Honey mushrooms are mushrooms widespread in Russia, characterized by high culinary value. However, due to the presence of toxic doubles, mushroom pickers often bypass them. In order not to be mistaken, you must familiarize yourself with the description and photos of honey mushrooms, as well as their dangerous double mushrooms, before the trip.
Content
Characteristics of honey mushrooms
Honey mushrooms are called a group of apparently similar mushrooms that grow well on dead wood. Sometimes these fungi belong not only to different genera, but also to different families.
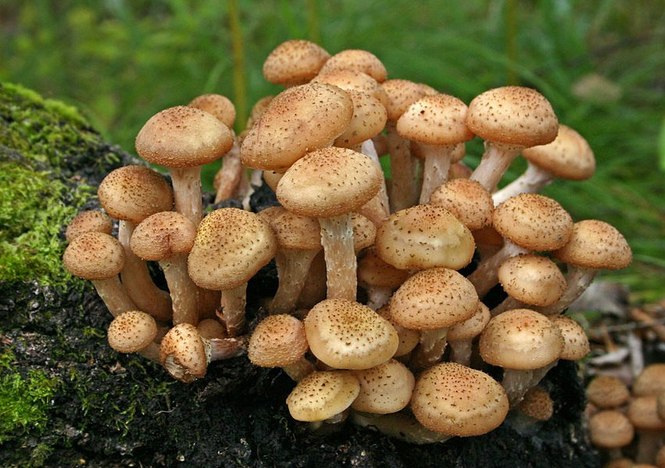
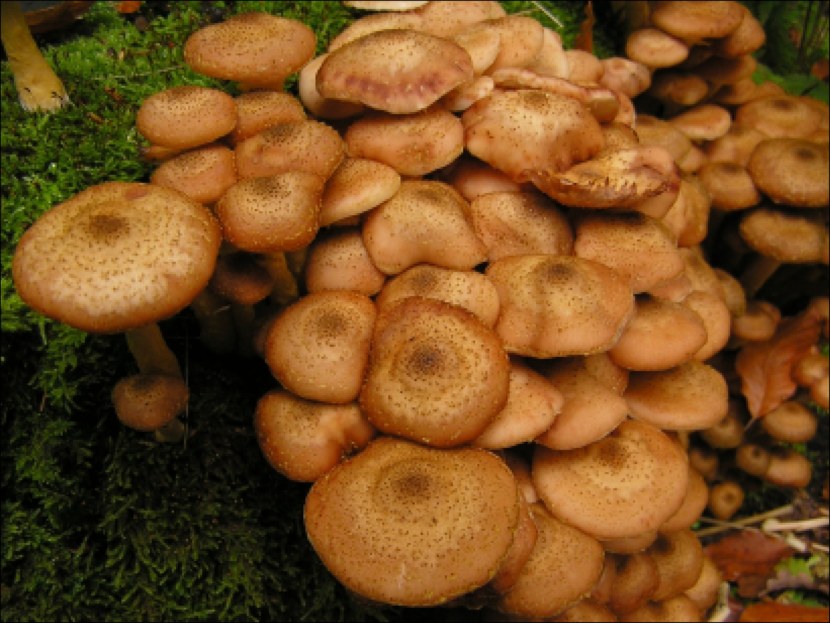
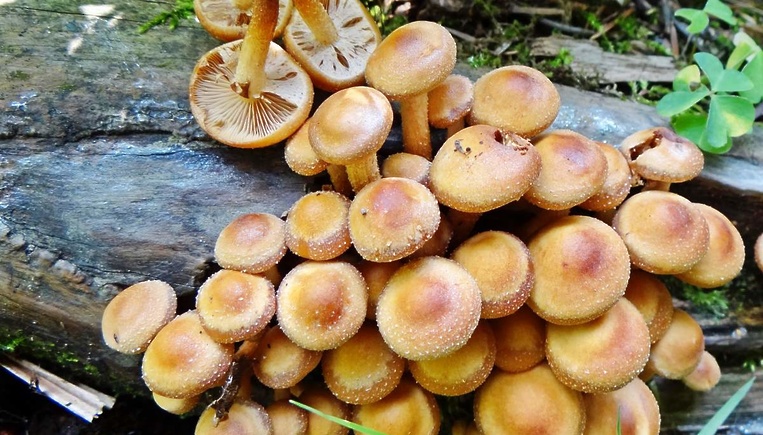
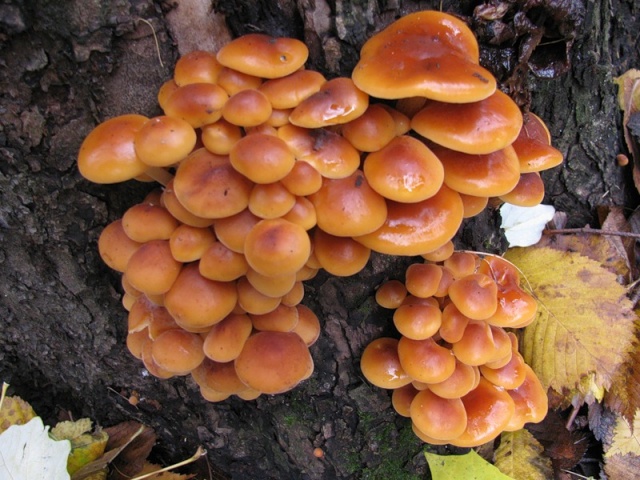
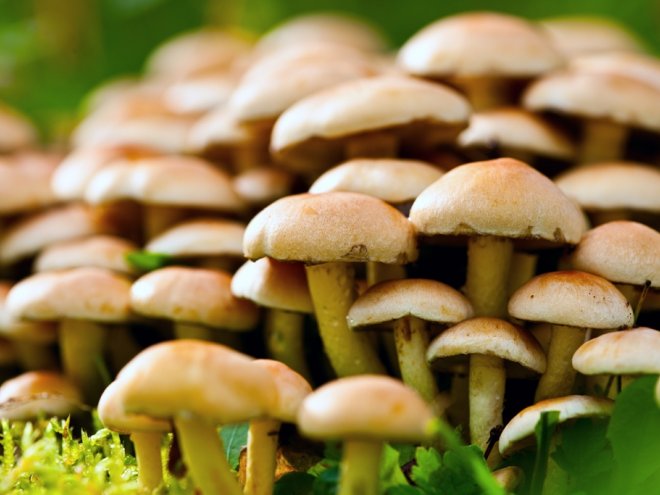
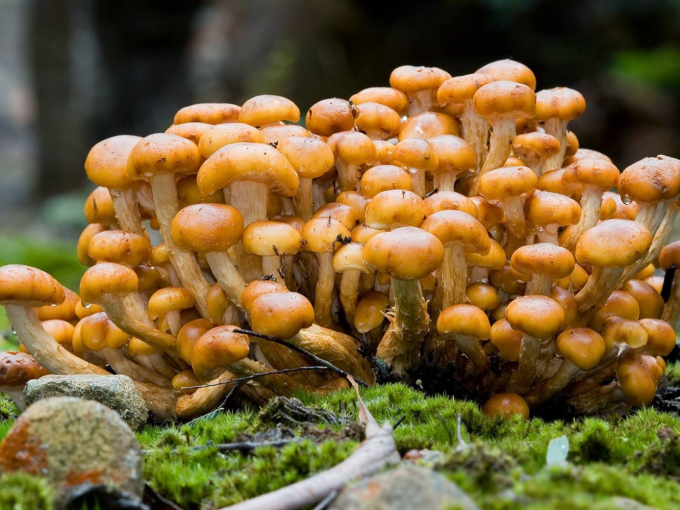
Appearance and photo
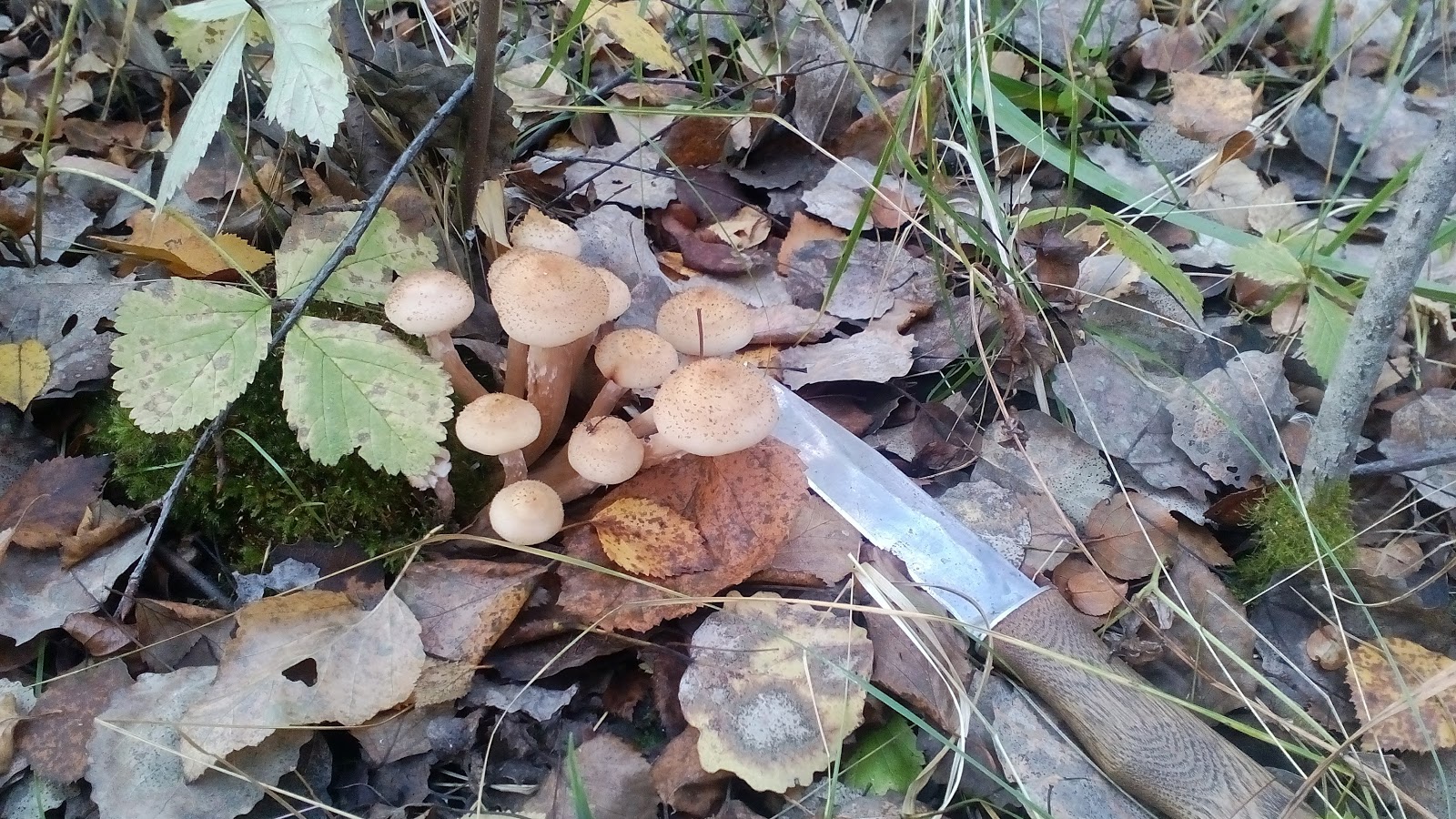
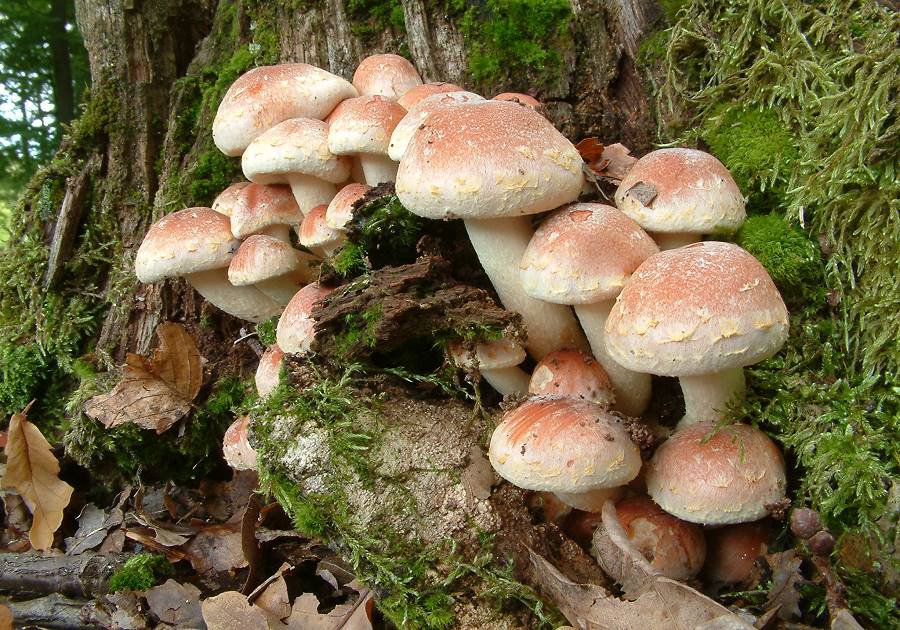
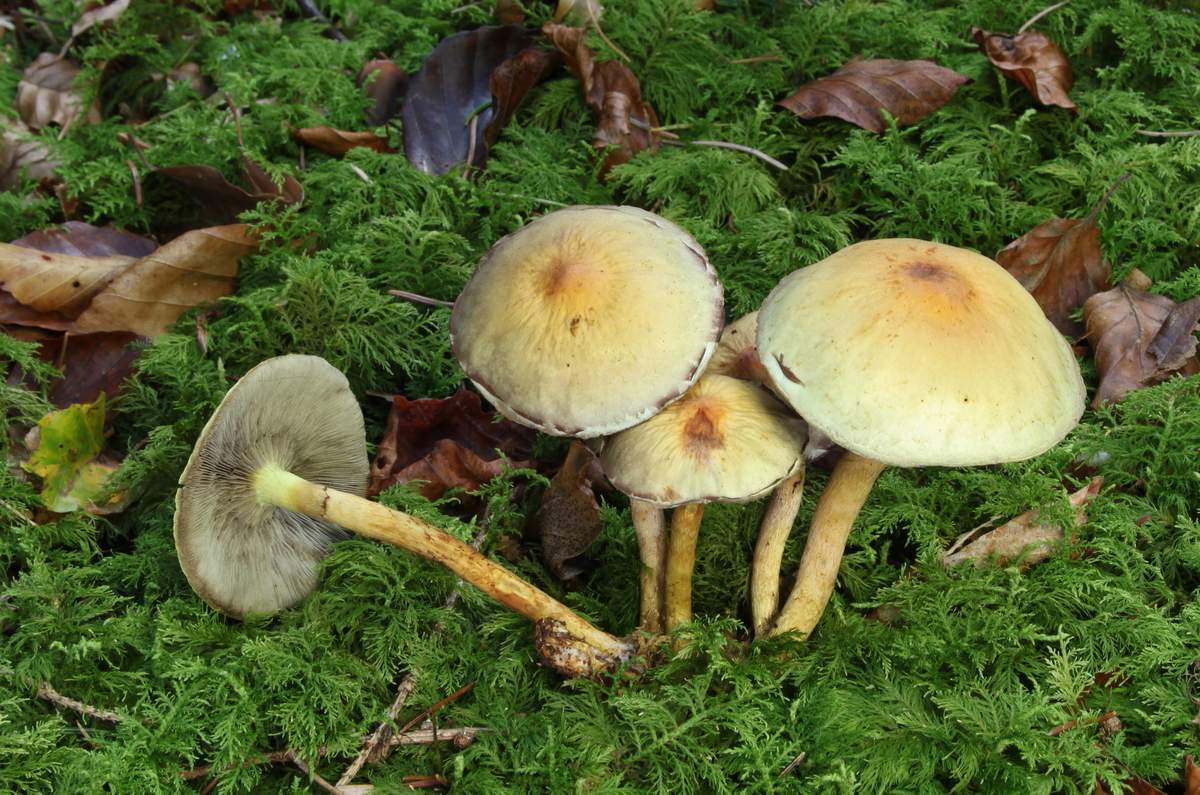
Mushrooms have round, often wet hats and thin legs. The color is mainly represented by all shades of brown, but there are species with a reddish, yellow or pinkish hat. The legs are also painted in brown tones. Several species have yellow or black legs.
Often mushrooms do not grow to large sizes. The exception is only the Royal view. The hat sizes range from 2 to 10 cm, the leg reaches a length of 15 cm. To have a complete picture of how honey mushrooms look, you can consider their photo.
Structure and species differences
In young fruits, the hat has a convex hemispherical shape. As they grow older, a tubercle appears in the center of it, and the hat becomes umbrella-shaped. In old fruits, it takes an open form. The surface of the hat changes color depending on the weather: in conditions of high humidity, it darkens and brightens in the sun. There are flakes on the surface of the hat. In many species, they disappear with age.
The leg of the honey agaric is cylindrical, mainly hollow, and may have a thickening at the base. Often it is curved. On the legs of many species there are rings or mushroom skirt. In adult fruits, the stem is always a tone or two darker than in young mushrooms.
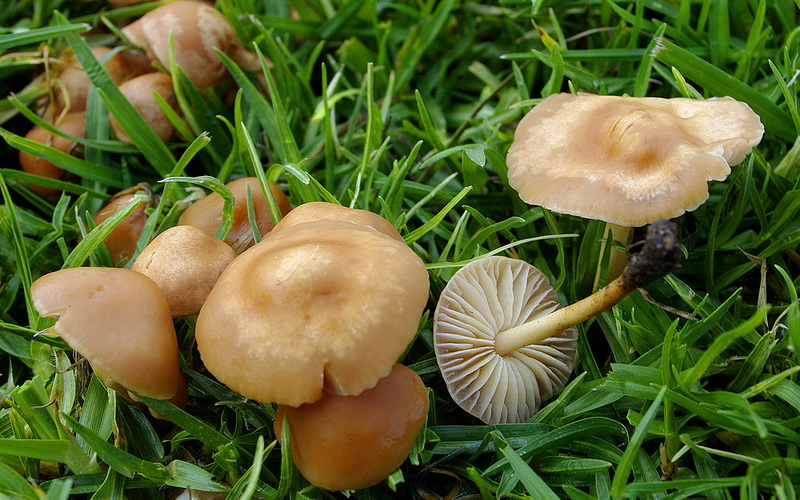
The pulp is tender, smooth, painted white, but may also have a yellowish tint. She is thin, often watery. In edible species, the pulp has a pleasant mushroom or clove aroma and a sweetish taste. Inedible species often differ in bitter flesh with a sharp unpleasant odor.
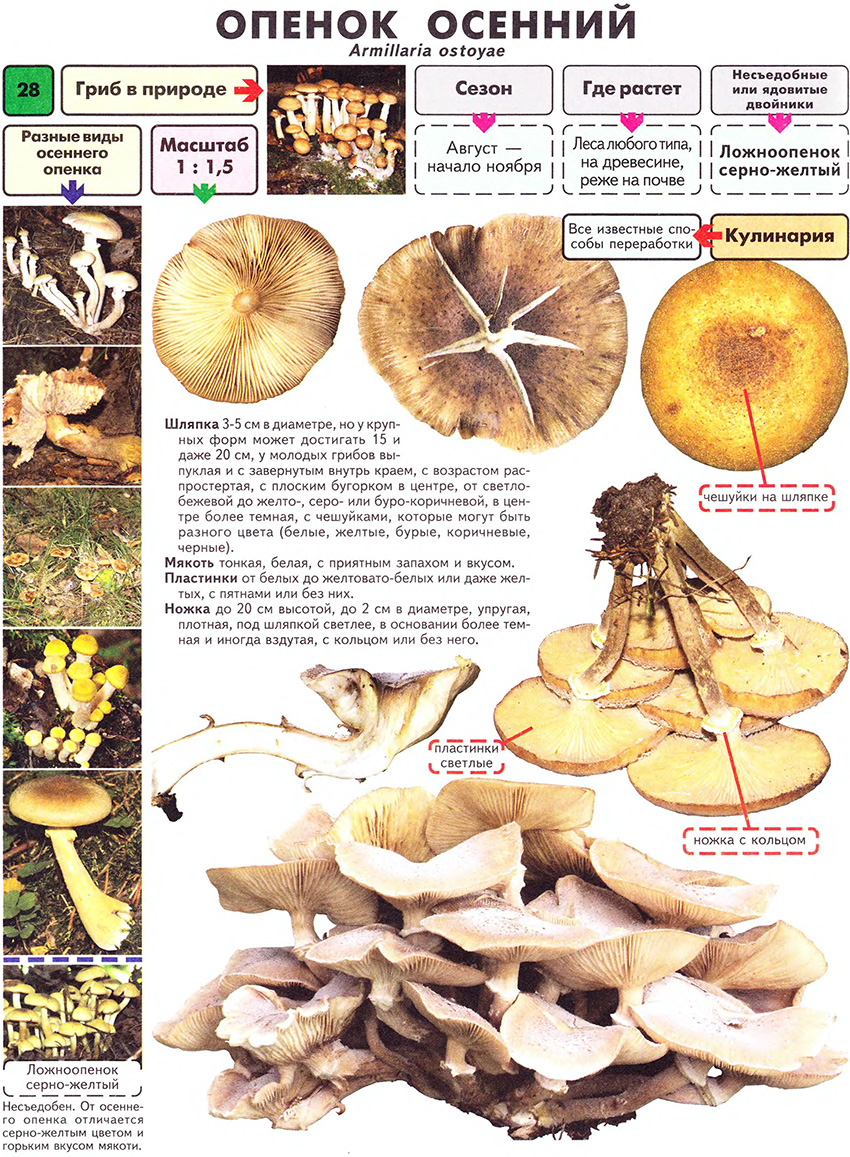
The mushroom plates are kept free or semi-free. In many species, they are painted in white and cream shades and can change color when damaged. Records of some types of honey mushrooms may have a gray-yellow, green or dark olive color.
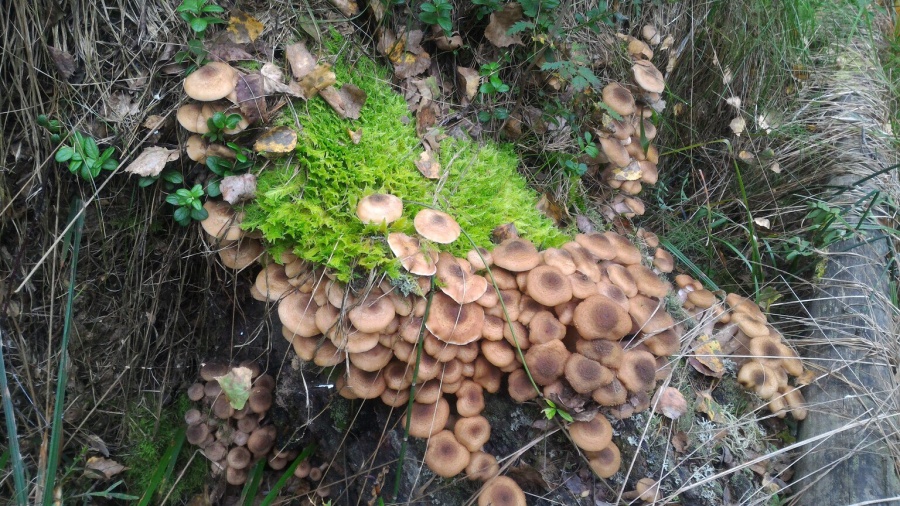
Habitat
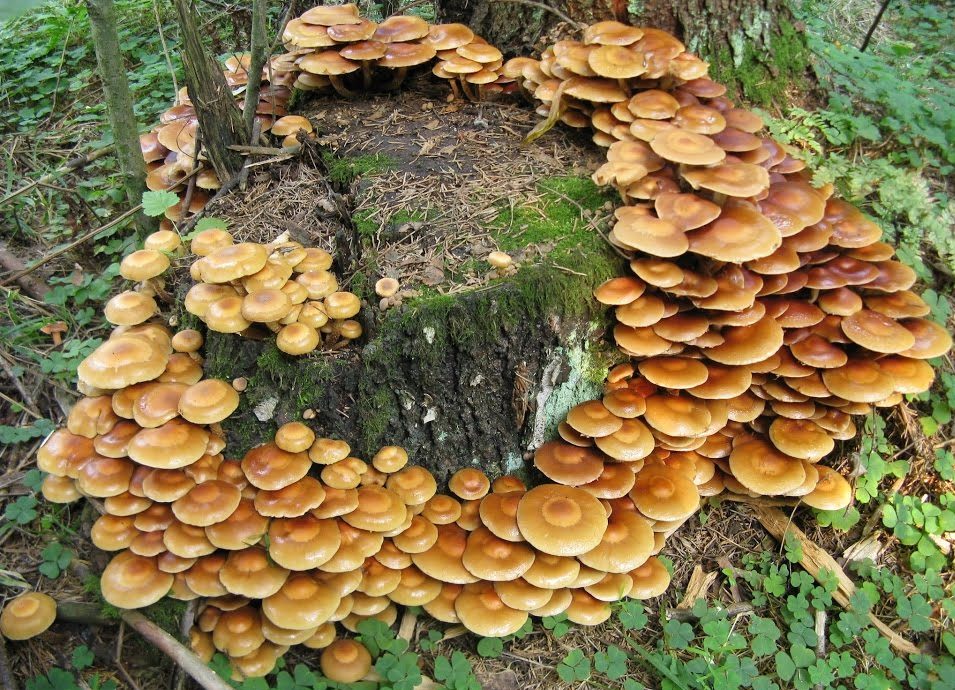
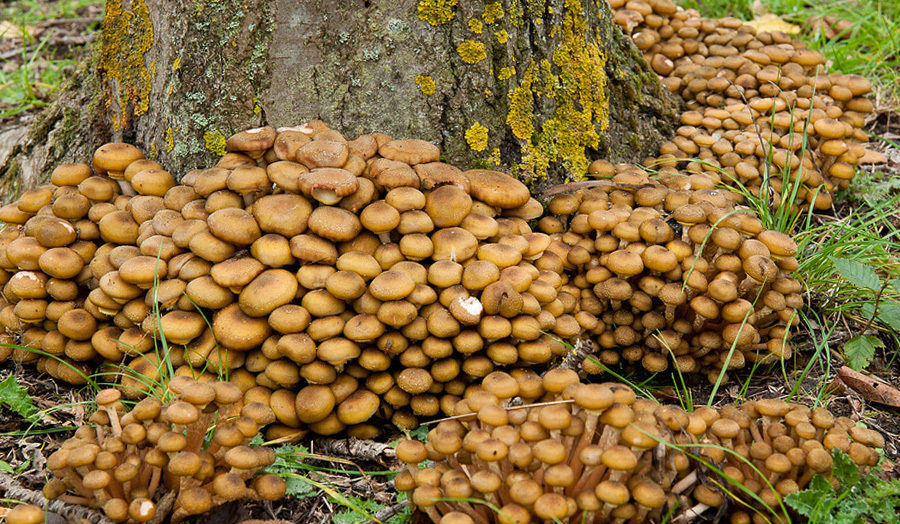
Honey mushrooms grow throughout the northern hemisphere, with the exception of permafrost zones. In Russia they are represented everywhere. Mushrooms are actively harvested and used for culinary purposes.
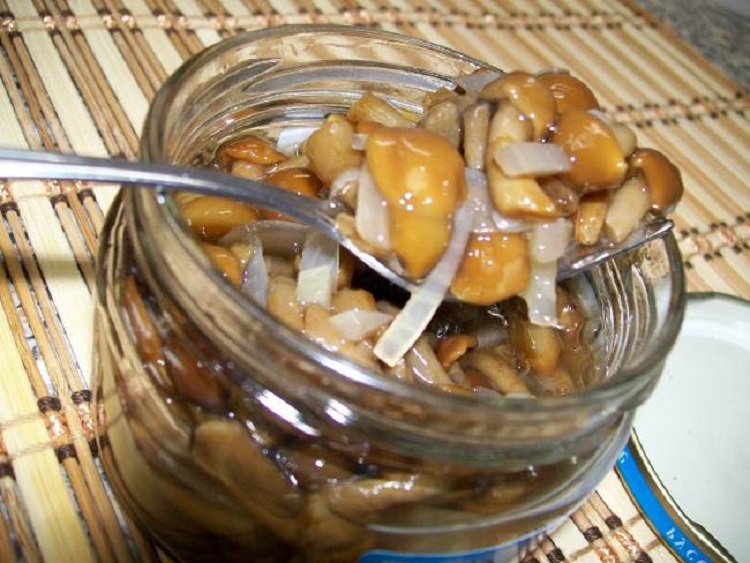
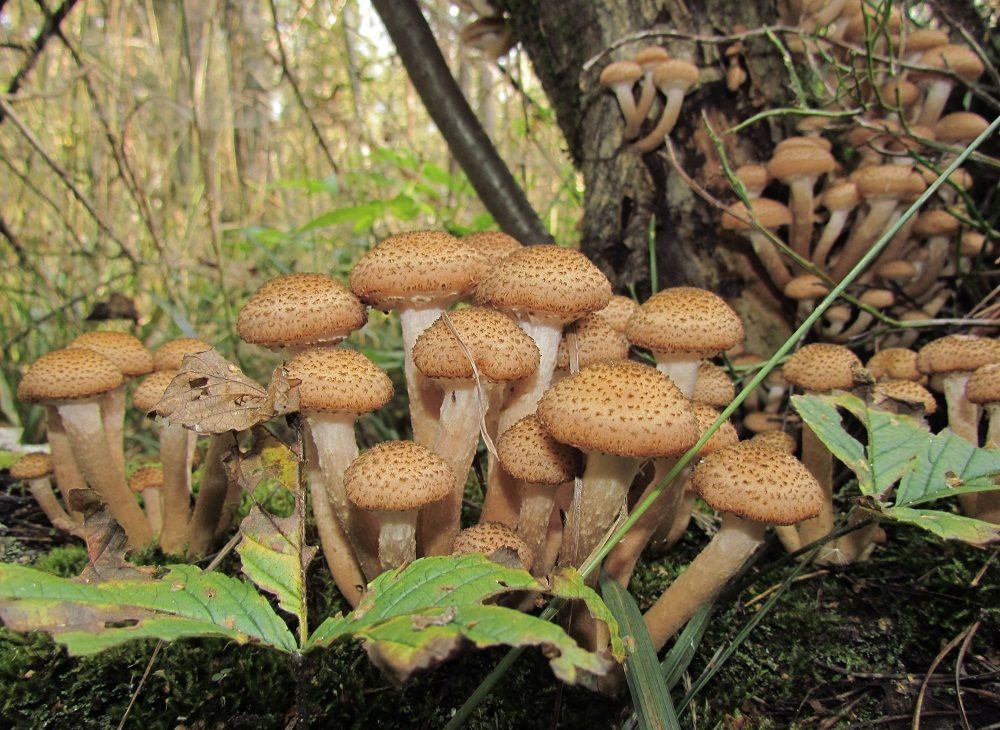
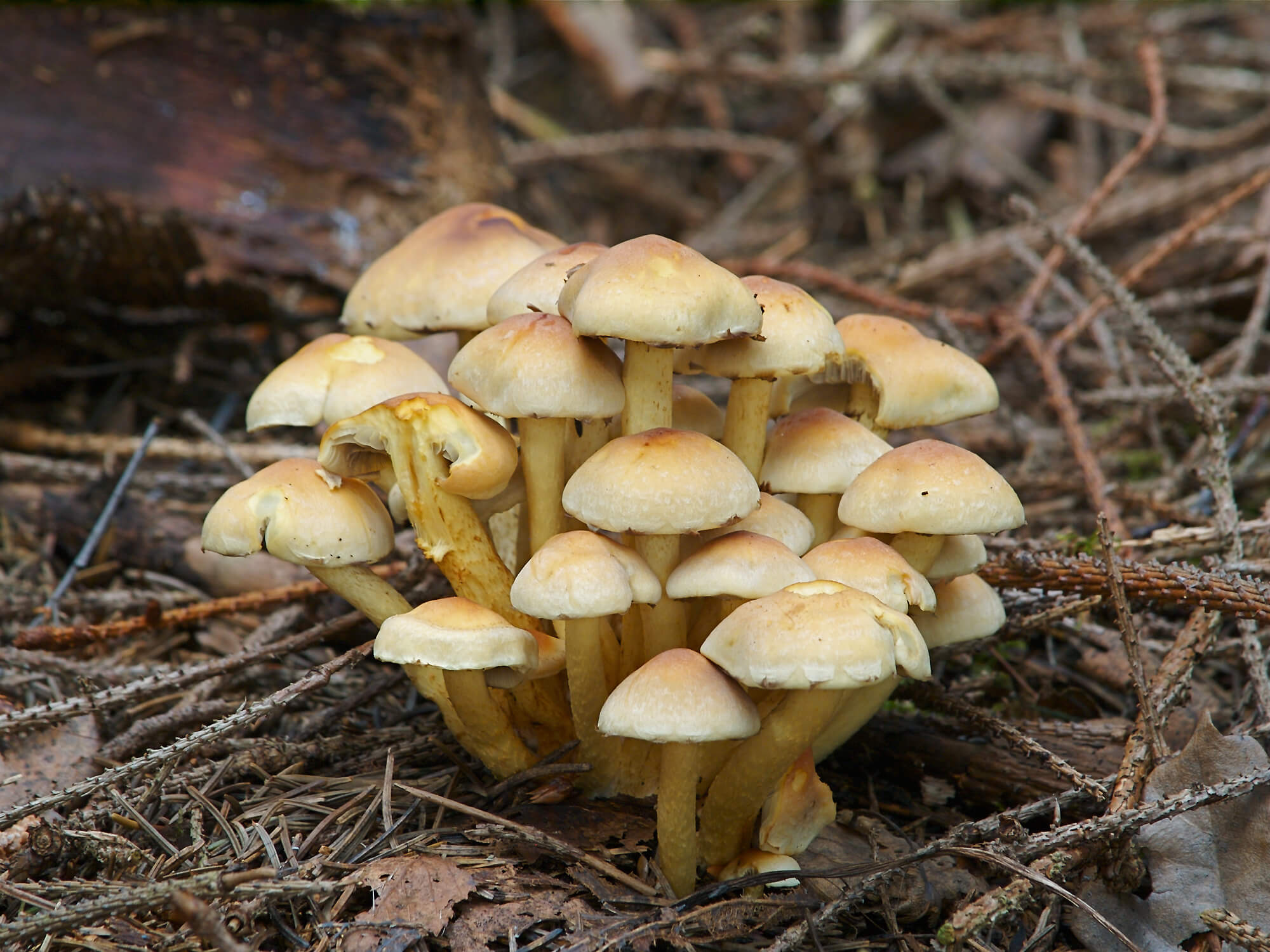
Honey mushrooms are collected in deciduous forests. Most often they can be found on rotten stumps or on fallen trees. However, some species, for example, Lugovoi, prefer to grow in open grassy areas - meadows, untouched fields, forest lawns and even park areas.
Eating
Various sources relate mushrooms to different categories. Some insist on their edibility, others call mushrooms conditionally edible. One way or another, some species are eaten, but not raw.
Collection rules
Mushrooms can be harvested year-round, as many species bear fruit in turn, replacing each other.But the peak of the mushroom season occurs in the autumn months, when most species of honey mushrooms bear fruit.
It is important to observe the following rules for collecting mushrooms:
- Do not pick up dubious fruits;
- go on a “quiet” hunt in the early morning;
- in no case do not break the mycelium using only sharpened tools;
- collect mushroom crops in a basket or crate, so as not to crush it along the road.
Edible species and their description with photos
Edible mushrooms have their own individual characteristics. The characteristics of the most common species are presented in the table.
| Title | Hat | Leg | Pulp |
|---|---|---|---|
| Spring | At first hemispherical, as it grows older it becomes prostrate. Diameter 2-6 cm. The surface has a reddish-brown color in the middle and is lighter along the edge. | Thin, cylindrical, from 2 to 6 cm. Fibrous, hollow inside. Has a slight extension at the base. The color matches the center of the hat. | It has a whitish hue, thin, without a pronounced taste and smell. The plates are light, frequent, semi-free. |
| Summer | At first it is convex, then it becomes flat. The pronounced central tubercle is pronounced. The circumference is 3-6 cm. The surface in wet weather becomes translucent with a brownish tint. Under the sun acquires a honey color. | Thin, cylindrical, grows up to 7 cm. Dense, has a ring. The top is lighter, the bottom is darker and covered with dark scales. | Thin, watery, brownish tint. The taste is pleasant, the smell of fresh wood. The plates are brown, frequent, semi-free. |
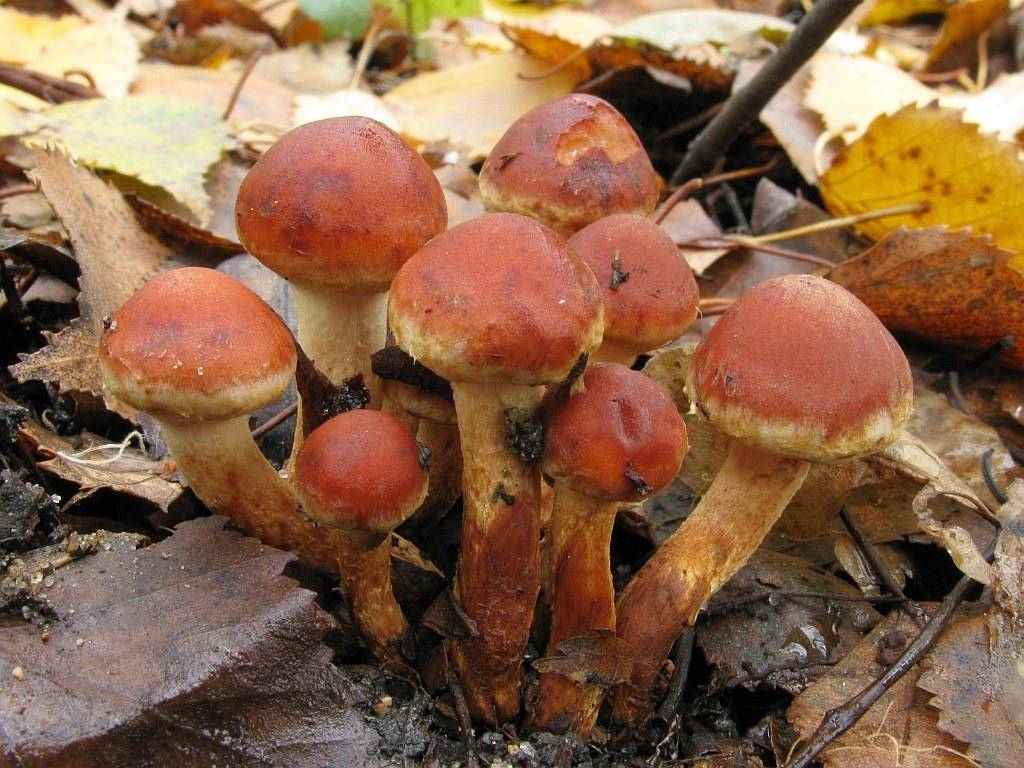
| Autumn | At first it is convex, with aging it becomes flat with wavy edges. Diameter 3-10 cm. The surface may have a color from honey to olive. On the surface are light scales. | Cylindrical, often curved, up to 10 cm. Solid, may have a slight expansion at the base. The leg is light brown above, the bottom is dark. The surface is covered with scales. | It has a whitish hue, dense, with a pleasant smell and taste. The plates are pinkish-brown, rare, grown. |
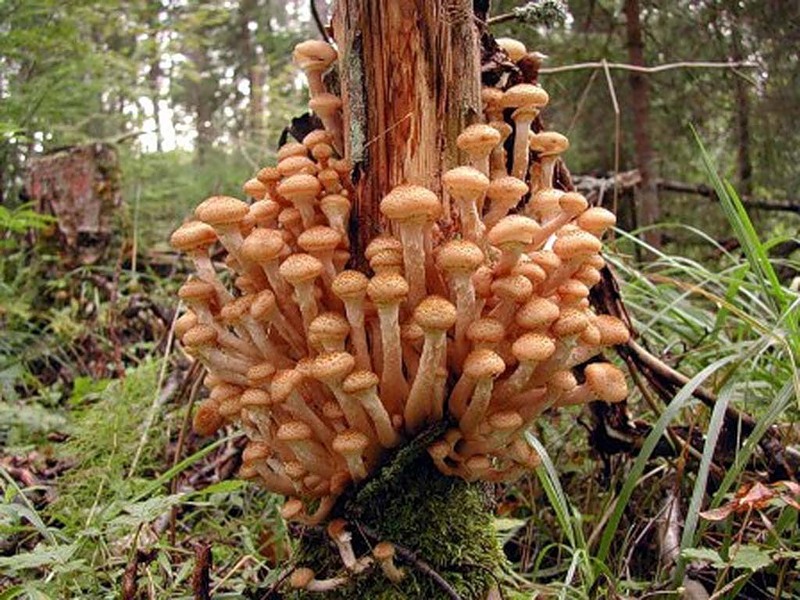
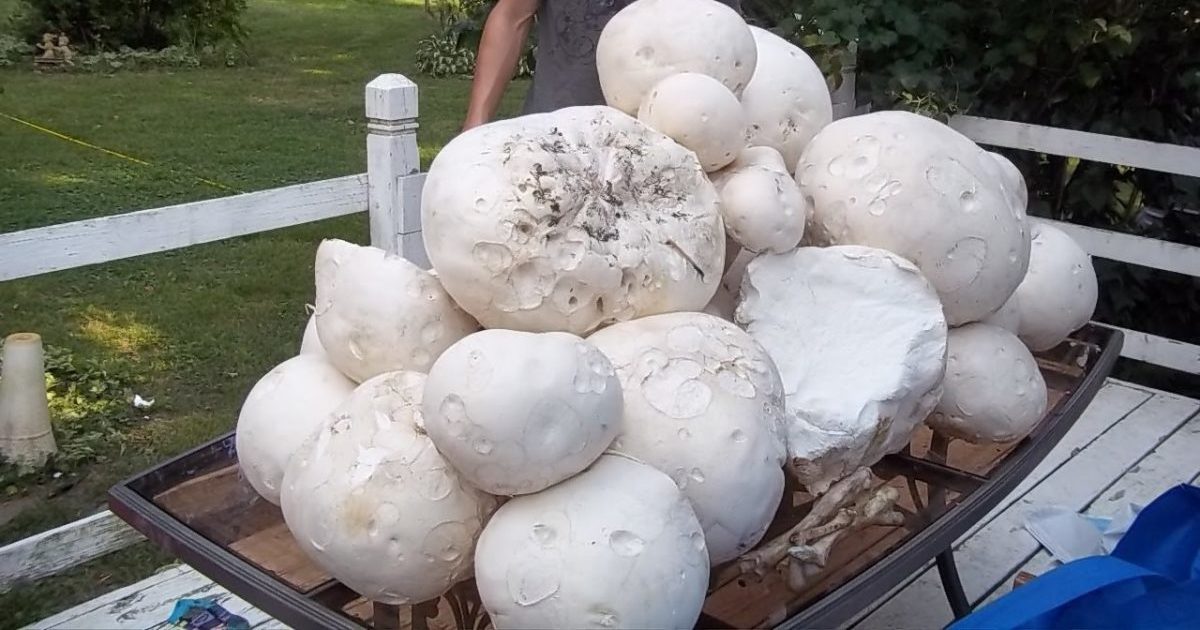
| Royal | At first hemispherical, straightens as it grows. It can reach up to 20 cm in diameter. The surface is painted with a honey-golden tone. On the surface are frequent spiky scales. | Thick, cylindrical, often curved. The color matches the shade of the hat. The surface is covered with spiky scales. | They are considered giant mushrooms. They have high culinary value. |
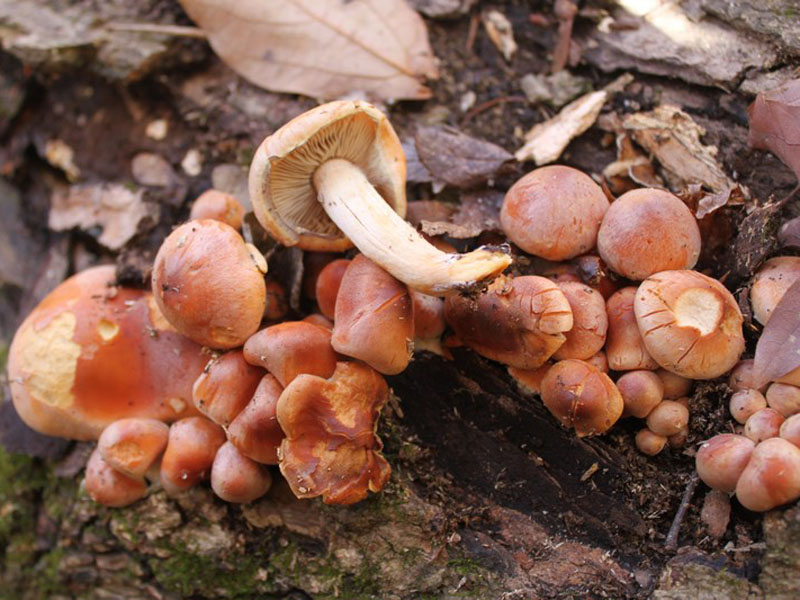
When harvesting these types of mushrooms, you must be extremely careful, since many of them have inedible twins.
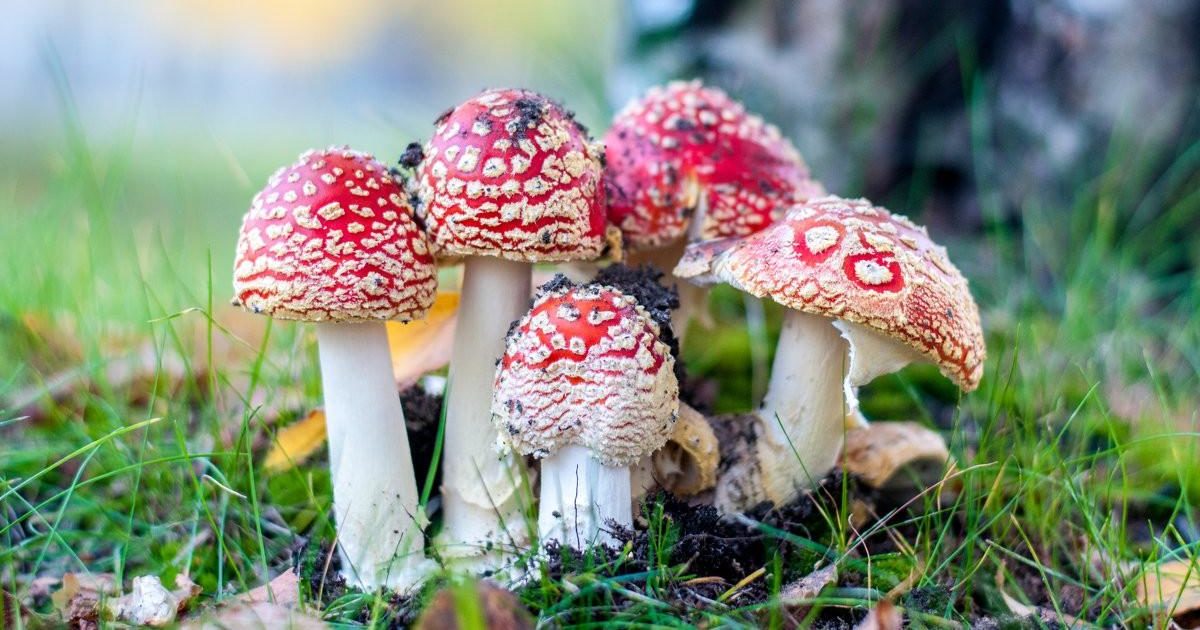
Inedible and poisonous mushrooms
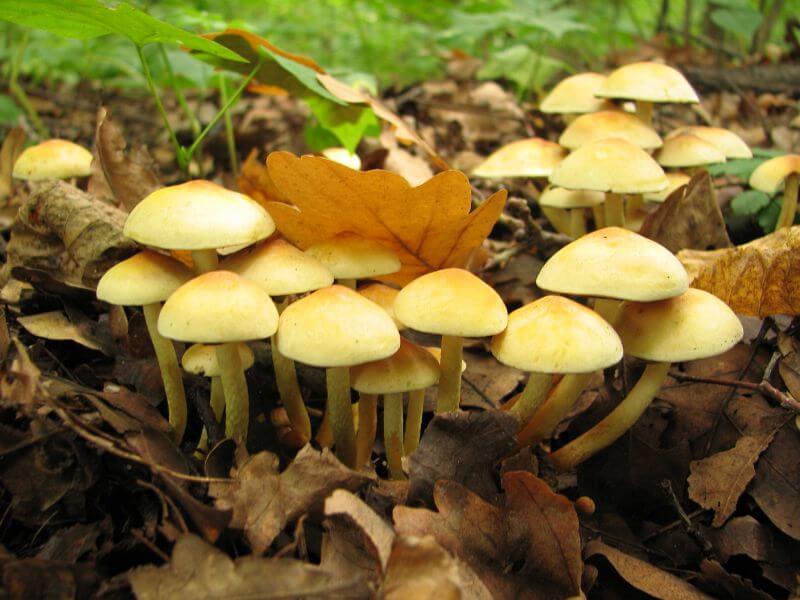
Most often, edible mushrooms are confused with representatives of the Brick-red and Sulfur-yellow species. Their main characteristics:
- Brick red mushrooms are distinguished by a spherical hat with a red-brown or red-brown surface. As a rule, in the center it is a little darker. Leg yellow-brown, without mushroom ring. The pulp is dark yellow, bitter, with a sharp unpleasant odor.
- The sulfur-yellow appearance is distinguished by a fleshy hat with a bright yellow surface. On the edge of the surface of the cap has a greenish tint. The leg is high, hollow, almost always curved. It has a yellow color, a little darker at the base. The pulp is white, sometimes with a yellowish tinge, has an unpleasant smell and taste.
The main differences between edible and false, inedible fruits
To distinguish edible mushrooms from inedible or poisonous mushrooms by the following criteria:
| Edible | Inedible |
|---|---|
| The presence of a filmy mushroom ring on the leg. | Lack of mushroom ring. |
| Pleasant mushroom or clove aroma. | Pungent odor. |
| Color in pastel colors. | Catchy, flashy shades. |
| The presence of young fruit flakes on hats. | The lack of scales on hats at any age. |
| White-cream plates that do not change color. | Plates of white-cream shades quickly darken; yellow, green, dark plates. |
| Fruiting year round. | Fruits only in spring and autumn. |
| Pulp in contact with water does not change its color. | Upon contact with water, the cut-off area darkens: it acquires a blue or black tint. |
The insidiousness of inedible species lies in the fact that they grow in close proximity to edible mushrooms.
Useful properties and restrictions for use
Honey mushrooms contain a large number of substances necessary for the human body:
- Vitamin B3 promotes proper metabolism, dilates blood vessels, improves the digestive tract;
- Vitamin B2 is involved in the recovery processes of the body, improves the functioning of the heart and the reproductive system;
- ascorbic acid increases immunity, has an antioxidant effect, strengthens blood vessels;
- potassium and magnesium stabilize the work of the heart, reduce blood viscosity, make blood vessels more elastic;
- iron directly affects the level of hemoglobin in the blood of a person and takes part in the transportation of nutrients.
With caution, mushrooms should be eaten by people with the following diseases:
- chronic gastrointestinal diseases;
- renal failure;
- liver disease.
It is contraindicated for future and nursing mothers, as well as children under 7 years of age, to eat mushrooms.
How to prepare mushrooms for the winter?
Honey mushrooms, as a rule, grow in large groups, so it is unlikely to leave the forest with an empty basket. Mistresses often make preparations for the winter: mushrooms can be salted or pickled.
How to peel mushrooms
Honey mushrooms must be processed immediately after collection, because they tend to quickly darken. Before cooking, be sure to clean the mushrooms, as bugs and other insects are often found under hats. Cleaning involves the following:
- Sort the fruits, discarding wrinkled, rotten and wormy specimens.
- Remove adhering debris from picked mushrooms: blades of grass, leaves, etc.
- Cut off all damaged areas and the lower half of the leg with a knife.
- Using a brush, remove the film from under the hat.
- Rinse fruits under running water.

After cleaning, the mushrooms must be boiled for half an hour.
Pickling and pickling recipes
Salt honey mushrooms for the winter is very easy. To do this, you only need salt, garlic and a few currant leaves. The algorithm is as follows:
- Mushrooms are laid in a single layer with their hats down. Then they are generously sprinkled with salt mixed with chopped garlic.
- Next is the next layer of mushrooms, which is also sprinkled with salt and garlic. The number of layers depends on the size of the salting tank.
- The very last layer is tightly covered with currant leaves.
- A gauze edge folded several times is placed on the leaves and a weight is installed.
- You can try pickles no earlier than 2 months after salting.

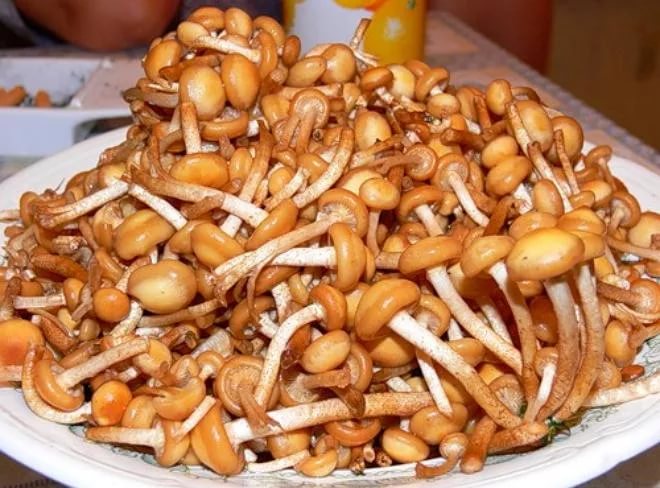
To pickle honey mushrooms, you must perform the following steps:
- Dissolve 1 tbsp in 3 l of water. l salt and 2 tbsp. l Sahara.
- The water is brought to a boil and boiled mushrooms are thrown there.
- After 10 minutes, add 50 g of vinegar to the water and remove the pan from the stove.
- The brine is poured into a separate container.
- The mushrooms are filled with pre-sterilized banks.
- The remaining space of the banks is poured with brine.
- If desired, horseradish root, currant leaves, bay leaf, chives, allspice and other seasonings can be added to each jar.
- Banks roll up. After complete cooling, they are taken out into a cold room.
- You can try conservation after 2 weeks.
Answers to Common Questions
Honey mushrooms are very tasty and healthy mushrooms. But you can eat them only after heat treatment and compliance with all the subtleties of cooking technology.
























 Care and use of Kombucha at home (+22 photo)
Care and use of Kombucha at home (+22 photo) Edibility of the fungus of the motley umbrella and its description (+19 photo)
Edibility of the fungus of the motley umbrella and its description (+19 photo)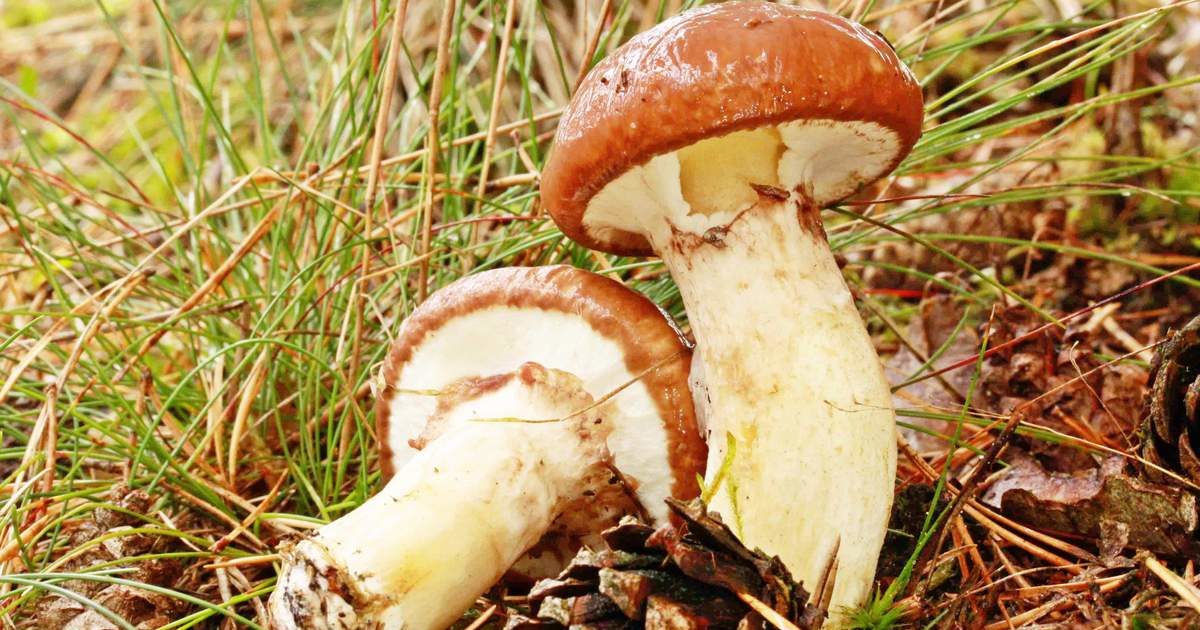 Description of edible and inedible oils, their poisonous counterparts (+40 photos)
Description of edible and inedible oils, their poisonous counterparts (+40 photos) Useful properties of milk mushroom and its contraindications (+17 photos)
Useful properties of milk mushroom and its contraindications (+17 photos)