To obtain a high strawberry crop, technology is applied that includes protecting plants from freezing in the cold season. Before you cover the strawberries for the winter, you should study the characteristics of the plant, the characteristics of the insulation and preparatory actions. The choice of material depends on many factors, the protective layer is made from improvised natural mixtures or finished insulation films.
Content
The benefits of sheltering
The question is whether cover strawberries for the winterstands in front of every gardener. The plant survives frosts well under the snow cover that warms the bushes. But the thickness of the layer cannot be less than 27-30 cm, and precipitation should lie on the bed with a continuous blanket for the entire cold period. In the regions of Russia, the weather is not constant.

Winds blow snow from the beds, the roots of the plant are exposed and become vulnerable to low temperatures. Under such conditions, strawberries can die even in small frosts. In some regions, thaws in winter are observed. During these periods, the bushes awaken from heat, which is quickly replaced by frost. Shelter will protect from unwanted changes.
 You may be interested in:
You may be interested in:The drying of the soil and the plant itself is bad for the conservation of the bush. Nutrients from the soil go deep, and roots close to the surface remain without moisture for the winter. In spring, such unprotected bushes look dead with weak buds and leaves.
Covering material for strawberries for the winter saves berry bushes from damage:

- Freezing the root system. Snowless winter and lingering cold autumn will not only destroy the upper part, but also negatively affect the plant.
- Weathering of the upper layer of the earth. Covering soil is carried away by the wind, and the plant remains unprotected.
- High humidity. Excess moisture leads to decay of the roots and the entire bush.
- Drying out. Arid climate and snowless winter will cause the death of the plant.
- Mechanical damage. This happens if animals or poultry walk along the beds and trample the bed.
Process features
The decision to close the beds with insulation is accompanied by the choice of material and the determination of the timing of work. Before warming strawberries for the winter, it needs to be prepared. Technological cycles are carried out in a certain sequence. This helps to get a good result when picking berries.
Young bushes are completely covered, and perennial plantings can be wrapped only in a circle. If a layer of snow already lies on the ground, then coniferous branches are laid on top of it. In the southern regions, it will be correct to mulch the root system and carry out a barrier along the perimeter of the bed to trap snow.

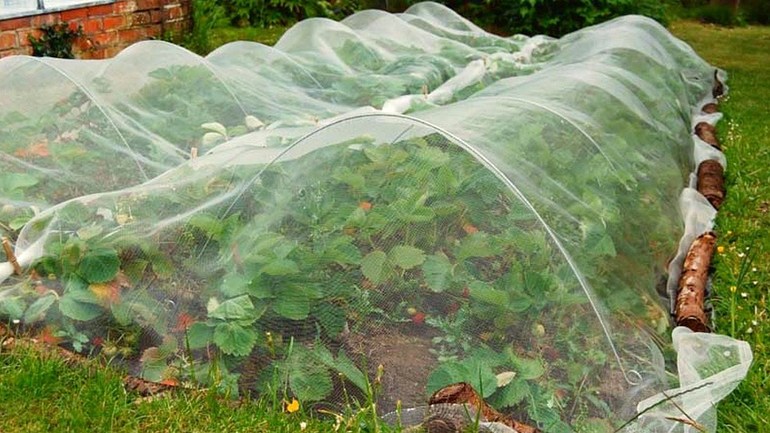
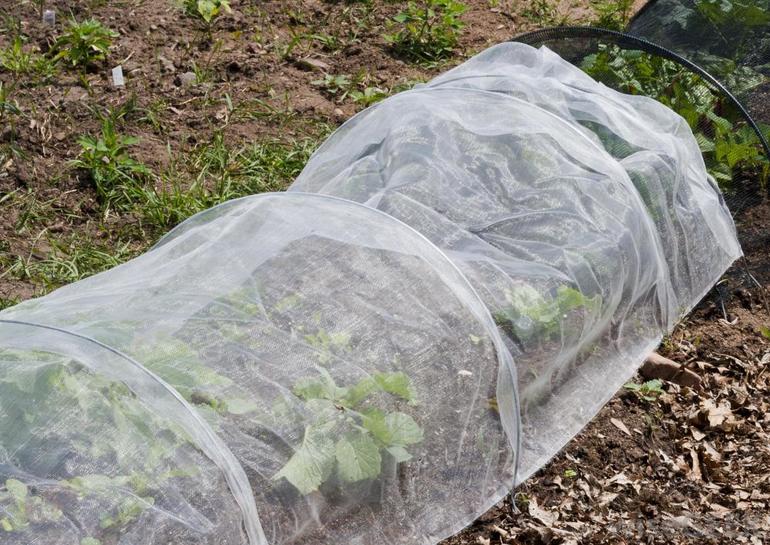
A mini-greenhouse is used, which is built over rows of bushes and wrapped in insulating material.The plant feels good in such conditions, but you need to monitor the aeration and open from time to time, if weather permits. The coated frame is taken apart in early spring.

The specificity of garden strawberries
Strawberries have some development features that are taken into account when choosing a method of insulation. The nuances are as follows:
- The root is shallow, located in the soil at 7−9 cm from the surface. The hope that frost will not affect the system at such a depth is not justified.
- The ground part of the plant and its roots can overwinter in small frosts, but there is a limit at which the plant can come to life with the arrival of heat - this is a temperature from -9 to ± 2 ° C. If at the same time there will be winds that will additionally cool the soil in the blown areas, then the indicated value will change.
- It is necessary to cover the bushes in due time, because under the protection layer, with early covering, the plant begins to bloom and can bear fruit under an insulating coating. The danger lies in the fact that in those days when the street is still warm, strawberries ripen. This threatens to plant new plants in spring instead of old damaged specimens.
 You may be interested in:
You may be interested in: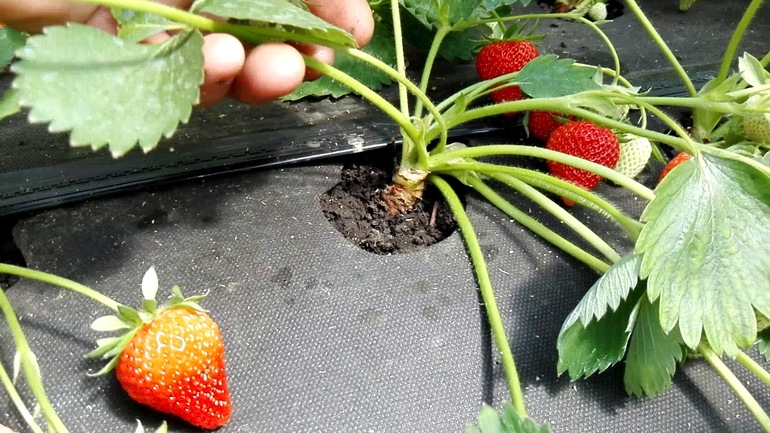
Wrap the bed after the average temperature, day and night, will be in the range from -4 to +8 ° C. For example, Victoria's strawberry is unpretentious, withstands frosts, but requires barriers to keep snow drifts on the bed, which is inclined towards the sun's rays.
Preliminary preparation
All required preparatory work is carried out in full, regardless of the protection option chosen. The operational actions are aimed at improving the plant before winter and preparing the soil. Outdoor air temperature is a universal reference, but there are separate recommendations for each grade. The characteristics of the soil, its composition, location relative to sunlight are also taken into account.
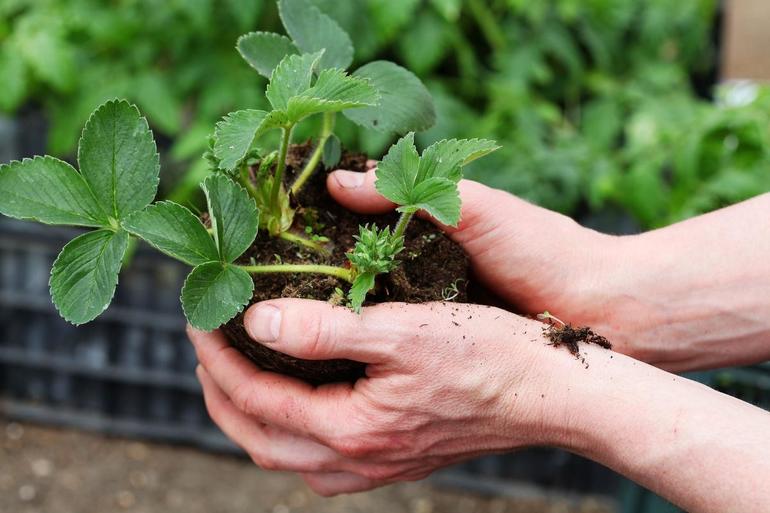

After the autumn transplantation of bushes, in order to obtain a good harvest in the future, at least a month and a half should pass. During this time, the bushes take root and adapt in new holes. The terms are determined, taking into account the specifics of the site and the variety of garden strawberries.
If the bushes are not transplanted, then the growing lashes are thinned out. The procedure is to tear off old leaves, long mustaches. Faded wilted bushes, dried specimens are removed from the earth. Healthy bushes are planted in their place. Thinning is done to optimize the nutrition of the remaining plants, which will receive a full amount of minerals and vitamins.
Old plants obscure new bushes and they do not receive ultraviolet rays. Negativity manifests itself in young plants that cannot develop in cramped conditions. The gardener removes a lot of pests from the bed, thinning the vegetation on the plot in front of the cold. Beetles are preparing to winter in the folds of obsolete leaves, so a mass with insects under the film is not required.
Preparatory measures before shelter for the winter:

- The earth is fed so that the plant tolerates winter without loss. Trace elements, vitamins strengthen the plant. The peculiarity of autumn enrichment is that only organic matter is introduced, nitrogen compounds are not practiced. Humus and manure are used in calculated quantities.
- The soil loosens after the end of the irrigation period. The procedure allows the root system to breathe, and moisture delivers nutrients faster.
- The neck of the plant is mulched at the root. The layer protects the earth from cracks and provides additional insulation. The absence of gaps is important because cold air enters the roots through them. Peat and humus, needles serve as material for mulch. These components not only protect against the cold, but also additionally feed the plants.
- Bushes are sprayed with Bordeaux liquid at a concentration of 3%. Plants are processed completely, left to dry (1.5−2 days) and after that they can be closed. To prepare the solution, 3 g of the substance is taken, dissolved in water with a temperature of 22-24 ° C (1 l). When processing the bushes are wetted, but not poured with the drug, it is allowed to hit the ground.
- A protective barrier is constructed around the bed to maintain a layer of first and subsequent snow. Used materials, pegs, the remains of the panels.
More severe climatic conditions require the creation of cover if dry winters without snow are expected. In the Volga region, strawberries are rarely grown, because care is expensive, and yields are low.
Backing material
The owners are sure to think about how to cover strawberries for the winter from frost. Different materials are used - natural or artificial. Each of the species differs in certain features.
Plast from natural products
Fallen leaves and weeds are not suitable to insulate beds with strawberries. Experienced gardeners immediately burn the accumulated mass so that harmful insects do not spread. Strawberry plot can be insulated:

- Corn stalks, trunks of pepper. To destroy incoming rodents, mouse poison is laid on top.
- The beds are covered with heavy leaves of maple, chestnut, poplar and oak trees. Gardeners still argue whether it is possible to cover strawberries with walnut leaves. It is important to review the mass in order to determine its safety from the point of view of pests. Rotten leaves are not suitable for a covering layer. Walnut foliage decomposes for a long time, ideally works as a heater. Heavy leaves are hard to deflate when freezing with gusts of wind.
- Sawdust is a good and cheap material. They are removed from the plot in early spring, because the mass contributes to the acidification of the earth. The material carefully covers the strawberries, and in the winter does not fly away from the wind, because it easily absorbs moisture and becomes heavy. Consumes a bucket of sawdust per 1 m².
- Bulrush refers to readily available materials; a layer about 2 cm thick insulates strawberries from the cold. The heavy reeds are not amenable to wind, easily fit into the formation and are removed in the spring.
- It is good to arrange a layer of fir branches, which are collected from trees felled from time to time. Coniferous spruce branches are most suitable for warming beds. Heavy material holds snow between the needles.
- Hay retains heat well, but due to its lightness it scatters from the site. When laying, straw or hay is crushed with spruce branches or heavy foliage. You can not put straw with the remains of grain, which will serve as a bait for mice. Straw rots from moisture, and strawberry bushes can hurt.
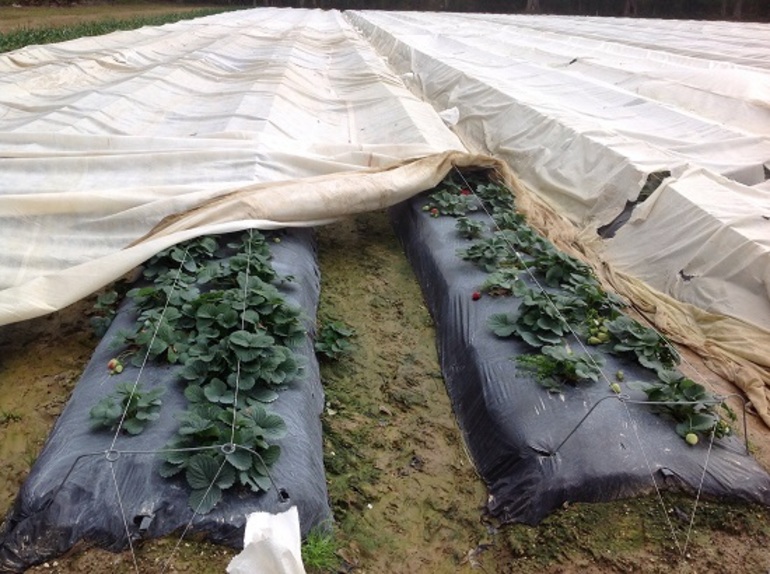
Polyvinyl chloride film
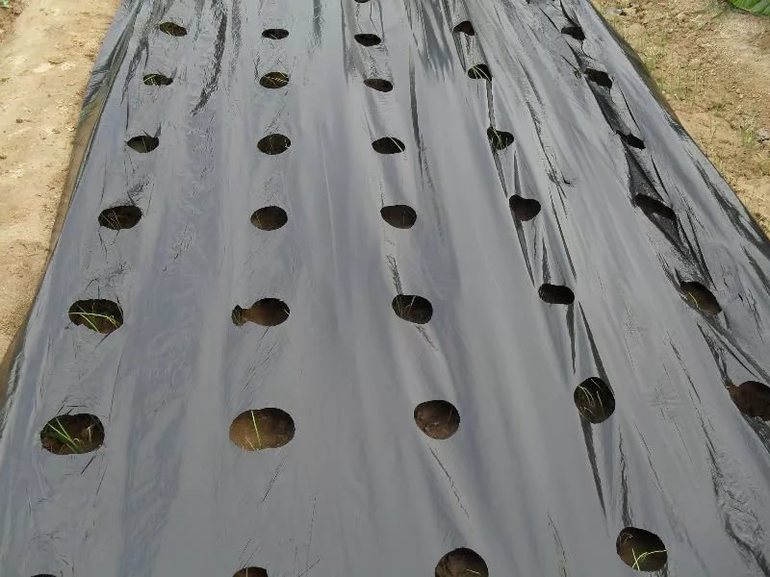

The towels are laid on the beds, bricks or other heavy objects are placed on all sides. The wear-resistant film does not respond to small mechanical stresses, it is possible to reuse the layer after removal the next year.The temperatures under the coating are close to ideal, but, unlike agrofibre, such material does not allow air particles to pass through.
Frame coating is also used. This is a laborious method, but reliable, plants feel free and breathe. Mini-greenhouse is easily carried out by a gardener and does not require large expenses. For the construction of the frame, used pipes, slats, bars of a small cross section are suitable - what is always on the farm.The film is stretched on the beds dug around the perimeter of the beds or along the length of the support rows and is fastened with the help of garters. Inside the makeshift house is light, air moves, and heat is retained. The disadvantages of this method The following points apply:
- work is more labor-intensive compared to a simple coating on the ground;
- requires constant monitoring of the weather and regular ventilation to prevent debate.
The top layer is made of agrofiber like a film.
Agrofibre for insulation
The second name of the material is spunbond. Available in rolls, the film has a different thickness and width, depending on the needs. The greater the thickness of the agrofibre, the more severe frosts withstand the bushes under the coating. Spanbond when used provides:
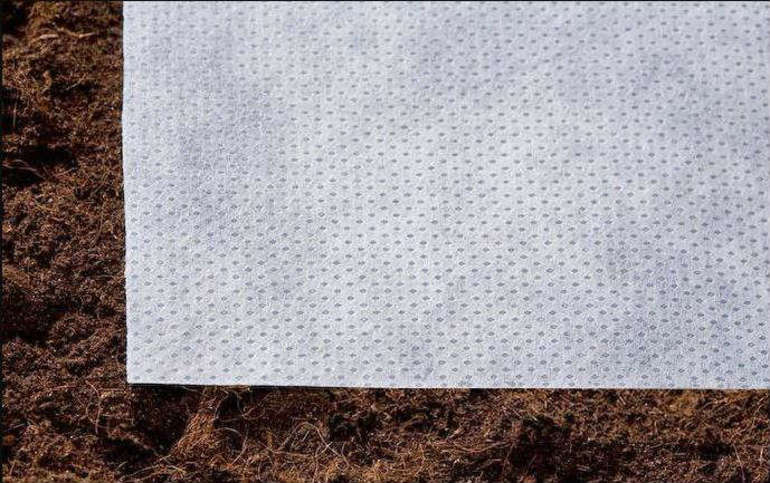
- microclimate required by technology;
- maximum warming;
- the ability to feed and water through the canvas with the beginning of spring;
- film turnover for 5 seasons.
The disadvantages include the high cost and the complexity of the preliminary measurements for the purchase of the required amount of material of the selected width. Agrofibre with slots for each bush laid on the ground, when harvesting in the spring, can damage plants.



 When to plant strawberries for seedlings from seeds in 2024
When to plant strawberries for seedlings from seeds in 2024 What month is better to choose for a strawberry transplant in the fall
What month is better to choose for a strawberry transplant in the fall How to cover strawberries for the winter
How to cover strawberries for the winter Proper care and pruning strawberries in the fall in the suburbs
Proper care and pruning strawberries in the fall in the suburbs