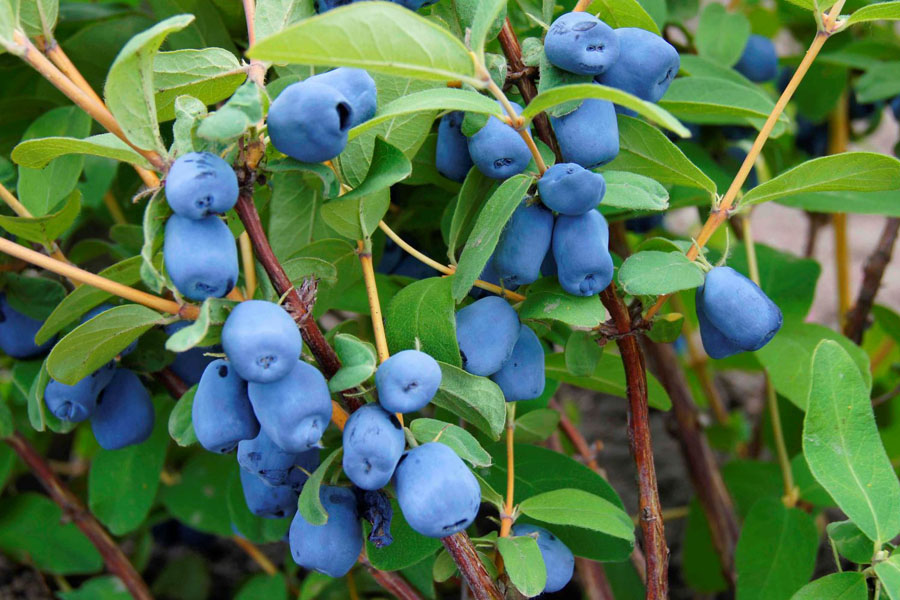
Among the varieties of honeysuckle, there are plants with edible and inedible fruits. They are distinguished by the color of the berries. Honeysuckle fruits contain many vitamins and minerals.
Gardeners are attracted to edible honeysuckle, since planting, care and reproduction do not require special skills. The shrub is unpretentious in growth on different soil, in different weather conditions, frost-resistant, gives a high yield of interesting fruits with seeds in shape.

The berries have glucose, fructose, sucrose. They have medicinal properties, are used in cooking and in traditional medicine. Unpretentious in the growth of shrubs of wild and cultivated species, there are about two hundred varieties. All of them are early, the fruits ripen by the end of May, but the shrubs bear fruit throughout the growing season, and ripening berries delight gardeners with an excellent harvest until the end of summer.
Content
Honeysuckle varieties
All varieties of edible shrubs are self-pollinated. The berries have an interesting color and taste. Garden shrubs are also decorated with shrubs, with them hedges can be formed or included in the general landscape.

Curly species of plants perfectly decorate arches, arbors, building facades. Edible honeysuckle is easy to plant, care and breed, the photo shows a variety of species of shrubs.
Shrub varieties:
- Bogdan. This is a cross-breeding hybrid. Shrub of small stature, with a compact crown. Gives large oval fruits of lilac or purple hues. The taste of berries is sweet and sour.

- Long-fruited. A low shrub with a spreading crown creating almost regular round outlines. Fruits in large berries of a cylindrical shape, sweet and sour taste.

- Mascot. It is appreciated by gardeners for high productivity. Bushes grow up to 2 meters, give fruits of medium size. They are distinguished by a delicate dessert flavor, from which excellent jams and jams are obtained.

- Bakcharsky giant. Shrub up to 2 meters in height, the crown is decorated with a beautiful oval. The berries are bright blue. It is resistant to diseases and pests.

- Cinderella. Differs in the taste of berries reminding strawberry. They can be eaten raw.

Edible honeysuckle berries are used in the preparation of canned food, wine.
Fresh berries should not be eaten by children under 5 years of age.
 You may be interested in:
You may be interested in:Planting honeysuckle in the garden
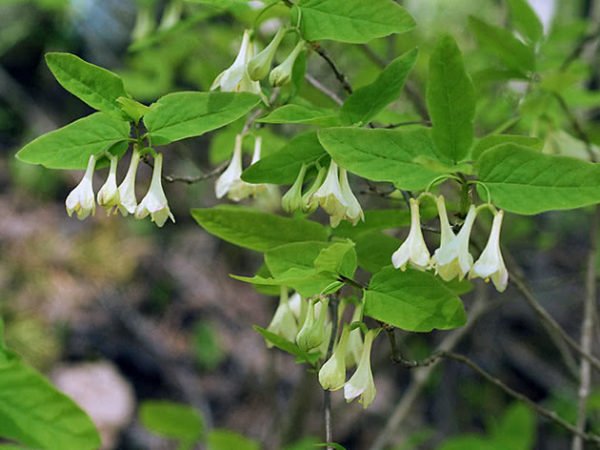

Experienced gardeners recommend taking low bushes for the initial planting of edible honeysuckle, and caring for them is the easiest. Choose bushes up to 1.5 meters, immediately acquire several varieties to ensure cross pollination.
Seedlings require a place well lit by the sun during the day. Honeysuckle takes root in any soil, only dry sand and obviously swampy places with stagnation of water should be avoided.Usually, bushes are planted in the spring, before the buds swell, at a stably warm night temperature. If seedlings are purchased in the fall, they must be planted in such a way that their root system takes root before the first frost.
Therefore, edible honeysuckle is actively cultivated in the Kuban, where for planting, care and breeding nature created favorable conditions.

To obtain a garden from a honeysuckle, it is planted in a square-nesting manner, according to the scheme 40x40x40 cm, with a distance between bushes not more than 1.5 m, between rows - not less than 2 meters.
To ensure full growth, active fruiting, prepare filling for each hole:
- rotted manure - 10 parts of the total amount of backfill;
- superphosphate - 100 g;
- potassium sulfate - 30-50 g;
- wood ash - 300-400 g.
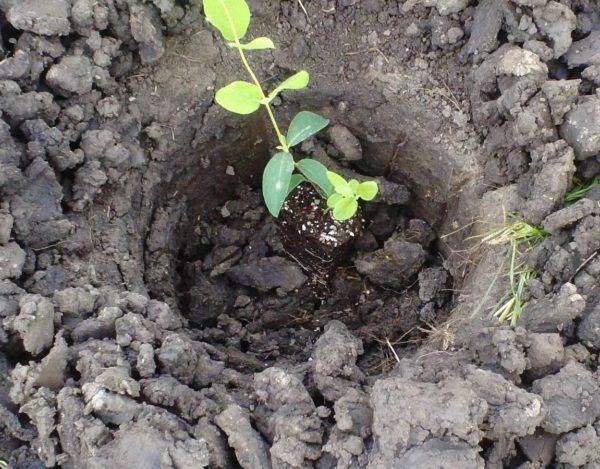

All components are mixed, poured into the pit with a knoll, the roots of the seedling are placed on it, without bending them. Top with earth, lightly tamped. Then water abundantly.
Care and propagation of honeysuckle
Honeysuckle is well established, is actively growing. In the first year after planting, it is recommended to fertilize the seedlings every 2 weeks. Nitrogen fertilizers are well suited.
Preparation of a useful mixture: 30 g of ammonium nitrate or urea are taken per 10 liters of water. This solution is divided into 1 liter per bush, under the root of seedlings.
 In summer, bushes should be watered abundantly. Loosen the soil around the seedling so as not to touch the roots with a sharp tool.
In summer, bushes should be watered abundantly. Loosen the soil around the seedling so as not to touch the roots with a sharp tool.
From the second year of growth, shrubs feed every 2-3 years, more often they do not need it. In spring, sometimes a little rotted manure is brought under the plants, in the autumn, closer to frost, they add wood ash to the trunks.
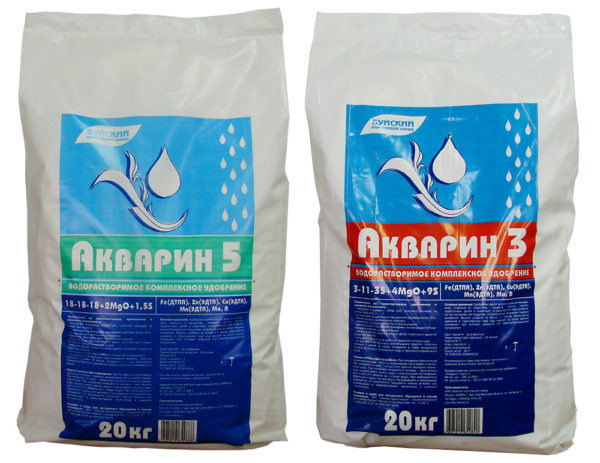
Plants at the height of summer should be sprayed with the use of drugs:
- Master.
- Solution.
- Epin.
- Aquarin.
20 g of one of the preparations is taken per 10 liters of water, mixed with water until completely dissolved. Spray the bushes in calm weather.

Honeysuckle is propagated by cuttings, dividing the bush or layering. Towards the end of autumn, layering is dug, choosing strong side branches for them. By spring, layering create its root system, well take root in the ground.
A young seedling will appear after 2 years. Propagation by cuttings of edible honeysuckle requires the ability to plant and care for different types of cuttings.
 You may be interested in:
You may be interested in:Cuttings are carried out with green or stiff parts of the plant. Green cuttings are cut in cloudy weather, after the appearance of the first berries. Strong shoots are cut diagonally, the knife is decontaminated before work.
The young branch is divided into several cuttings with 2-3 buds. Leaves are removed from the cuttings, put them in water for a day, then planted.

In winter, a plot with planted cuttings is covered. In spring, strong, well-established cuttings are transplanted to a new place.
Lumber cuttings are cut in the fall, choosing annual strong shoots with 2-3 buds. The prepared material is wrapped in a wet bag, dripped with sand or sawdust. In warm spring, they are planted in the soil at a slope of 45 degrees, one kidney is left on the surface. This method of reproduction gives the least survival.
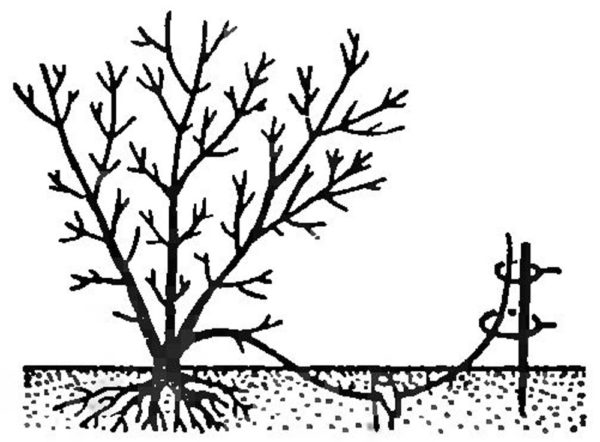
Reproduction of edible honeysuckle independent of its variety. Planting and caring for new seedlings require knowledge of the order and rules of propagation of the shrub.
Honeysuckle is planted by dividing bushes. Bushes are completely dug out usually when changing their place on the site. This is a convenient time to carefully divide the rhizome, often not 3 but even 4 young seedlings are obtained. They are planted in a new place according to general rules.
Honeysuckle Diseases and Pests
It is necessary to provide plants with protection against diseases and damage by various pests. Many gardeners carry out preventive treatment of shrubs.When the first signs of the disease or insects appear, special treatment must be performed.

Characteristic for honeysuckle insect damage:
- Aphids. She sits tightly on the branches, the lower parts of the foliage, drinks juices from the plant. From this bush grows pale, wilts. For preventive purposes, spring treatment of bushes by Eleksar, Confidor, Karate, Actellik is needed. There are folk ways to scare away small pests: spray the bushes with a solution infused with onions, garlic, pepper, tobacco. Successfully used coniferous extract, infusions of chamomile, celandine.
- Leaf wrench. Her defeat is immediately noticeable: the leaves are curled with a tube. In early spring, from this pest, the bushes are treated with solutions of Fuvanol, Actara, biological products of Lepidocide, Biotlin.
- Cherry fly. She lays white larvae on all parts of the plant. They damage the bushes, and when they grow to the stage of worms, they eat berries. In general, the entire bush is inhibited. Processed from a cherry fly with insecticides.
There are many methods for getting rid of insects (folk methods, chemicals). They must be correctly selected to be suitable for the destruction of a specific type of pest.
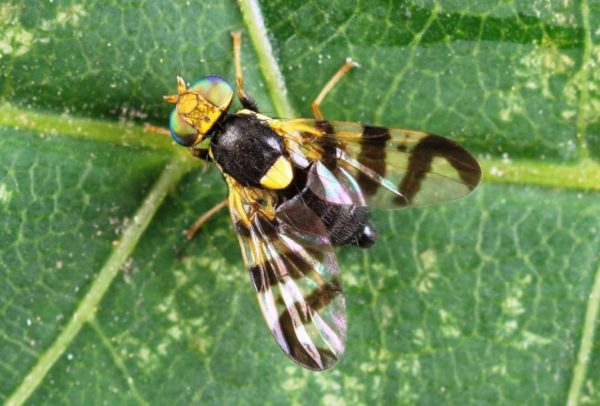

The diseases affecting honeysuckle are the same as in other crops. Experienced gardeners are also familiar with the problems, methods of treating plants using folk or chemical agents.

The main diseases of honeysuckle:
- Mosaic. Its signs are the appearance of bright yellow spots on the leaves. This disease is incurable, you must quickly uproot and burn the whole bush.
- Ramulariosis Signs - cool, humid weather gives manifestation on the leaves of spots of gray and brown shades, with a white coating. The plant is treated by spraying and watering with Fundazol, Oksikhom, Horus.
- Powdery Mildew
- Sooty fungus.
- Cercosporosis.
- Rust.
Any diseases of honeysuckle are prevented by the correct regime of planting, care, treatment with different drugs. Honeysuckle loves cold regions, planting it in the middle lane and southern latitudes of Russia is the desire of gardeners who are ready to organize proper care for the bush.
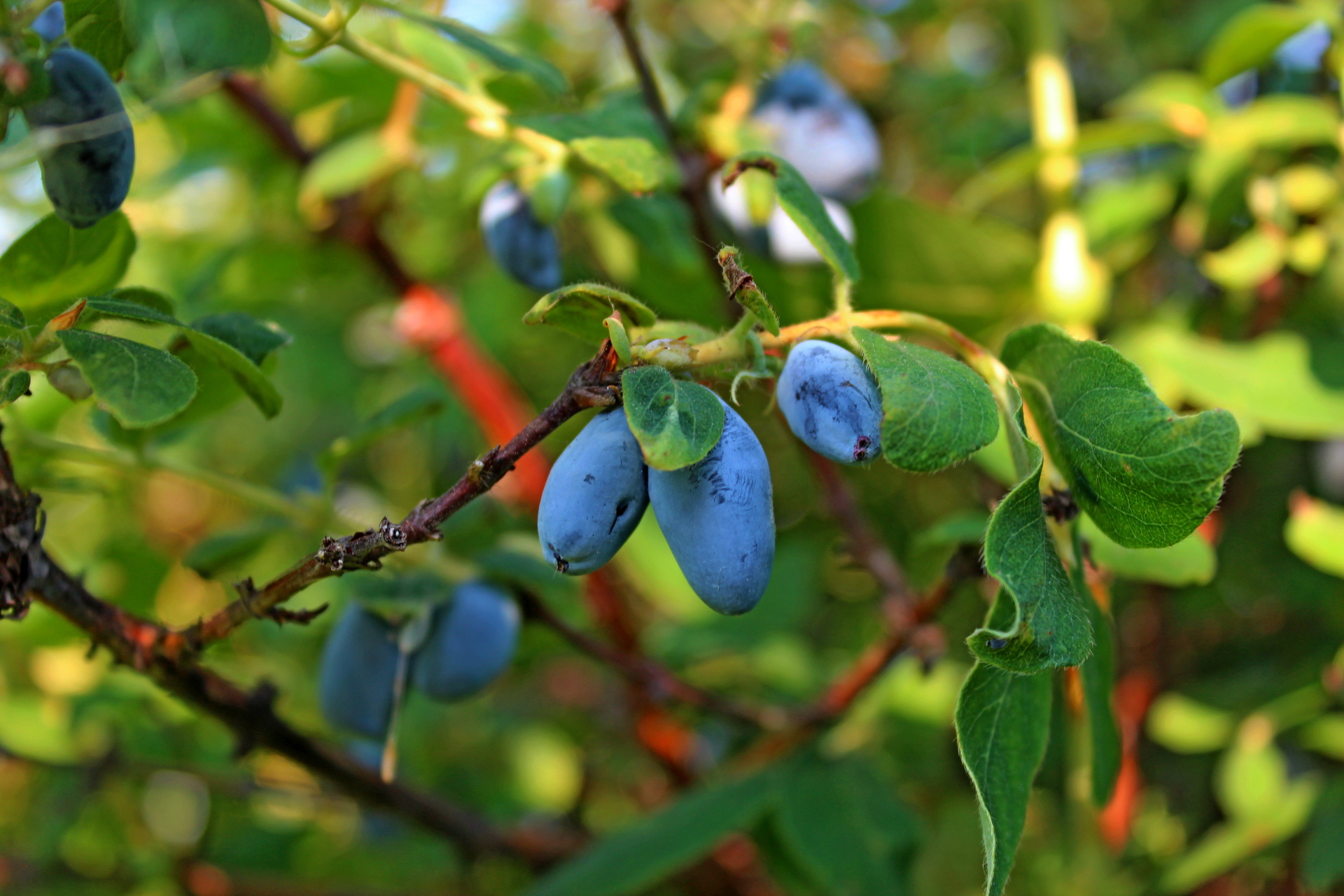
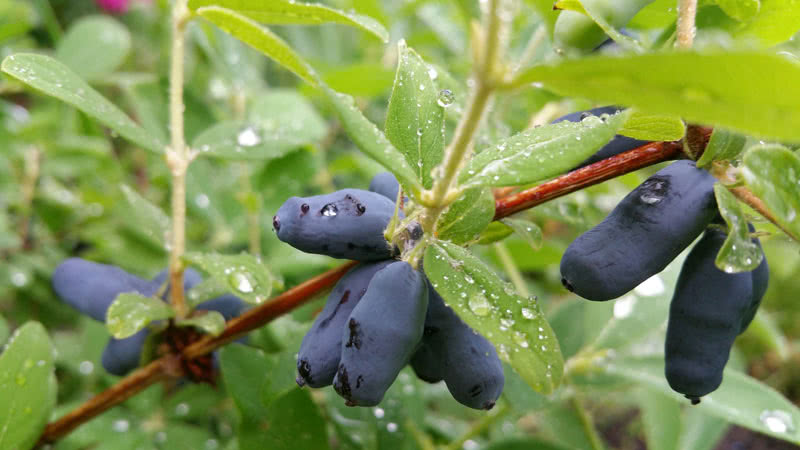



 Edible honeysuckle: planting and care, methods of reproduction, disease
Edible honeysuckle: planting and care, methods of reproduction, disease Honeysuckle in the fall: planting and care, transplanting, breeding, shelter for the winter
Honeysuckle in the fall: planting and care, transplanting, breeding, shelter for the winter