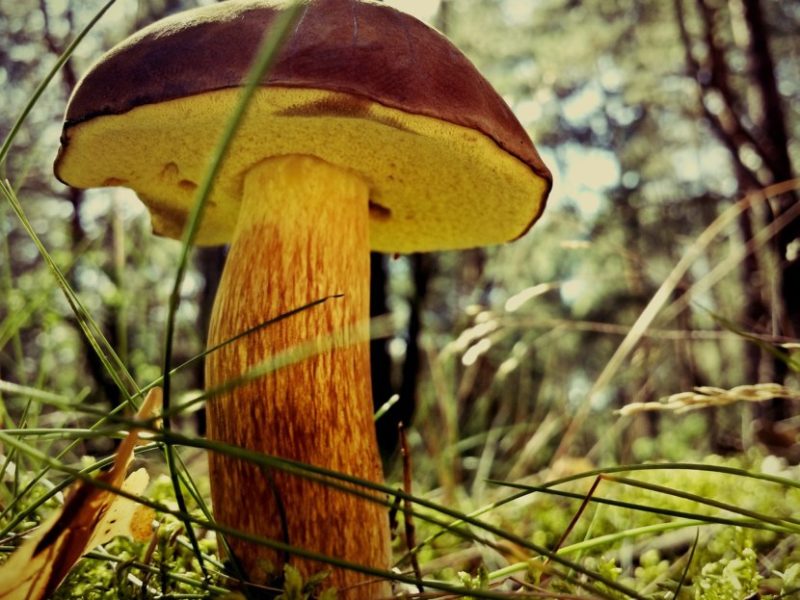
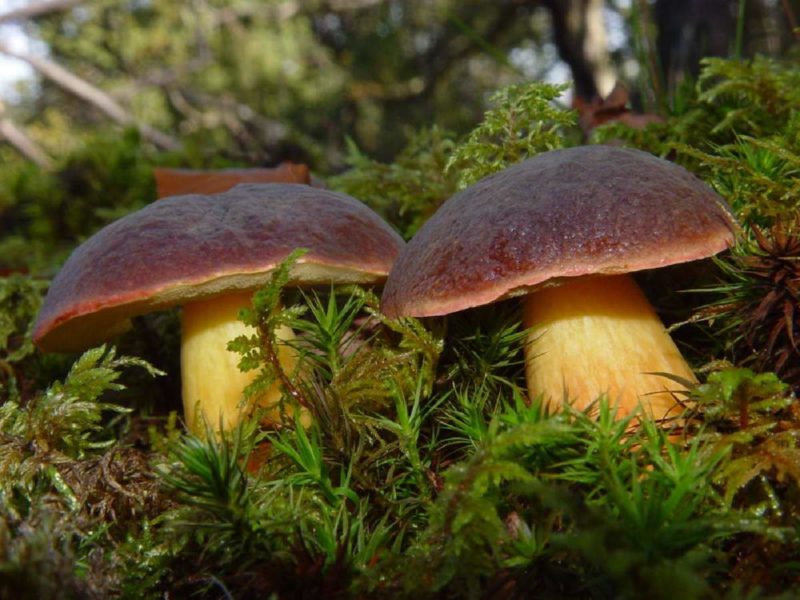
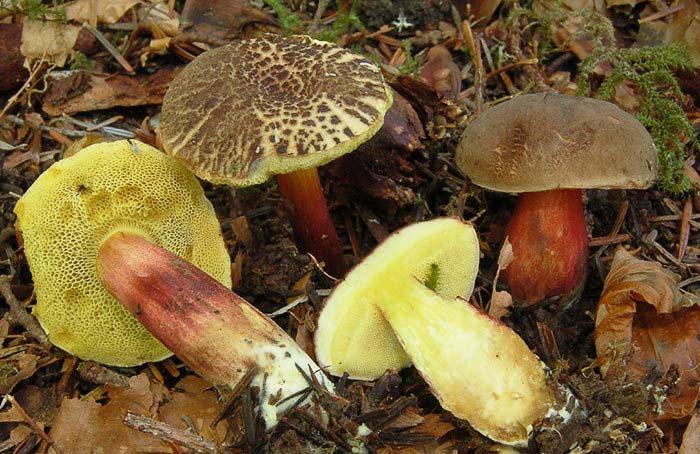
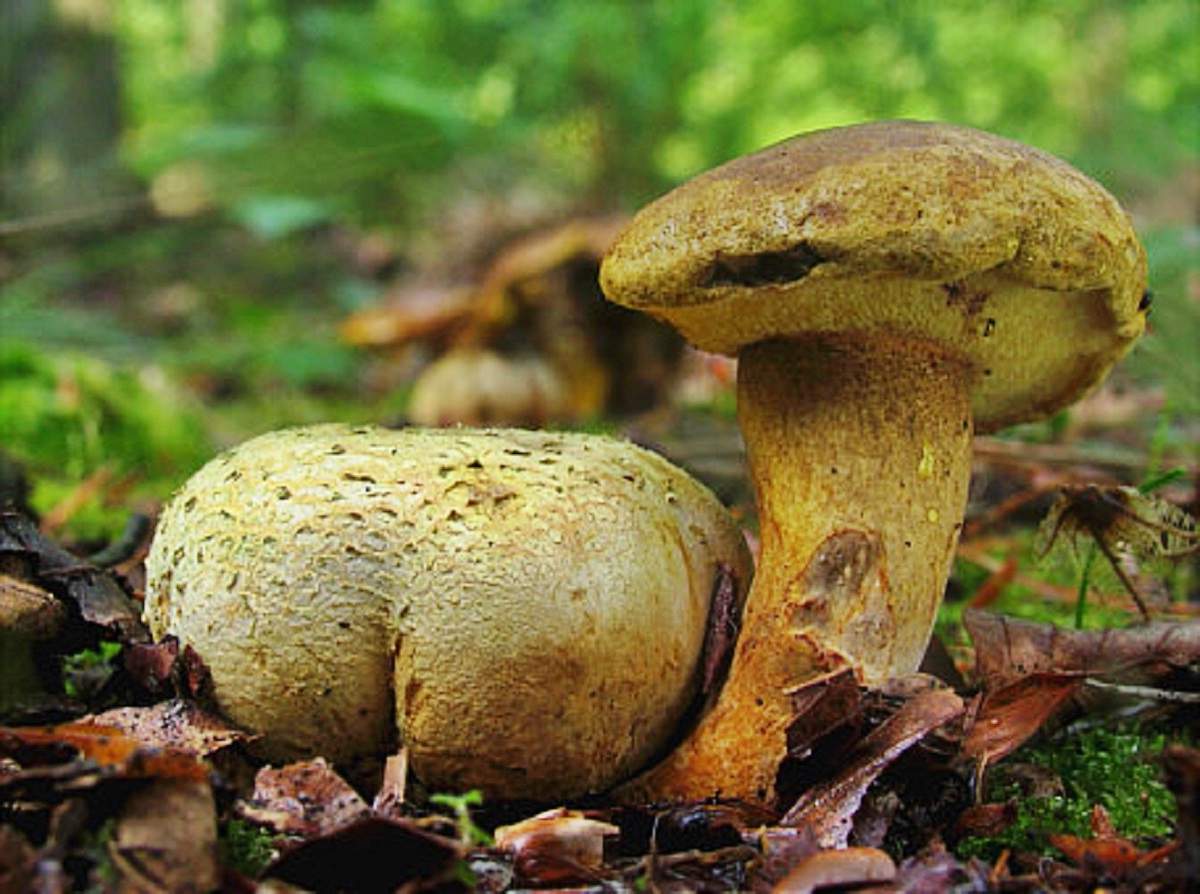
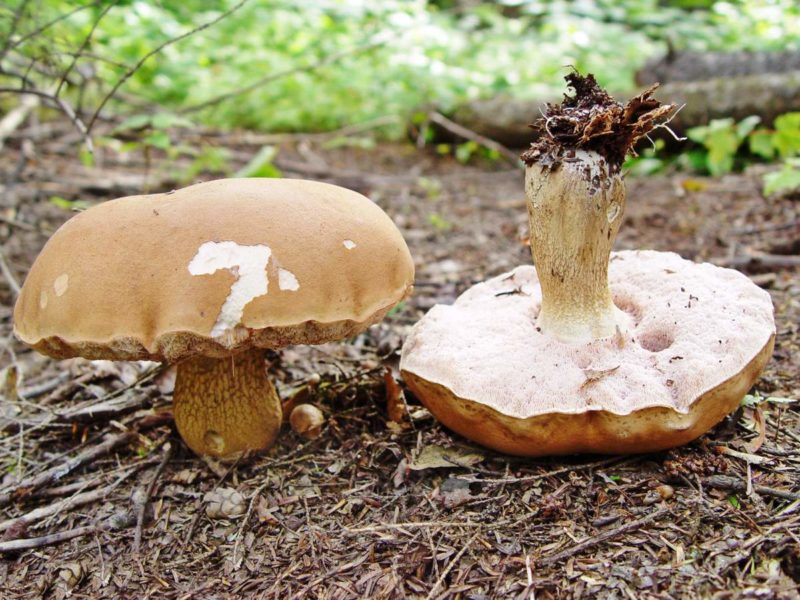
- The Polish mushroom has a fleshy convex hat with a diameter of 5-15 cm. Color - chestnut or reddish brown or just brown. Dry or wet surface (adhesiveand I during rains). The skin of young specimens is velvety, old - smooth.
Leg 4-12 cm long and 0.8-4 cm in diameter – smooth, light brown or yellow with redeatingand fibers, cylindrical, sometimes thickened at the bottom. The pulp is white or slightly yellow, it can also turn blue when tissue is disturbed.
 You may be interested in:
You may be interested in:Differences from false, inedible mushrooms?
The edible flywheel has the ability to quickly turn blue at the point of cut or in the place where they pressed it, while the false one does not. False mushrooms are usually odorless or barely noticeable. The edible flywheel cannot be found on the mycelium of the false raincoat, while the “deceiver” loves such a neighborhood.
False mosses look like this:
- The parasitic flywheel is modest in size. A convex, velvety and oily hat 2-7 cm in size is painted in yellow, brown or walnut color. The flesh is pale yellow, odorless, not able to turn blue. The leg is solid, in the shape of a cylinder. Its height is 3-6 cm, its thickness is 0.8-1.5 cm. The parasitic is often found in the company with false raincoats.
- Pepper mushroom is colored in various shades of brown. Leg lighter than cap, yellow at base. The dense and fragile pulp tastes like hot pepper. It is easier to recognize the mushroom by a brown-gray or yellow-gray slice of pulp, which subsequently turns red.
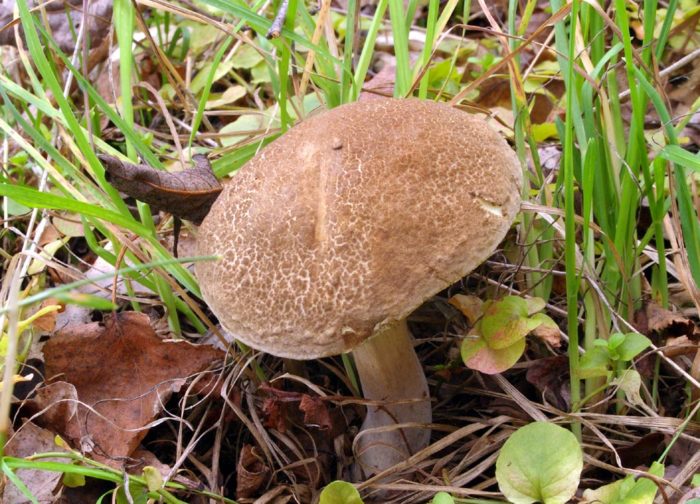
- The bile mushroom cap is larger in diameter than that of edible ones. It happens to be 10 and even 15 cm. It looks like a hemisphere (in older ones it is flatter). The surface is dry and sticky at high humidity. The fruit body is brown, with yellowish brown or sometimes chestnut tint. White tubes of hymenfora gradually turn pink, when pressed redden.
Cylindrical or The club-shaped leg reaches a height of 12 cm and a thickness of 3 cm. The pulp has no smell. Often the bile fungus grows at the base of trees and near rotten stumps; it is never wormy.
Time and collection rules
Flywheels enter the period of mass fruiting from July to September. However, each has its own deadlines. For example, the first fissured flywheels begin to appear in the last decade of June and may catch the eye of mushroom pickers until the end of September. The main collection of these mushrooms is carried out from the second half of August until the second half of September.
Polish mushroom can be hunted quietly from June to November. Often it is discovered when the season of other tubular mushrooms is over. The harvesting time of the green flywheel is May-October, red - August-September.
A suitable time of day to harvest is early morning, before the sun warms up the mushrooms. In this case, they are stored for a long time. When collecting mushrooms, each instance must be carefully cut with a sharp knife at the base.
Old and overgrown mosses should be left in place. For a long time, they could well accumulate substances harmful to humans. Each found and cut mushroom must be cleaned of soil, grass, foliage, needles and placed in a container for collection with the hat down for good preservation.
Useful properties and restrictions for use
The nutritional benefits of these mushrooms are quite high, they have the following effect:
- used as a natural antibiotic, help in the treatment of inflammatory processes;
- contribute to the normalization of the mucous membranes of the eyes and improve vision;
- vitamins A, B, C, D, PP contained in fruits and minerals (especially molybdenum) restore the normal functioning of the thyroid gland;
- improve the condition of nails and hair;
- B vitamins contribute to the renewal of nerve cells;
- frequent use of these mushrooms reduces the risk of developing atherosclerosis, helps to remove toxins and toxins, strengthens the immune system, and renews the blood;
- help to maintain a diet (calorie content of the product - 19 kcal per 100 g);
- A large amount of protein in mushrooms restores the strength of athletes and builds up their muscle mass.
With all the positive properties of the moss, we must not forget that mushrooms are heavy food. It is not recommended for people with problems of the gastrointestinal tract and digestive glands.
Features of cooking and answers to common questions
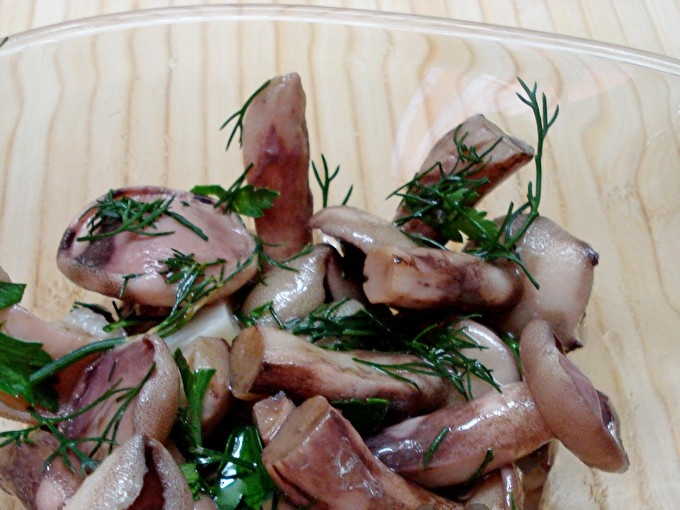
This product can be stewed and boiled, fried and dried, marinated and salted - in any form it is very tasty.
But it needs to be prepared correctly:
- rinse with running water;
- to separate the hats and legs;
- clean all parts of the fungus from dust and earth with a hard brush;
- with a sharp knife to cut dark spots and hard areas;
- get rid of the spore layer under the hat;

Rules for the preparation of mushrooms - fill with cold water for 10 minutes (to remove residual dirt);
- put in a colander until water drains;
- dry with a paper towel.
Cook for at least 30 minutes. Before the cooking process, they need to be divided into pieces and pour boiling water for 10 minutes. Boiled mushrooms can be fried. The maximum time is 10 minutes. No lid needed. Fire is minimal.
 You may be interested in:
You may be interested in:
Before frying the hats of raw mushrooms should be separated from the legs and soaked for 1 hour in cold water. Then they must be rolled in flour and sent to a pan with a small amount of sunflower oil. Cooking over low heat is about 40 minutes.
Most common questions
Edible moss fly can be recognized not only by their external characteristics, the main clue is the ability to turn blue. False flywheels are not particularly dangerous, but due to poor taste they are considered conditionally edible and often unsuitable for eating. The advantages of the moss flies are a long fruiting season and benefits to the human body.

































 Care and use of Kombucha at home (+22 photo)
Care and use of Kombucha at home (+22 photo) Edibility of the fungus of the motley umbrella and its description (+19 photo)
Edibility of the fungus of the motley umbrella and its description (+19 photo) Description of edible and inedible oils, their poisonous counterparts (+40 photos)
Description of edible and inedible oils, their poisonous counterparts (+40 photos) Useful properties of milk mushroom and its contraindications (+17 photos)
Useful properties of milk mushroom and its contraindications (+17 photos)