 Even if grapes are planted in spring with seedlings, preparation for it should begin in the fall. Will you need to prepare a pit, soil, planting material and just decide whether to plant seedlings or cuttings? If you use purchased material for planting, you should give preference to the latter, since the seedlings tolerate transportation worse. In the case of self-propagation of bushes, one must take into account that the care of cuttings is more difficult, and the survival rate is higher for seedlings. In both cases, you can plant in such a way as to lay a good foundation for the future grape harvest.
Even if grapes are planted in spring with seedlings, preparation for it should begin in the fall. Will you need to prepare a pit, soil, planting material and just decide whether to plant seedlings or cuttings? If you use purchased material for planting, you should give preference to the latter, since the seedlings tolerate transportation worse. In the case of self-propagation of bushes, one must take into account that the care of cuttings is more difficult, and the survival rate is higher for seedlings. In both cases, you can plant in such a way as to lay a good foundation for the future grape harvest.
Content
Pros and cons of spring planting

Autumn and spring are considered equally favorable times for grape planting. In favor of spring planting, the opportunity to qualitatively prepare the plants for wintering speaks: during the summer, the young bush manages to acclimatize and take root firmly in a new place, which will make it more resistant to frost. Also, spring grapes begin to bear fruit a year earlier than autumn seedlings.
The disadvantages of planting in the spring include a high probability of being affected by pests and diseases, which is especially dangerous for immature plants, as well as the need for watering - in autumn, seedlings get moisture from rainfall. When buying planting material in the spring, there is a risk of acquiring frozen and weakened plants.
Preparing planting material
If you want to expand the plantation of grapes of an existing variety, you can prepare seedlings or cuttings yourself.
Seedling preparation

To obtain planting material, you need to choose a uterine plant - a healthy and strong grape bush. In autumn, a furrow should be dug near it and one of the young vines should be laid in it. Layers need to be fixed, for example, with hooks, and sprinkled with turfy earth or rotted manure. Watering the shoot is necessary to frost.
By spring, a vine laid in the ground will develop the root system, giving several seedlings. Before digging, you need to trim the vine as close to the roots as possible.
Preparing for landing:
- Remove roots above 2 lower nodes, as well as all rotten, dry and damaged.
- Shorten the remaining roots to 12 cm.
- Trim the seedling, leaving 4-5 eyes.
- Treat the plant with a solution of hexachloran (2%). Clay is recommended to be added to the solution - 2 parts per 1 part hexachloran.
- Immediately before being placed in the ground, the roots of the seedling must be kept for 30 minutes in water with a growth stimulant. Plants will experience less stress in the new environment if they soak the roots in a mixture of a bucket of water in 2 buckets of soil and a bucket of manure or compost.
Preparation of cuttings

After picking berries, you should choose a healthy and strong one-year-old vine on the mother plant and cut it off. Immediately after this, you need to remove the lower leaves and cut the shoot, leaving a stalk about 45 cm long with 3-4 buds. The upper cut should be flat and extend 2 cm from the crown of the kidney. The lower section should be made oblique, departing 1 cm from the first kidney. Cropped sprouts need to be put in water at room temperature for 2 days.
After soaking:
- treat the stalk with copper sulfate (1%);
- to dry;
- dip the crown at a level of 6 cm in molten paraffin (in 100 g of water put 100 g of paraffin, 5 g of wax and the same amount of resin, then warm the mixture, continuously mixing);
- Immerse immediately in cold water;
- wrap in cling film.
Treated cuttings must be stored in a dark room with a temperature of 0 to + 2 ° C until spring (cellar, basement or refrigerator).
At the end of winter or the beginning of spring, plants should be soaked in warm water for 2-3 days, after - for a day in water with the addition of growth stimulants. Cuttings need to be planted in seedlings, deepened so that 5 cm below the upper kidney remains above the soil surface. Sprouts should be in a room with good lighting and a temperature of + 20 ... + 25 ° C. Do not water the soil from above, water needs to be added to pallets.
When 2-3 leaves appear on the handle, it is ready for transplantation, but first it should be hardened. To do this, “seedlings” need to be taken out into the fresh air during the day and kept in the shade for the first 6-7 days, and the next 10 days under the sun. If the room had poor lighting or the temperature was above + 25 ° C, the hardening period should be extended to 10-11 days in the shade and 15 in the sun.
Selection of seedlings
When buying seedlings, you need to make sure that the plants are healthy, without damage, with dense buds, have at least 3 roots up to 12 cm long. The buds should not crumble from touch. The cut for lignified seedlings should be white, for cuttings to have a bright green color. A brown shade of the cut is unacceptable.
Grade selection

By acquiring new grapes, you should pay attention to varietal features:
- Destination Grapes can be technical, intended for the production of wine, or table. The latter are sweeter.
- Ripening dates. For planting in the northern regions, it is not recommended to choose late varieties, since the crop does not have time to ripen before a cold snap. For the southern or middle strip, this option is worth considering - late berries, as a rule, are the sweetest and largest.
- Zoning. It is dangerous to experiment with varieties intended for more southern regions - either the berries will not have time to ripen, or the vine will be damaged by frost. Often it is not possible to detect a problem before the bush begins to bear fruit.
- Height. Vigorous grapes require considerable area, in a small area it is worthwhile to prefer medium-sized bushes.
- Sustainability. If a fungus or pest has appeared on the site, you can find grapes that are not subject to them. But there are varieties that are characterized by increased vulnerability to bacteria and fungi.
Site preparation

In many ways, the size of the crop is determined by the choice of plot and planting planning. Plants need to be arranged so that they, upon reaching maturity, continue to receive enough light, nutrition and moisture.
Seat selection
The best option for grapes would be a well-lit area near the western or southern wall of the house or outbuildings. In this place, the vine will be protected from the north wind, in addition, heating up during the day, the barrier will give part of the heat at night.
Another good option for landing is the south or southeast slope of the hill. Lowlands should be avoided, where it is always colder and moisture accumulates. Any areas prone to stagnant water are not suitable for culture. The soil should combine fertility and good drainage properties. Ground water at the landing site should not rise closer than 1.5 m to the surface.
The main condition for a good harvest is the illumination of the site throughout the day. In the shade, the strength of the plant will go to the growth of vines; there will be no nutrients left to ripen berries.Lack of lighting also reduces the proportion of sugars accumulated in berries.
Distance
When planting several plants, it is necessary to maintain a distance of 1.3-1.5 m between tall and medium-sized bushes, and 1.8-2 m between tall ones. 2-2.5 meters should be left on the aisles.
The distance to the wall or fence should be at least 0.5 meters. It is not recommended to plant closer than 3-6 m from tall trees - their powerful roots greatly deplete and dehydrate the soil.
Landing depth
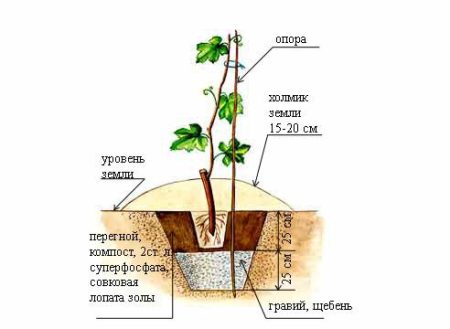
If the sapling is not deep enough in the hole, its roots will be in the upper layers of the soil, which quickly leaves moisture, so you will have to water the grapes more often. But planting too deep is harmful, because the deep layers of the soil do not warm well, so the seedling will grow slowly. For annual plants, the optimum depth of the pit is 40 cm, for vegetative cuttings - 50 cm.
Landing pit preparation
It is recommended to dig a hole in the fall: by spring, the soil will absorb the fertilizers and shrink. For planting, make a pit that has 80 cm in diameter and the same depth. The excavated soil should be folded in 2 heaps: in one - the upper layer, where the most fertile soil is located, in the second - the lower layer.
Pit filling scheme:
- At the bottom put a layer of drainage of 10 cm (broken brick or crushed stone).
- From above, 25 cm of fertile soil (from the first pile) are filled up and tamped. It is recommended to mix the soil with rotted manure or compost in a ratio of 1: 1.
- On top lay a 10 cm layer of fertilizer. To do this, mix 5 kg of ash and fertile soil, add 0.5 kg of potassium sulfate and superphosphate.
- The fertilizer layer is covered with a layer of earth of 5 cm.
- The embankment is watered abundantly so that the soil sags.
- After this, the pit is filled up to the top with earth and left until spring. Shortly before planting, part of the soil is removed, forming a hole of the required depth.
Landing procedure

Planting of lignified seedlings should be carried out when the average daily air temperature reaches + 15 ° C, and the soil warms up to + 10 ° C. In the middle lane, suitable conditions will be established from mid-April to mid-May, in the northern regions - from late May to early June. In the south, landing is possible at the end of March. Cuttings need to be planted later, in a temperate climate - in the last decade of May or during June.
Step-by-step instruction
The procedure begins with abundant watering of the hole. When water is absorbed, a seedling can be placed.
Landing scheme:
- In the center of the hole, you need to make a small depression in which the seedling is placed, evenly distributing the roots around the stem. If the seedling is longer than 25 cm, it must be installed under a slight slope.
- The hole should be covered with soil up to half, without tamping the soil.
- Pour 2-3 buckets of water into the pit.
- After the water is absorbed, fill the pit with soil.
- From above it is necessary to fill a mound with a height of 15-20 cm. After 2 weeks, when the plant adapts, it will be necessary to remove it.
The first fruits when planting seedlings should be expected in a year, and a full crop - after 2-3 years.
Planting cuttings
The development of vegetative sprouts to adulthood will require more time, fruiting will begin only after 3-4 years.
Landing Plan:
- After watering, the stalk should be placed in the center of the pit. Nearby, you can install a support (peg) for future garter plants.
- The hole should be filled in the same way as when planting a seedling, but you can water the green cuttings only with warm water.
- A knoll is not needed, but if the handle has not been hardened, the first 10 days are required to shade it.
Follow-up care

Young plants are vulnerable and require careful care. Improper agricultural technology is the main reason for the death of seedlings in the first year after planting.
Watering, loosening, top dressing
The first watering should be carried out 10-12 days after planting, using well-maintained warm water. After 14 days, repeat the irrigation. Subsequently, you need to give 10 liters of water to the bush every 7 days.
After each watering, you need to carry out cultivation, combining them with the removal of weeds. The frequency of weeding can be reduced by mulching. For summer time, straw or hay, laid in a thin layer, is suitable.
Fertilizers introduced during planting are enough to power the seedling for 3-4 years, after which you need to give top dressing. At the beginning of the growing season, grapes need nitrogen, in the phases of ovary formation, fruit growth and preparation for winter, phosphorus plays the leading role.
Pest and Disease Treatment

Every year immediately after harvesting the winter shelter, it is necessary to prophylactically treat grapes from pests and diseases. If necessary, the vine can be sprayed before budding, but after flowering begins, the chemical effect on the plant must be excluded.
For preventive purposes, a wide range of products are recommended that can protect against insects, but primarily from fungi to which grapes are vulnerable:
- vitriol (3%);
- Bordeaux liquid (3%);
- Ridomil Gold (1%);
- Tsineb (0.5%).
Pruning

The first time pruning young plants is done at the age of 3 years. In the autumn, after harvesting, sanitary pruning is performed, which involves the removal of sick, damaged, old branches, fruitful shoots of this year and most of the growth. In spring, formative pruning is carried out that determines the structure of the bush.
In the first year, only the upper roots should be removed from the seedlings. To do this, remove a 20 cm soil layer from the trunk circle and cut off the upper roots near the stem. After that, fill up with soil. The procedure is done twice - at the beginning and at the end of summer.
Garter
After the spring forming pruning, you need to tie up the overgrown shoots, attaching them to the stakes installed in the hole, or to the trellis. For tying, you need to choose soft materials, preferably from natural fibers. Twine, nylon stockings, fishing line and other hard materials can injure the vines.
Wintering
Depending on the region of cultivation and frost resistance grape varieties winter warming may be required. To do this, the vines need to be laid on the ground or in the furrows, secured with hooks. Poison bait for rats should be put near the shoots, otherwise pests will gnaw the shoots. At the base of the bush, a mound of dry earth should be poured to protect the roots. Top grapes are covered with mulch (spruce branches) or covering materials (tarpaulin, agrofibre).
Reviews
Elena, 48 years old:
“I prefer spring planting, since autumn cooling in our region (Kaluga region) is more difficult to predict. I'm afraid to freeze seedlings. In the spring, planting always goes well, by the fall the vine has time to stretch 2 meters in length, the plants winter well ”.
Anna, 36 years old:
“I try not to use purchased drugs, to get by with natural means. So, I never stand grape cuttings in stimulants, but I do it on the advice of my grandmother - I dissolve a spoonful of honey in a liter of water and soak the roots in it. Growing great. Another life hack, the seedling should be placed so that the roots are directed to the south, and the buds are directed to the north. "
Michael, 40 years old:
“It is difficult to determine the time for planting cuttings. Several times they beat me with frost, began to put 2 cuttings in each hole, at least one will be accepted. If both take root, I leave the one that is stronger. "
Planting grapes is not the easiest procedure, but pays off with a long-term harvest of berries. It is important to carry it out qualitatively, so that in the future it is not required to carry the bushes. Spring planting gives a good start to grape seedlings - plants immediately fall into favorable conditions for growth and develop rapidly.



 Non-covering winter-hardy grape varieties for Moscow region
Non-covering winter-hardy grape varieties for Moscow region How to keep the vine in winter
How to keep the vine in winter When can I transfer grapes to another place in the fall
When can I transfer grapes to another place in the fall How to cover and prepare grapes for the winter in the suburbs
How to cover and prepare grapes for the winter in the suburbs