Mushrooms are organisms that belong to a separate large kingdom and have a number of characteristic features. They are numerous inhabitants of all forests and are famous for their diversity.
Despite the fact that, depending on the classification, each representative has an individual structure, all fungi (except yeast) have mycelium in their structure. This element of the body plays an important role, as it is responsible for nutrition and fastening in the substrate. Also, due to its presence, the formation of symbiosis with plants is possible.
Content
The concept of fungal mycelium, structure, reproduction
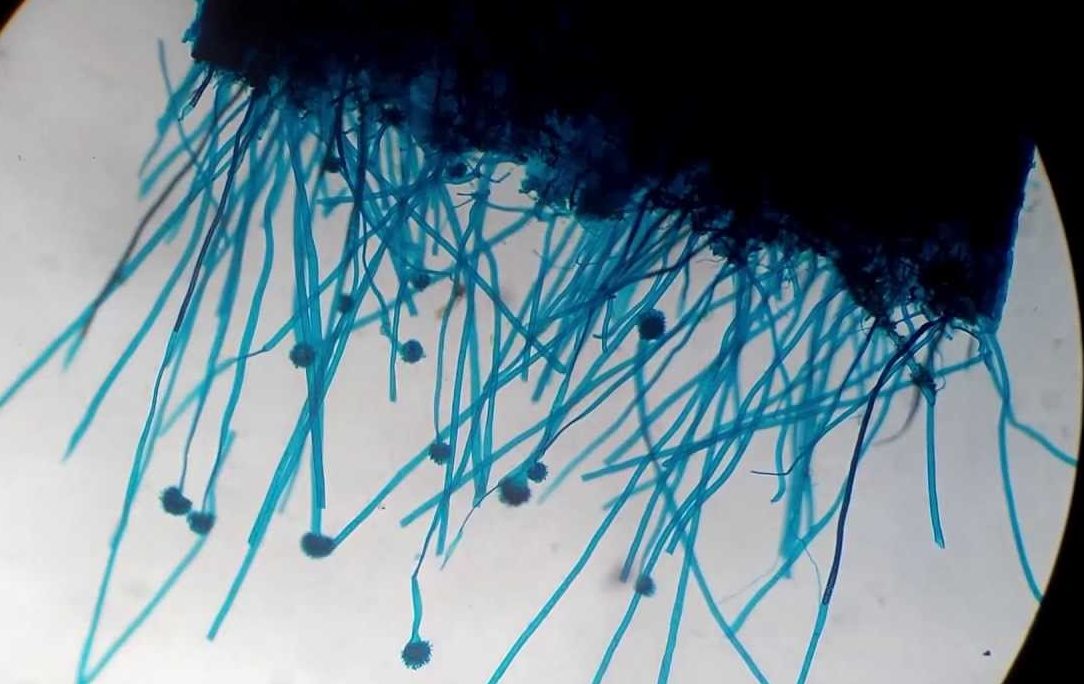
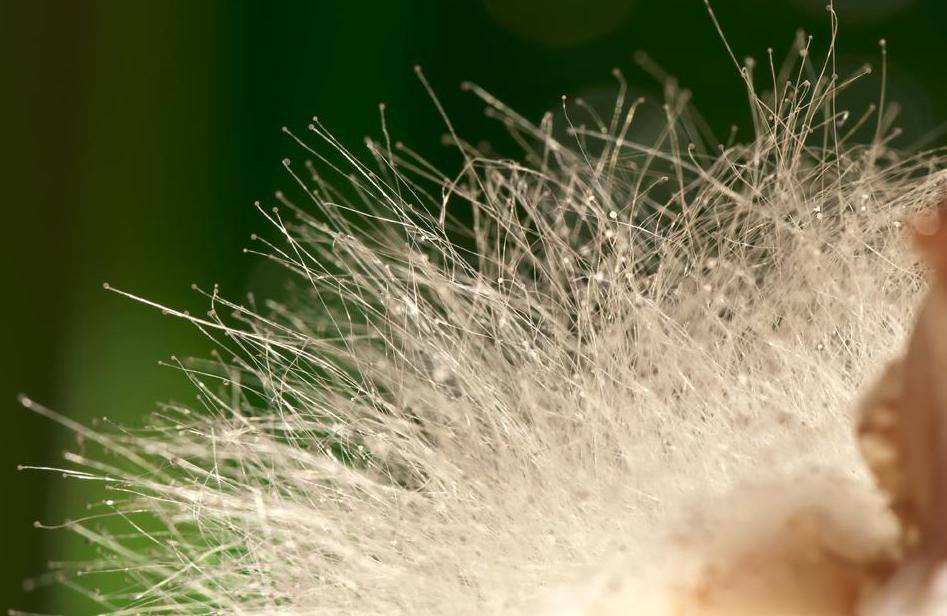
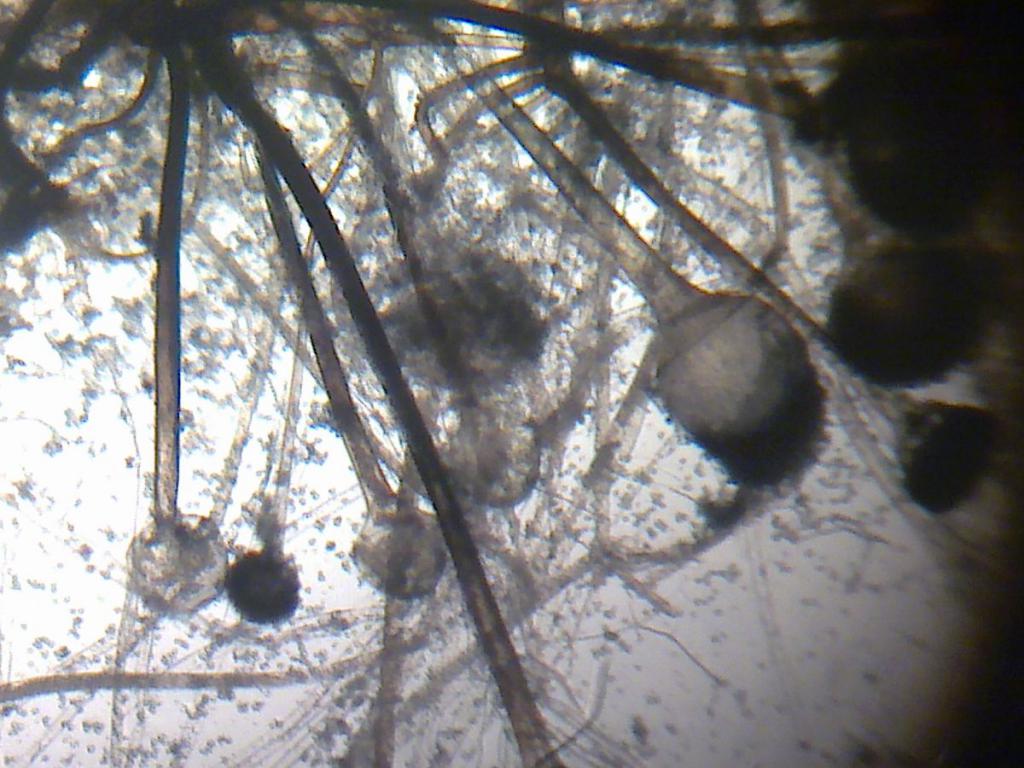
Mycelium is a vegetative body, which consists of a large number of white thin threads - hyphae. Gifs can reach different sizes and branch in all directions. They have a transport, fixing, pigment and reproductive function. All mushrooms are divided into lower and higher. The lower ones consist of one cell, and the higher ones have a multicellular structure.
Mushrooms with mycelium
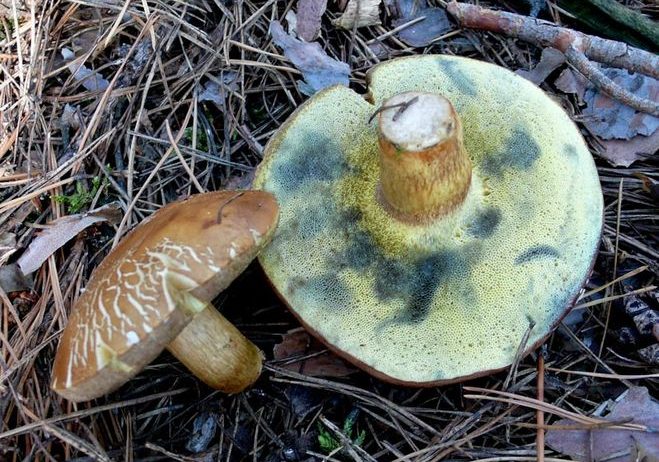
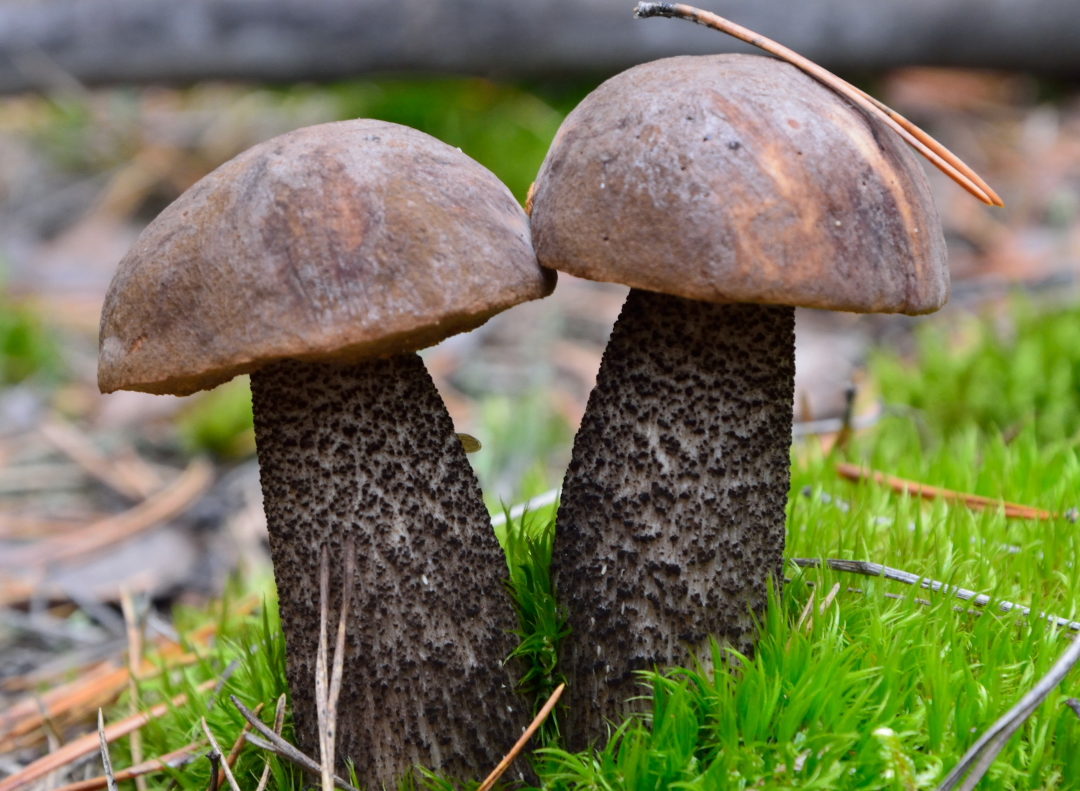
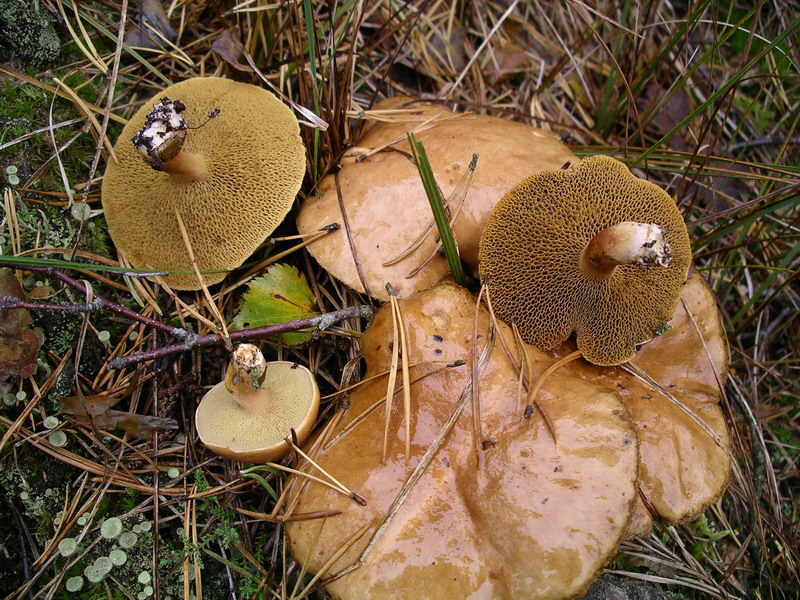
The most common higher mushrooms are cap. They consist of a vegetative body and a fruiting body. The fruit body, in turn, consists of legs and hats, which are formed from bundles of threads.

The hat of organisms has several layers. The upper one is uniform and covered with skin, pigmented, and the lower one is often represented by lamellae in lamellae or tubules in tubular ones. Tubules and plates are arranged circularly, a large number of spores are formed in them, which are subsequently carried by water and wind and contribute to reproduction.
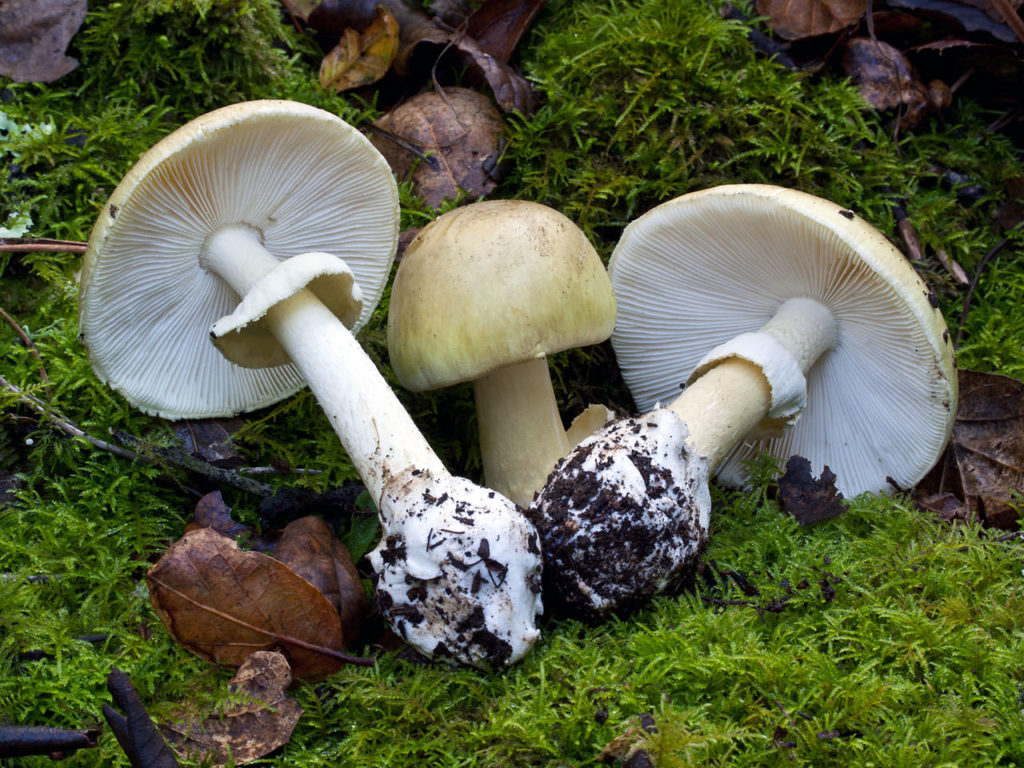
Hats can be edible or poisonous. The most common edible are considered white, milk mushrooms, saffron milk mushrooms, champignons, boletus. A pale grebe and fly agaric are poisonous, and also have distinctive features in appearance, which greatly facilitates the life of mushroom pickers.
 You may be interested in:
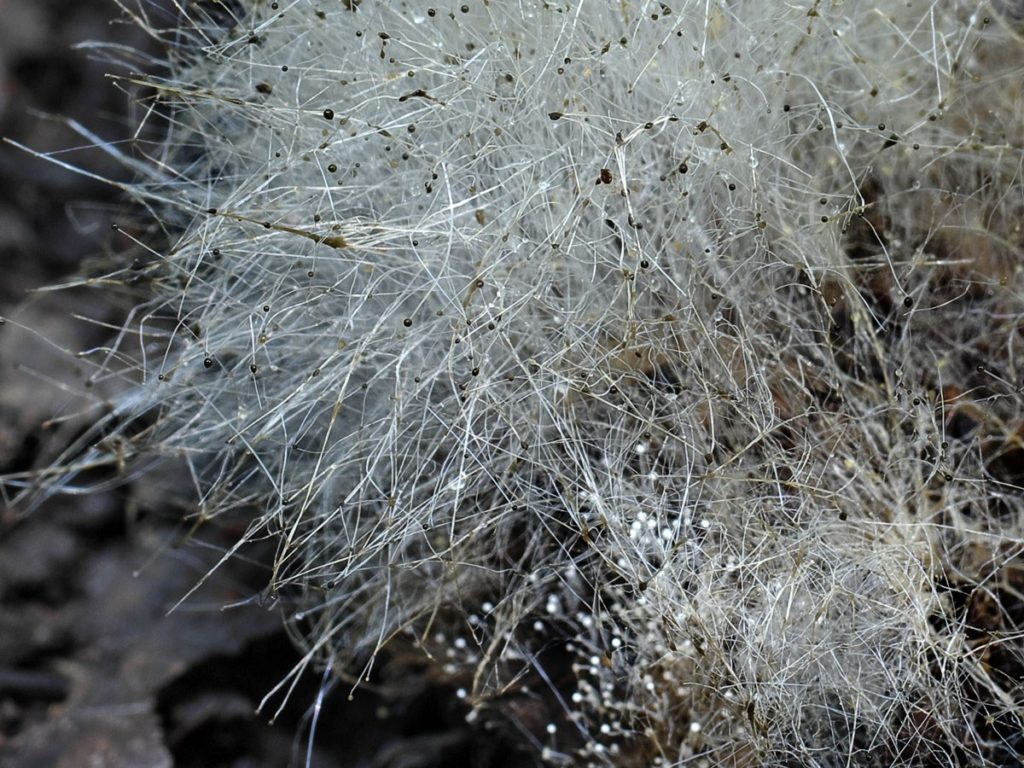
You may be interested in:The lower species include mold. Mold is unpretentious, therefore it is widespread in nature. It grows in the presence of high humidity and temperature. The most common mold species is white mold or the genus Mucor. By structure, these are colonies with a rough surface and consisting of thousands of erect hairs, at the ends of which sporangia are located.
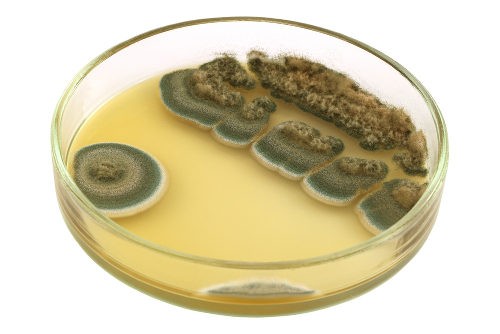
The genus of penicillas deserves special attention. Representatives of this genus are widespread in natural conditions, have conidiophores, thanks to which they multiply and form large dense colonies.
Mushrooms without mycelium
Yeast has become widespread in human activities. The size of yeast-like fungi does not exceed 10 microns, and they multiply by budding and division.
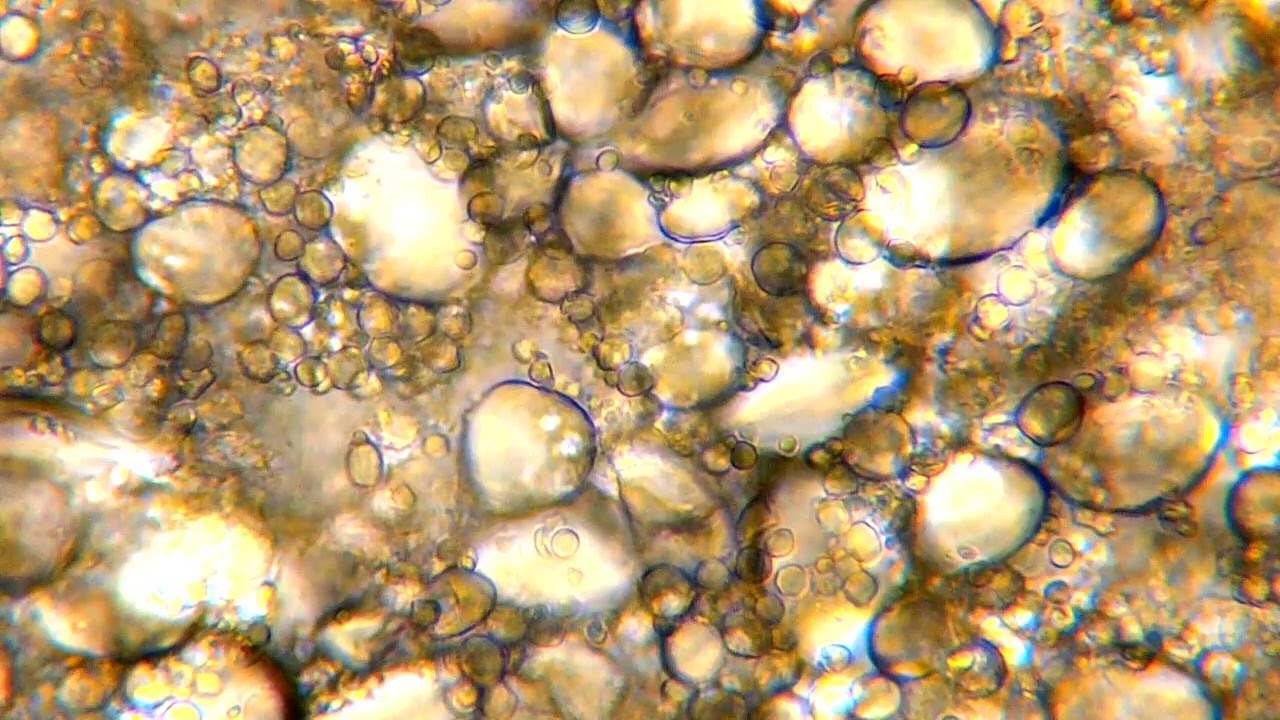
The most common type of yeast is baker's yeast, which is divided into wine, brewery, and baker's. They are widely used by man in cooking.
The main types of mushrooms and mycelium
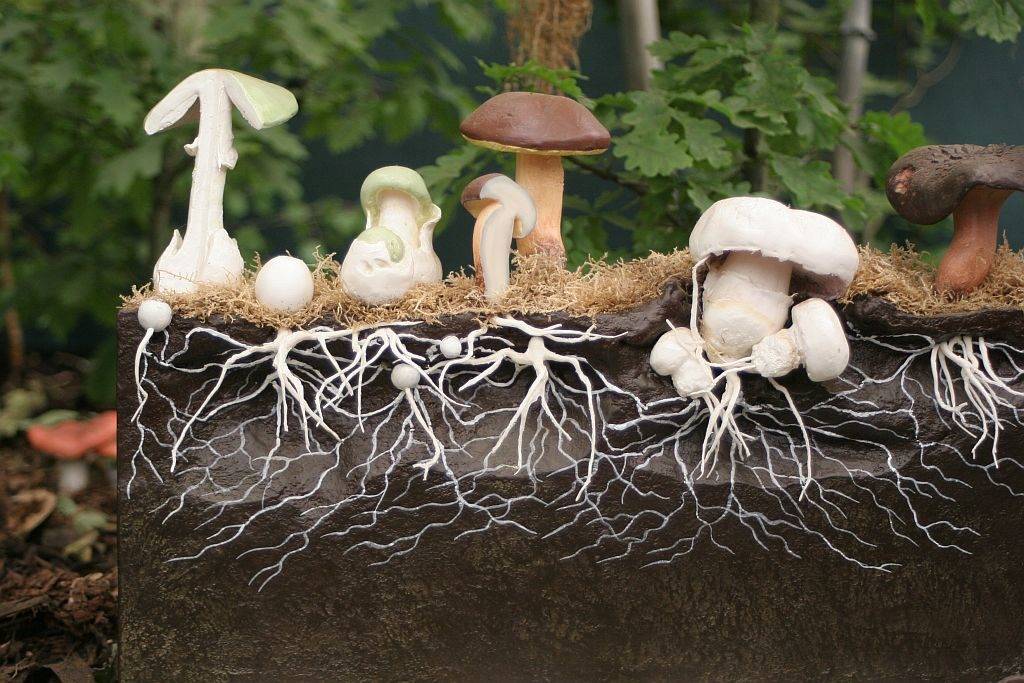
The mycelium itself is divided into two parts - air and substrate.The first rises above the substrate and is responsible for the formation of reproductive organs, and the substrate ensures the attachment of the fungus in the substrate, the transportation of water and organic substances to the body.
In some organisms, it can be modified, which is associated with the living conditions of a particular species. So, stolons contribute to the rapid spread and growth of the substrate, rhizoids and appressoria are responsible for fixing the body on the substrate, and using haustoria parasitic species suck out organic matter from plants.

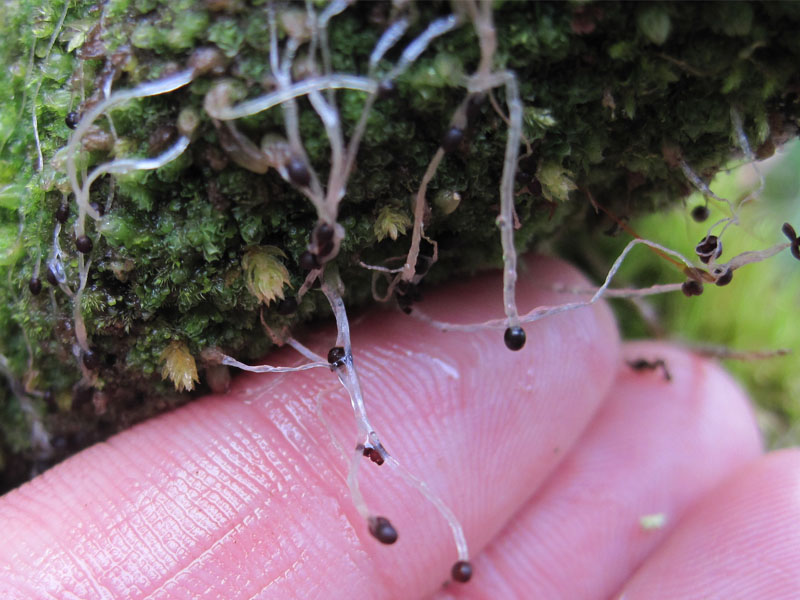
In addition to the above, the mycelium performs the function of asexual reproduction. In this case, reproduction occurs in parts or exogenous spores. Exogenous spores - conidia - are formed in conidiophores, special outgrowths at the ends of the mycelium. Under favorable conditions, a new one develops from a spore or part of the maternal mycelium.
 You may be interested in:
You may be interested in:The appearance of mycelium also depends on the method of nutrition. In saprotrophs, organisms that feed on organic matter from dead bodies, the length of hyphae per day can increase to 1 km. This feature is possible due to a special type of relationship with the environment.

The mycelium is also characterized by constant branching and rapid growth, therefore it is closely associated with the substrate. The hyphae themselves are composed of nuclear cells separated from each other by partitions. In each such cell, specific digestive enzymes are produced and secreted, which contribute to the digestion and absorption of the substrate material.
Penicillin, Mucor, and Yeast
The mycelium of mold representatives consists of thin branched hyphae that become thinner towards the periphery and consist of nuclear cells separated by a septum.
Mycelium of the genus Mukor is fluffy in appearance, which is associated with a large number of hyphae. The vegetative body of mucor is involved in reproduction by spores. At the ends of some threads are sporangia in which spores mature.
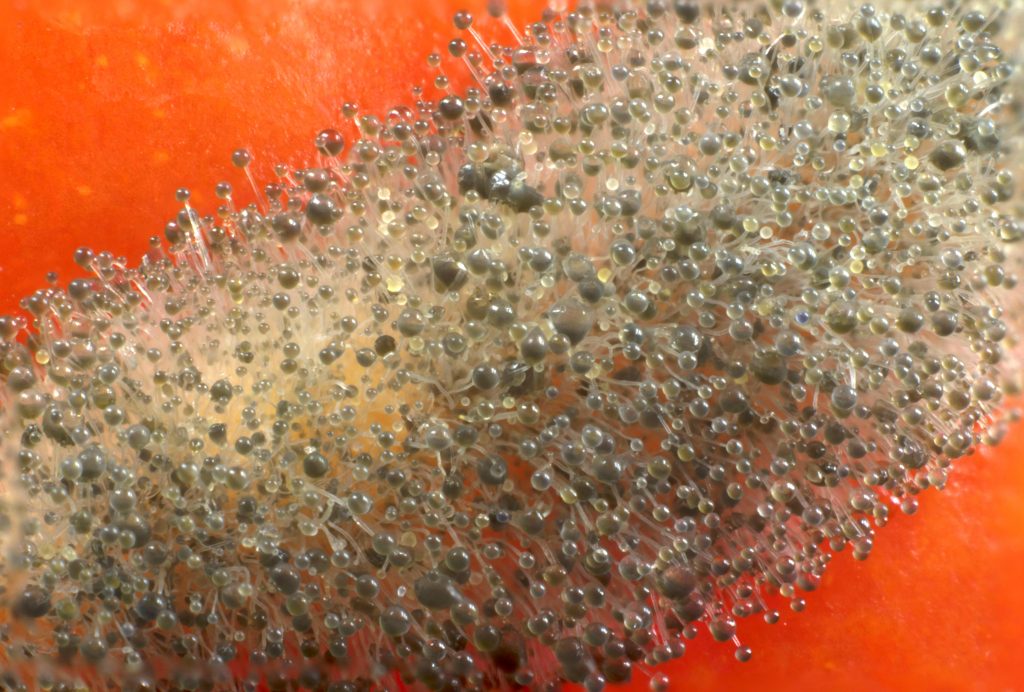
Of particular note is the penicillium, which is known for its use in medicine. The fungal mycelium of the penicillus genus is multicellular, separated by partitions, in structure similar to the vegetative body of hat species. The plexus of hyphae form a mycelium. Threads branch in a chaotic manner, not dyed. At the ends of the threads there are conidia, which are responsible for the reproduction of spores.
The only unicellular organisms that do not have mycelium but retain other signs and properties of fungi are yeast.
White and other hats
A feature of mycelium of cap mushrooms, including ceps, is considered to be that hyphae take part in the formation of the fruiting body - hats and legs.
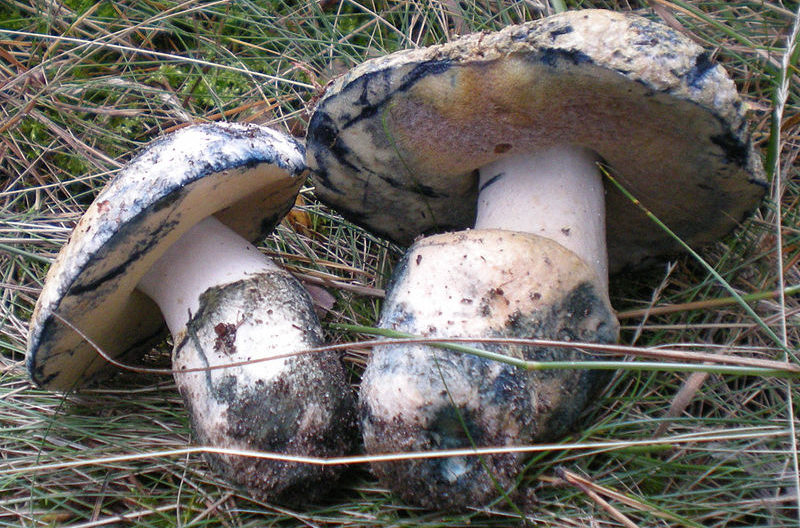

Covering varieties of hyphae of hatched species are also responsible for the pigmentation of the body. The mycelium has a loose structure and can resemble a film.
 You may be interested in:
You may be interested in:Useful properties, application and restrictions on the use
Mushrooms are an indispensable part of the earth’s ecosystem, without which many plants cannot develop. Mushrooms are also widely used in many areas of human activity, and in medicine and cooking most often.
Symbiosis of the mycelium of the fungus and the roots of a higher plant
The symbiosis of a plant and a fungus is called mycorrhiza.This coexistence benefits both organisms. Thanks to mycorrhiza:
- the plant consumes soil resources as much as possible, and its root system has less load;
- mycorrhiza improves the quality of the soil, provides aeration and increases porosity.

Mycorrhiza is divided into ectomycorrhiza and endomycorrhiza. The composition of ectomycorrhiza includes basidial or ascomycetic species and temperate forest trees. This subtype of symbiosis has a positive effect on tree growth.
Endomycorrhiza is a fungal part in the root of a tree. Significant is the arbuscular type of endomycorrhiza. This type of symbiosis is considered one of the most important on the planet and is a connection between fungal tree filaments and cortical cells of the tree root.
In medicine
Mushrooms are widely used in medicine due to the polysaccharides that make up their composition. Penicillin is an antibiotic made from penicillin, which is used to treat bacterial etiology in humans.

In medicine, they are used for the preparation of laxatives, anti-tuberculosis, anti-typhoid drugs. In folk practice, hoods and decoctions are often prepared. Tinctures and extracts of red fly agaric are often used to treat rheumatism and inflammatory processes on the skin.
On the other hand, when certain types of fungi are detected in a smear taken from human mucous membranes, it speaks of the development of serious diseases that require immediate treatment.
In nutrition
Mushrooms are also widely used in cooking. Fruit bodies of the cap species are eaten in a pickled, fried or boiled form. Experts recommend carefully selecting specimens, choosing only those that they are sure of.
Answers to Common Questions
The most common are questions about mold poisoning, the propagation of fungi with mycelium:
In a new place near a tree, they dig a hole about 40 cm deep. Dust and leaves are poured there, covered with a layer of earth from above and watered abundantly. After that, you can plant mushrooms there. Transplanted mushrooms are watered every day for several weeks.
Mycelium is an important component of each fungus, which consists of filamentous hyphae. The vegetative body performs many functions and can vary in size and appearance depending on the genus and environmental conditions.















 Care and use of Kombucha at home (+22 photo)
Care and use of Kombucha at home (+22 photo) Edibility of the fungus of the motley umbrella and its description (+19 photo)
Edibility of the fungus of the motley umbrella and its description (+19 photo) Description of edible and inedible oils, their poisonous counterparts (+40 photos)
Description of edible and inedible oils, their poisonous counterparts (+40 photos) Useful properties of milk mushroom and its contraindications (+17 photos)
Useful properties of milk mushroom and its contraindications (+17 photos)