Pepper is the joint name for the genus of plants in the nightshade family. In nature, this culture can be found in the form of vines, shrubs and grassy. The vegetable, brought for the first time from Central America, very quickly occupied its niche in gardening. Today it is difficult to imagine a garden plot without a row of neat bushes with colorful conical fruits at the ready.
Botany knows more than 2000 varieties of this plant. Regardless of the type of pepper, the color and size of its fruits, growing this vegetable requires a serious approach. One of the most significant moments of this process is the preparation of sweet pepper seeds for sowing. Compliance with the preparation procedure guarantees a high percentage of germination of planting material and a large yield of bushes.
Content
Why seed preparation for planting, basic rules and deadlines
Pepper can not be called unpretentious plant. Even experienced gardeners face a number of difficulties in growing this vegetable. Pepper reacts very sharply to changes in environmental conditions, so many gardeners prefer to grow it in greenhouses.
The ripening time of the fruit of the plant is not small: from 150 to 200 days. Throughout this time, pepper should provide suitable conditions for growth and development. Therefore, in the open ground, the vegetable is grown from seedlings, which can be purchased on the market or grown independently from seeds.
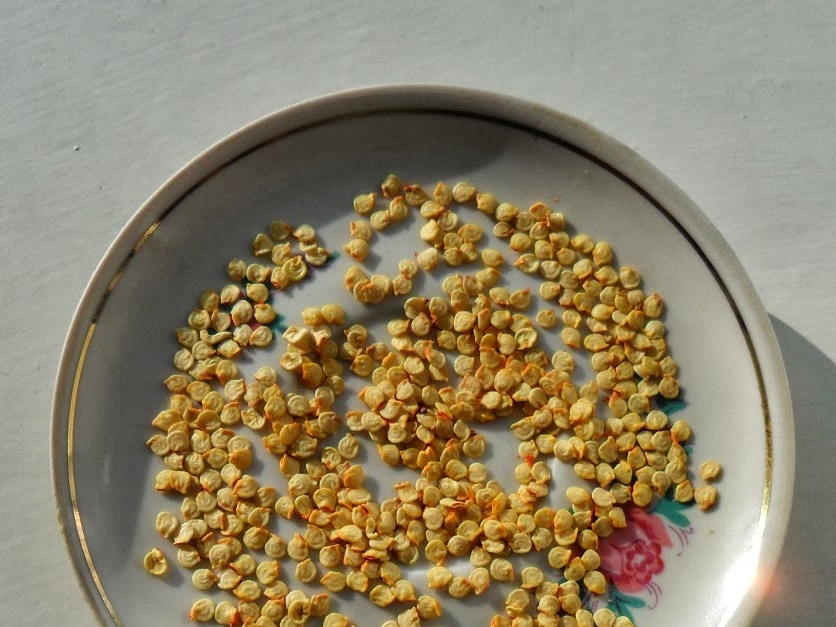

Thanks to it, seeds give great germination, and pepper bushes grown from them are highly resistant to infectious diseases and weather conditions.
 You may be interested in:
You may be interested in:Proper preparation involves a series of actions. First, the seeds are calibrated and tested for hollowness. Then, the seeds already selected are disinfected and saturated with nutrients necessary for normal growth. Before planting, they are soaked and tempered at low temperature.
Planting dates depend on the variety of pepper. Early hybrids are planted in late February. Late ripe peppers are planted in early March. The amount of future harvest depends on how well the planting time is determined.
The algorithm for preparing pepper seeds for sowing
Preparing seeds for sowing consists of several stages. Some are mandatory, others are carried out at the request of the gardener. One way or another, experts advise following all recommended procedures for good growth and high yield of pepper.
Seed selection
Selection of seed material of pepper is carried out in 2 stages:
- To size. To ensure synchronous germination, seeds are sorted by size. It is known that small seeds hatch much longer than large ones. Therefore, before planting, the seeds are poured onto a paper sheet and sorted by size.

Experts recommend sowing seeds of medium size. - By fullness. Hollow seeds are unsuitable for planting due to lack of germination. Therefore, before sowing seeds should be checked for dummies.To do this, they are poured with a glass of salted water and left for 30 minutes. After the specified time, all the seeds floating on the surface are removed, and the drowned seeds are washed, dried and prepared for planting.
Seed selection saves planting space. Thanks to this procedure, peppers sprout evenly, almost all seeds are pecked.
Disinfection
Disinfected material before planting is much better protected against viral and fungal infections. For disinfection, the seeds are placed in a weak solution of potassium permanganate and incubated for 15 minutes.
Alternative disinfectants exist. Very good recommendations have drugs "Maxim", "Fitosporin-M", "Vitaros." Drugs are bred according to the section on the prevention of fungal infections in the instructions attached to them.
Many agronomists add growth stimulants to a disinfectant solution. This trick significantly increases the percentage of germination and the growth rate of seedlings. Among gardeners, the Epin stimulator is very popular.
Food
Many gardeners consider this step optional. But those who follow the procedure for feeding seeds before planting are satisfied.
There are two ways to feed planting material with microelements:
- Place the seeds in special mineral mixtures available at the store.
- Provide folk remedies.
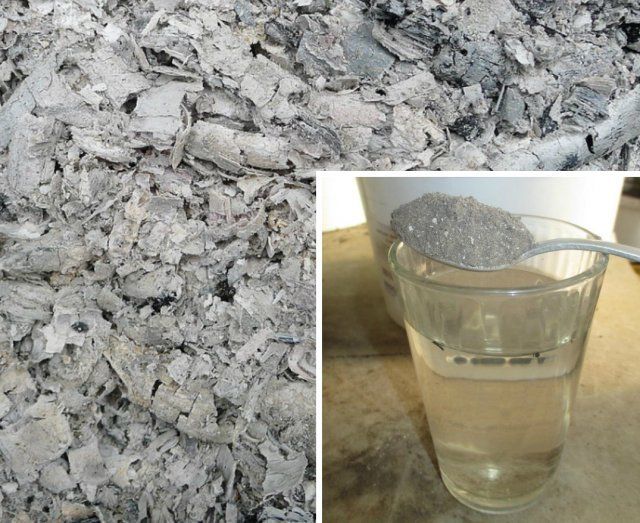

It contains about 30 useful trace elements and is considered one of the best fertilizers for this plant.
20 g of ash are diluted in 1 liter of water. The resulting mixture is insisted during the day. Seeds are wrapped in a gauze cut and immersed in an ash solution for 5 hours. After extraction, they are dried on a piece of paper.
Soak
Soak pepper before sowing. To do this, the seeds are wrapped in a damp cloth and left to swell. Punching speed depends on the variety. Early hybrids can germinate in a week, and later varieties may need up to 15 days to hatch.
You can sow both swollen seeds and seeds that have produced sprouts. Strongly germinating the seed is not recommended, since fragile sprouts can be easily injured during planting.
Hardening
To hardening gardeners are contradictory. Some consider this procedure mandatory, while others say that hardening can spoil the seeds. Therefore, to temper their planting material or not, everyone decides on their own.
The hardening procedure involves creating a stressful situation for the pepper by drastically moving it from a comfortable room temperature to cold.
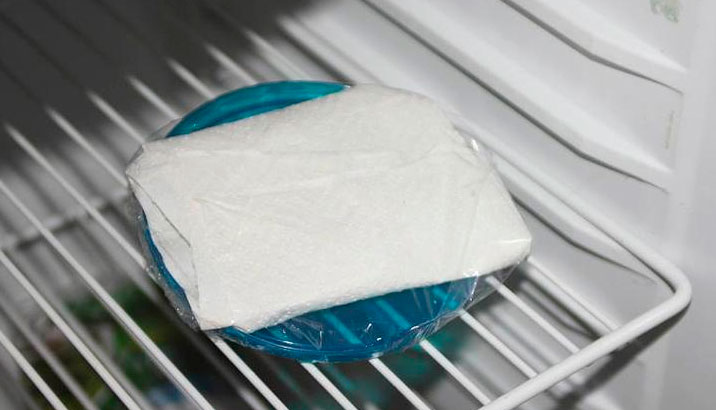

Fans of hardening notice that seeds that survived a sharp jump in temperature better tolerate planting. Such pepper will be more resistant to adverse environmental conditions.
Soil preparation for planting seeds for seedlings
Good soil for pepper seedlings meets the following requirements:
- Friability. The soil should have a light porous structure in order to provide the root system with good gas exchange and prevent moisture stagnation.
- Fertility. The combination of minerals such as nitrogen, potassium, copper, iron, zinc and phosphorus with organic compounds is one of the mandatory soil requirements.
- Acidity.The acidity level from 5 to 7 protects the plant from damage by the "black leg".
Preparing the soil for planting involves disinfection. There are several ways to disinfect the soil:
- Treatment with fungicides and insecticides. This method is guaranteed to protect against all pests and infectious diseases. Many gardeners avoid it because of its high toxicity and are advised to treat the soil with a solution of ordinary potassium permanganate.
- Heat treatment. The soil can be heated in the oven or steamed in a water bath. The disadvantage of this method is the death of beneficial bacteria.
- Freezing. Experienced agronomists leave pre-prepared soil mixtures in the cold.
Soil mix for seedlings can be bought in a store or prepared independently. To do this, sand, peat, humus and leafy soil are mixed in equal parts.
Rules for sowing pepper seeds and growing seedlings
Growing pepper seedlings - This is a rather lengthy and time-consuming process. An inexperienced gardener needs to follow existing recommendations so that the seedlings grow large and strong.
Seeds are planted to a depth of 2-3 cm. Wet seeds are placed in previously moistened soil, and dry seeds are placed in dried soil, followed by moistening from a spray bottle. The container with seeds is tightly covered with polyethylene, glass or a transparent plastic cover. Germination is carried out in high temperature conditions. When the sprouts grow a little, the film is removed.

Seedling care provides for compliance with 3 modes:
- lighting;
- glaze;
- feed.
Pepper is considered a photophilous plant. He needs to provide daylight hours of at least 12 hours. Light should be diffused, as direct sunlight can harm young plants, especially if the containers are located on the south side. If the bushes begin to stretch the stems, this indicates insufficient lighting. In this case, the gardener should install additional illumination for seedlings.
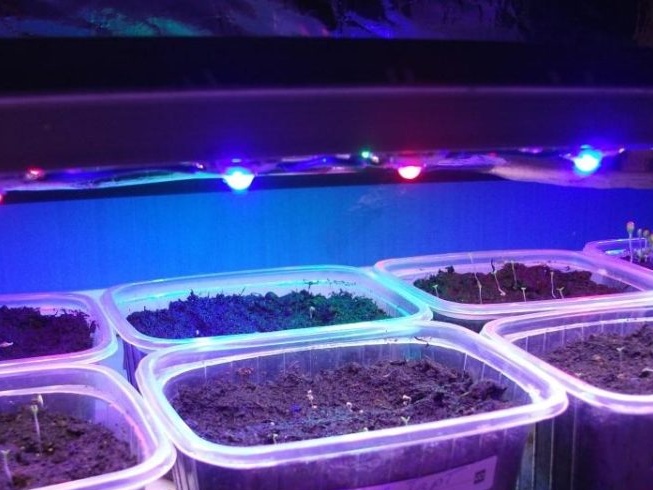

Watering seedlings is necessary on demand: the soil is moistened as its top layer dries. In addition to watering, peppers should also be sprayed 2-3 times a day from the spray gun. Such a measure will allow the plants to maintain an increased level of humidity.
Feeding is permissible to enter from the 2nd week after diving seedlings. The need for fertilizer application depends on the quality of the soil: if the soil is selected correctly, the gardener can do without feeding. Peppers growing in poor soil require fertilizer with nitrogen mixtures.
How to avoid mistakes when growing pepper
The reasons for slow growth, poor development, and death of seedlings are often associated with improper actions. The most common are the following errors:
- Missing or improperly prepared seeds for planting.
- Use of unsuitable soil mixture for pepper or planting seedlings on depleted areas.
- Too early planting - it contributes to the overgrowth of seedlings, such bushes adapt worse after transplantation.
- Late planting - accompanied by stunted plant growth.
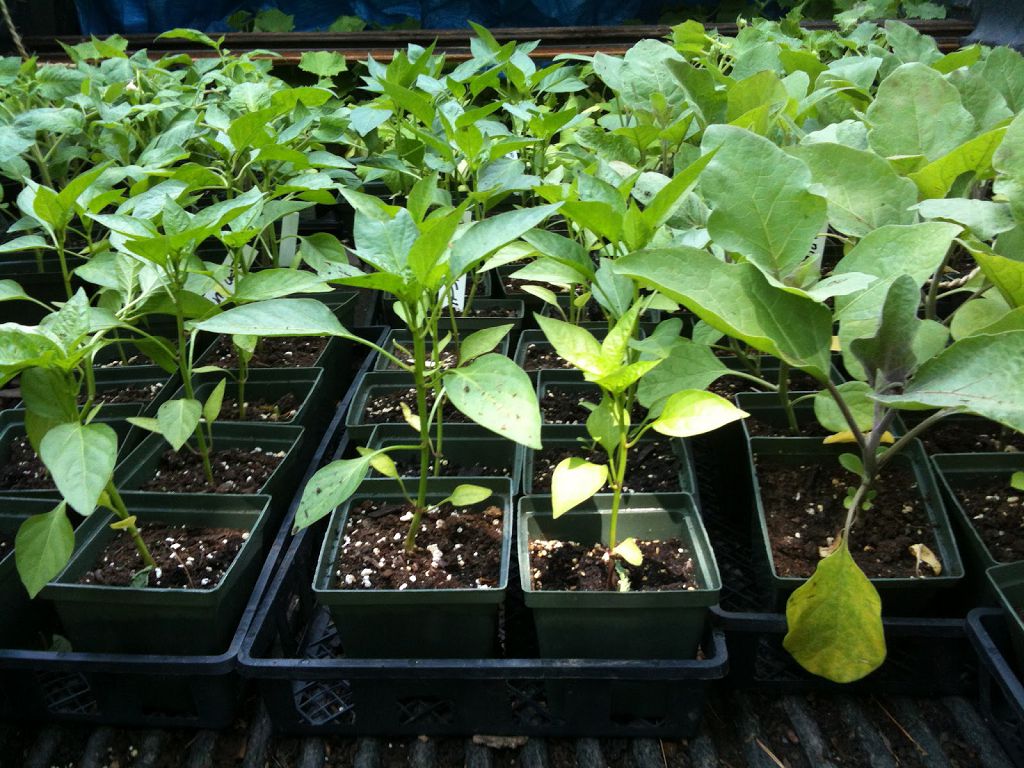

Pepper seedlings - Lack of light - provokes stretching of stems and weakening of bushes.
- Non-compliance with the temperature regime - leads to a slowdown or stopping the growth of pepper.
- Mechanical damage to the root system during picking negatively affects the growth rate and development of seedlings.
- Improperly organized watering and feeding - significantly affect the quantity and quality of the crop.
The most dangerous mistake gardeners make is neglect of pests and diseases. Innocent, at first glance, insects can cause enormous damage to the plant, and one bush infected with a fungal infection can infect the entire pepper bed and other closely growing crops.
 You may be interested in:
You may be interested in:Common questions
Growing pepper is a rather complicated process. One of its key points is the preparation of planting material. Do not neglect it, since the crop largely depends on it.



 Calorie pepper stuffed with meat and rice - BZHU per 100 grams
Calorie pepper stuffed with meat and rice - BZHU per 100 grams Gorky pepper - the best varieties for open ground
Gorky pepper - the best varieties for open ground Hot pepper seeds - the best varieties for open ground and reviews
Hot pepper seeds - the best varieties for open ground and reviews Capsicum tincture for hair - how to use and reviews
Capsicum tincture for hair - how to use and reviews