A few decades ago, bell pepper was grown only in certain regions of the Soviet Union. The mild climate of Moldova, the southern part of Ukraine, allowed to collect a large crop of vegetable crops. Today, the selection has an extensive assortment of varieties and hybrids adapted to the conditions of central Russia, Siberia and the Urals. However heat-loving vegetable plants grow better in a greenhouseto bring the ripening conditions closer to the family.
For greenhouses, tall varieties are most suitable, giving larger fruits and high yields, compared with low-growing pepper species. They have a greater number of ovaries, early ripening, resistance to many diseases of nightshade crops. However, they need adequate lighting, airing, pinching and other agricultural practices.
Content
The most fruitful varieties of tall peppers for greenhouses
Indeterminate varieties are characterized by powerful stems with great leafiness, grow more than two meters in height. One of the main conditions for germination is the proper selection of seeds. The most productive varieties are listed below in alphabetical order.
Accord F1
The hybrid is not particularly tall, but this is offset by early fruiting, high productivity and large-fruited. Technical ripeness occurs 115 days after sowing, with full peppers acquire red hues. The weight of the vegetable reaches 200 g.
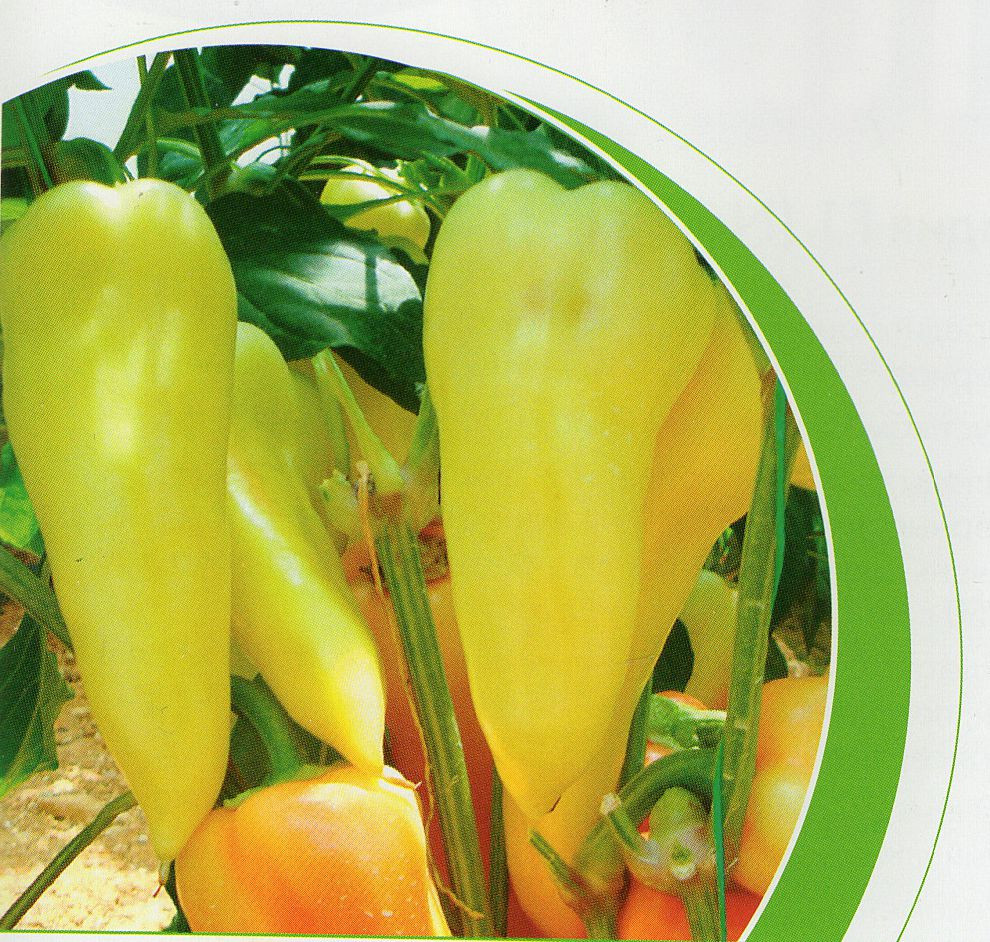

Atlant
Early variety, bush height - more than a meter. Development occurs about three months from the date of germination. The fruit has a red tint of the correct conical shape, the average weight of the vegetable is 150 grams, from the bush you can get up to 6 kg of the crop.
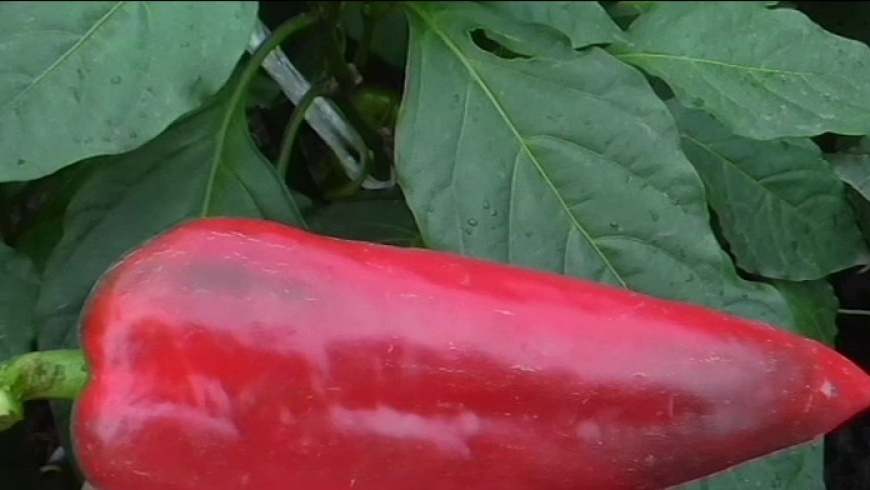

Barguzin
An early ripe variety, technical ripeness occurs after 100 days, biological ripeness occurs after 125 days. The fruit is cone-shaped, weighing up to 200 g, green and yellow in color, yield from the bush is up to 17 kg.
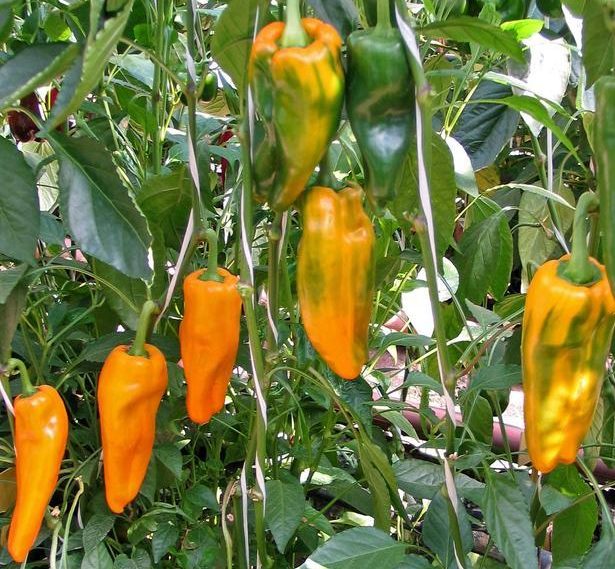

Big Mama
Bell peppers Big mom gardeners consider early ripe or mid-ripening. Technical maturation lasts 120 days. The weight of the fetus reaches 200 g with biological ripeness, which occurs three weeks later.
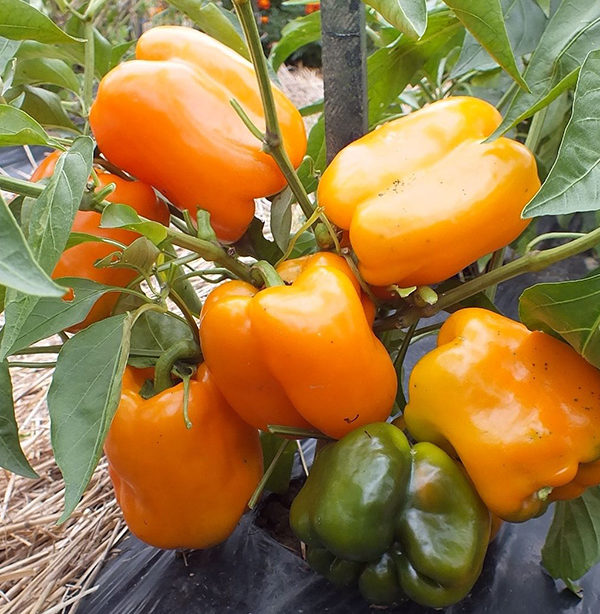

Hercules
It is considered the lowest among all tall varieties. A cube-shaped vegetable with a dense sweetish skin, average weight is about 200 g. The variety has a low yield, but is resistant to long-term storage and transportation.
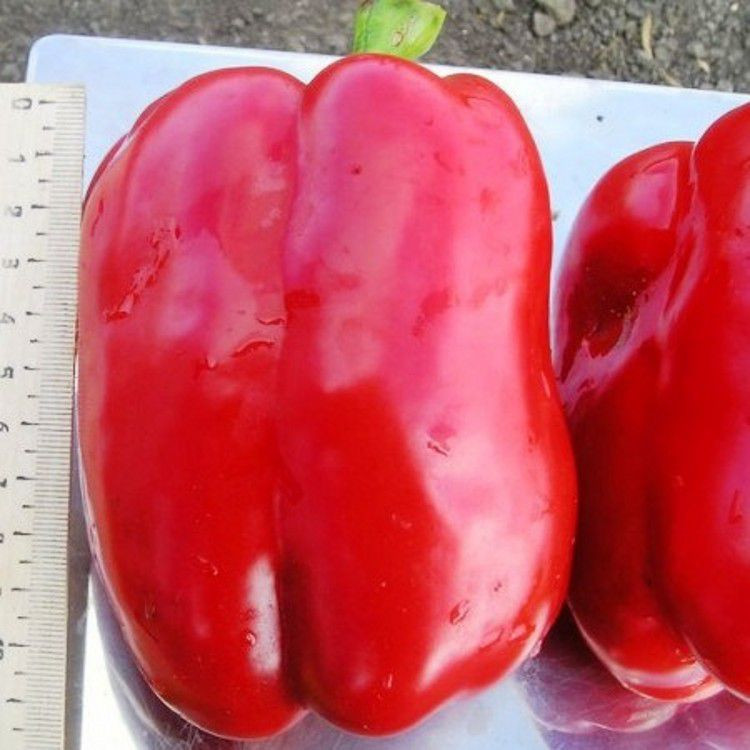

Health
It is the earliest variety for growing in covered ground. The bush reaches a height of two meters, which allows you to collect up to 5 kg of prismatic fruits weighing 50-65 g. After three months, full maturity sets in, as evidenced by the red color of the pepper.
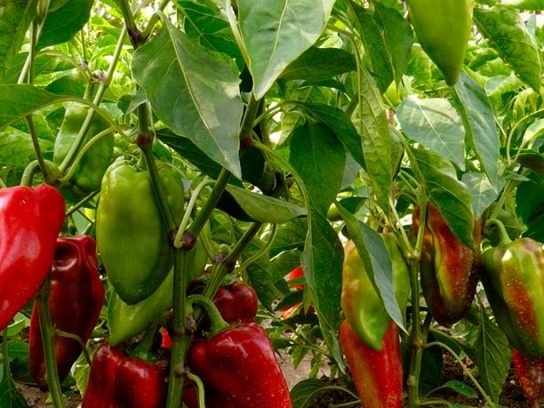

Indalo F1
Mid-season, thick-walled indeterminate hybrid with bright yellow fruits of 250-300 grams. Copies of a large cuboid shape, output - from 7 to 14 kg per m2, depending on growing conditions.
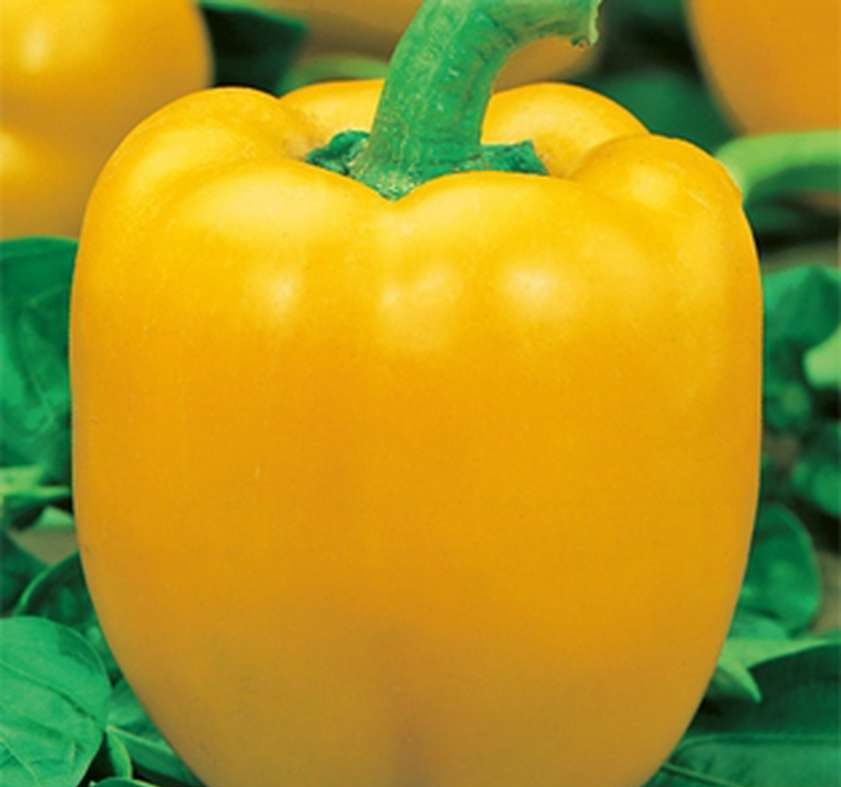

Cockatoo F1
A hybrid vegetable was so named because of the similarity of the fetus with the beak of the bird of the same name. Each conical, slightly curved specimen reaches a weight of up to half a kilogram and a length of almost 30 cm.Technical ripeness is characterized by green color, which soon changes to red, and the fetus takes on a cylindrical shape.
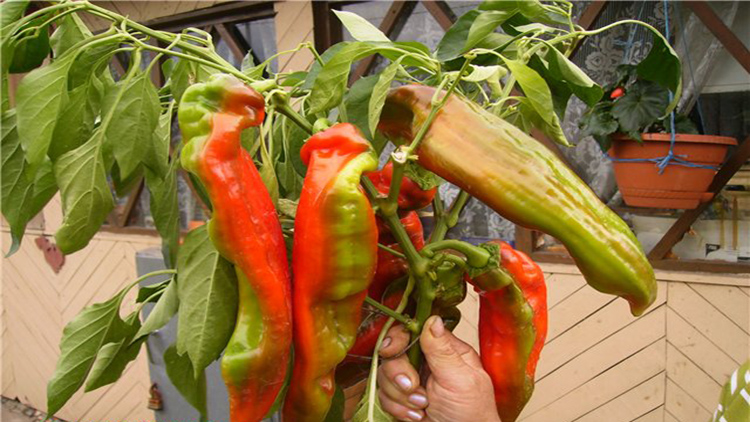

California Miracle
Mid-early variety, fruits appear 100-110 days after sowing seeds. When fully ripened, the fruit weighs about 200 g, the yield from one bush is 6 kg. Needs constant feeding with nitrogen and inorganic fertilizers.
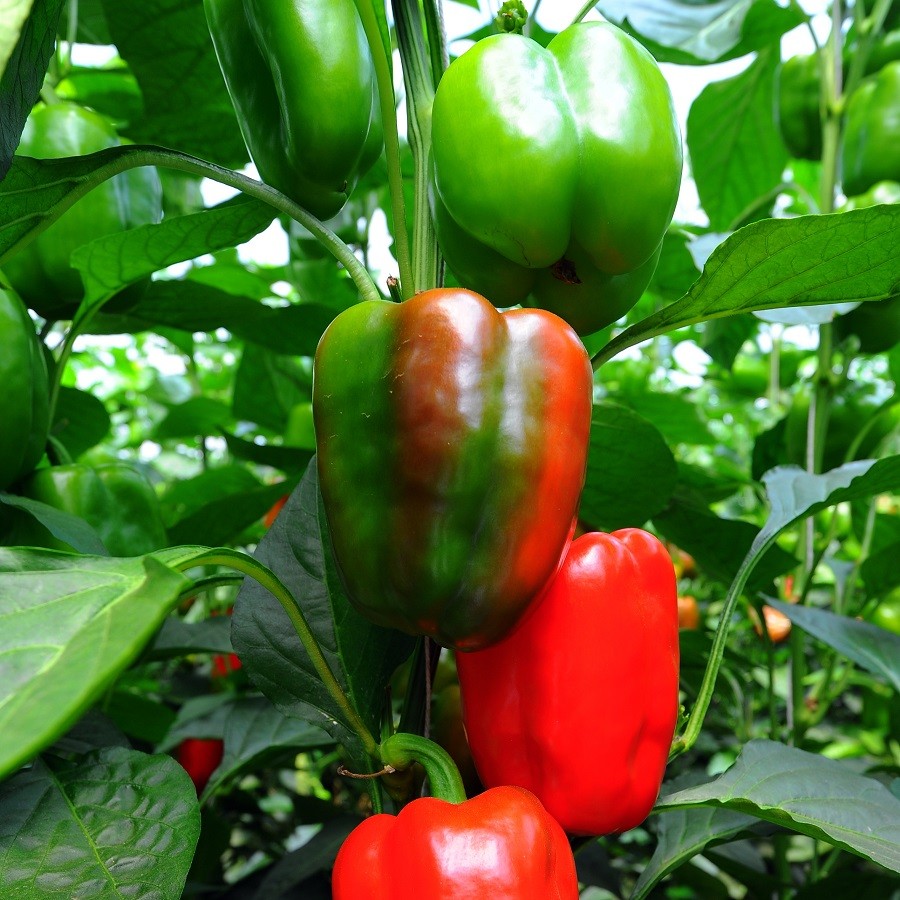

Claudio F1
Hybrid conical shape, bright red. Belongs to mid-season grades. The height of the bush is 130 cm, the weight of one pepper is more than 250 g. One of the most productive species: up to 10 kg of fruits are collected from the bush.

Cornet
Early ripe appearance. Peppers grow in the shape of a cone with a stable brown color and weighing more than 250 g. It has a high resistance to diseases, stable strong ovary of inflorescences and good productivity.
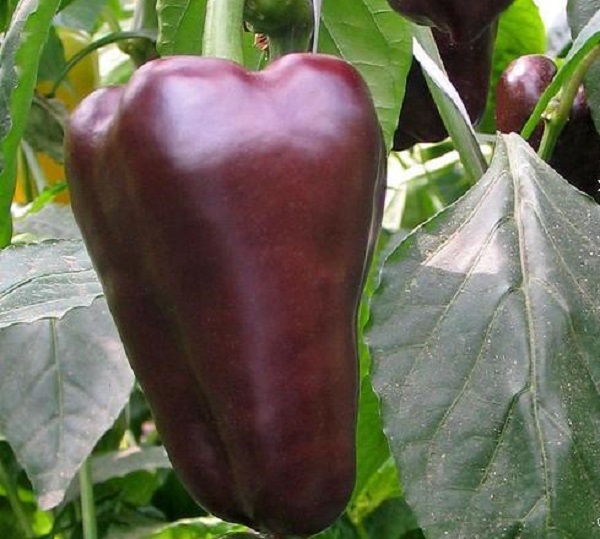

Merchant
Early ripe tall variety with fruits of a pyramidal shape. The pinkish-red pepper has a mass of about 150 g. The yield is 5 kg from a bush in a greenhouse and 4 kg in open ground. The growing season is short - 95-100 days.
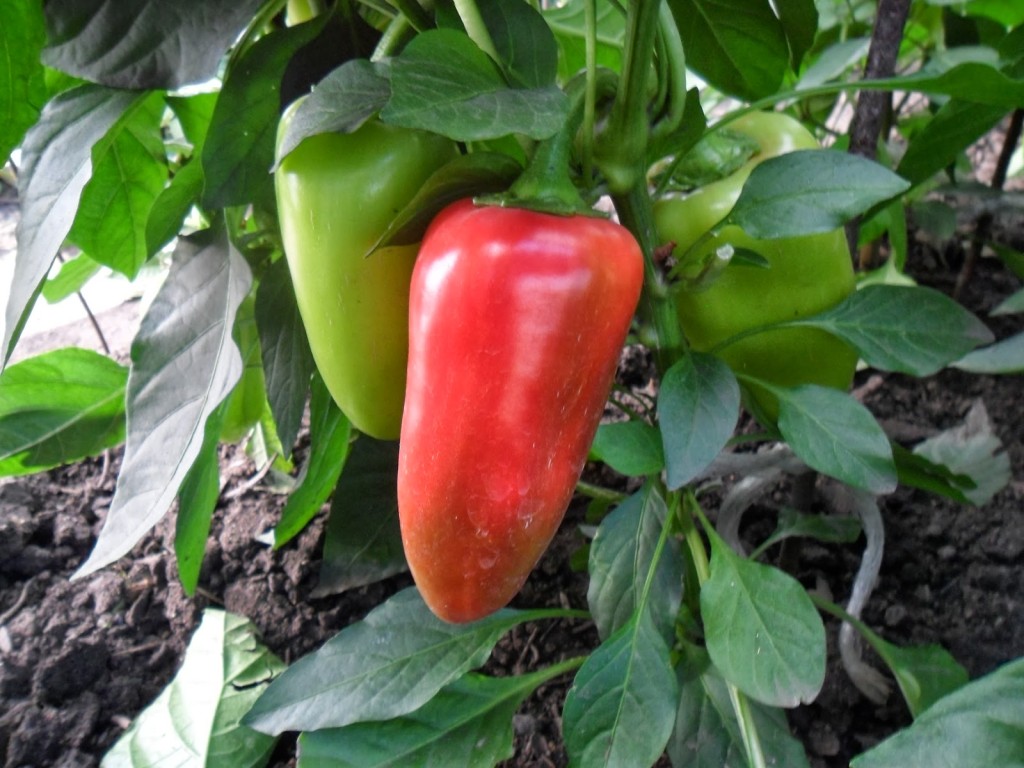

Latino F1
The fruits are small, cuboid in shape, their mass is 220 g, the wall thickness is 100 mm. The first red fruits are removed from the bush after three and a half months.
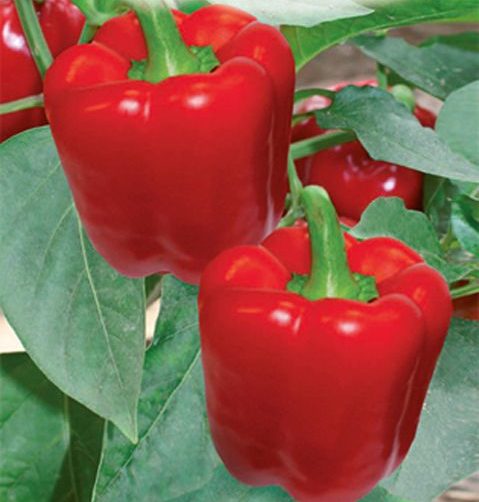

Orange miracle
An early ripe variety, which determines the technical harvest on the hundredth day, full maturation occurs after 125 days. The fruits of the cubic form of a sunny shade reach a weight of more than 250 g, and each bush carries 12 large vegetables.
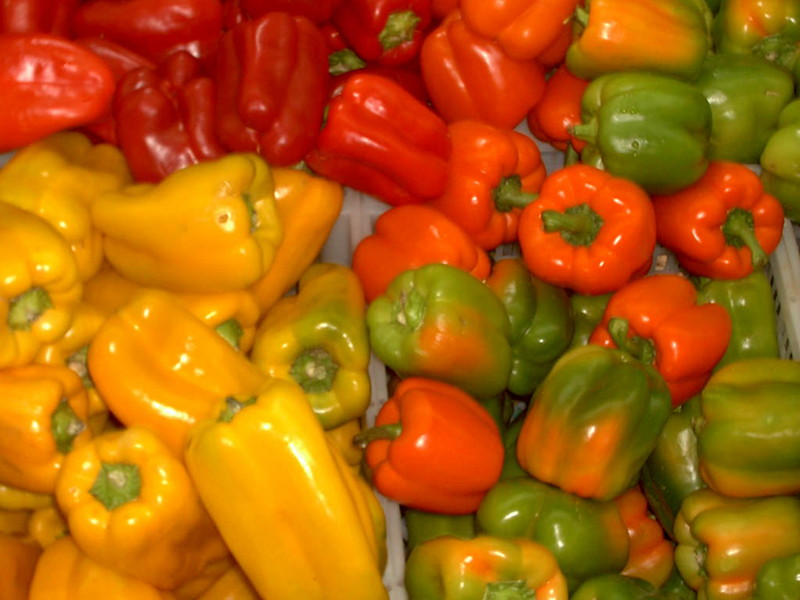 You may be interested in:
You may be interested in:
Miracle Tree F1
The hybrid with its structure is like a small tree, with 20 juicy peppers on a bush. Prismatic fruits with dense skin of bright red color do not exceed the average weight of 50-70 g.

How to grow tall peppers in a greenhouse
Tall varieties of pepper are grown in covered ground only by planting seedlings. It will be possible to obtain increased productivity on the soil where cabbage, carrots or onions were previously planted.
Preparation of seedlings and soil
To prepare the soil for the next season, the soil in the greenhouse needs to be dug up, freed from dry leaves and root crops, and humus added. Not earlier than a week before planting, the greenhouse must be ventilated, and the walls treated with a pesticide against fungal diseases. After that, re-dig the soil and season with phosphoric and potash fertilizers.
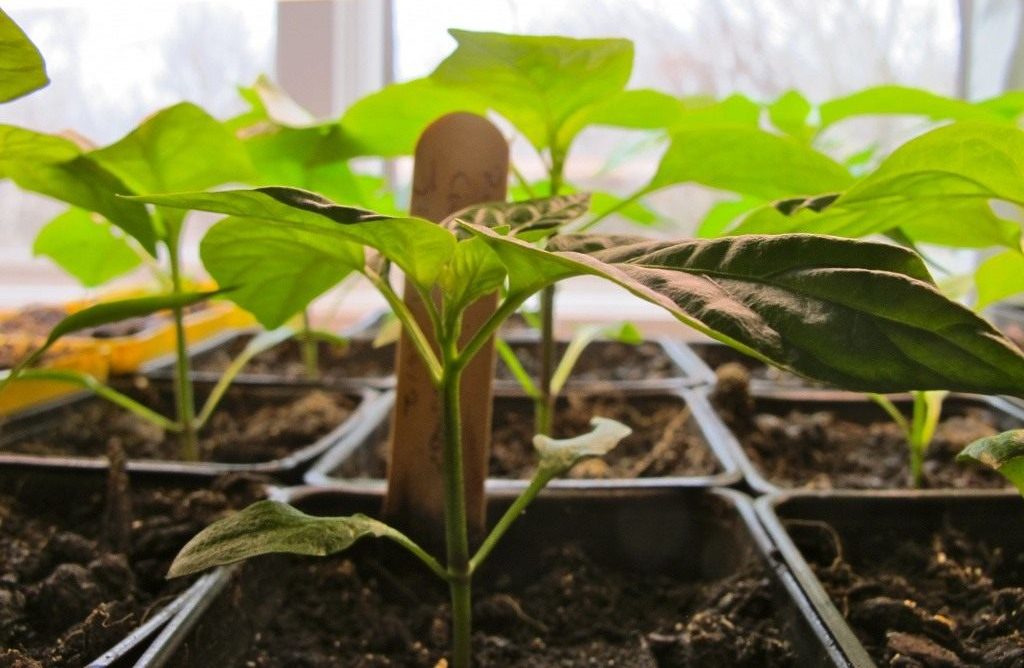

Seeds of pepper for seedlings are sown from the last days of February to April 15, which will allow you to collect fruits from July to late autumn. To grow seedlings for a good harvest, you need to use the same soil in which the adult culture will grow. The best mix would be old garden soil with humus. Seedlings are watered at least once a week.
Landing technology
Transplanted seedlings in the greenhouse after the formation of 6 or 7 pairs of leaves and the formation of a thick stem. The process is carried out according to the following algorithm:
- small holes are made in the garden, where a liter of warm water is poured;
- plants are reloaded into recesses, trunks are squeezed with earth;
- planting a little watered, the base of the stem is covered with dry peat.
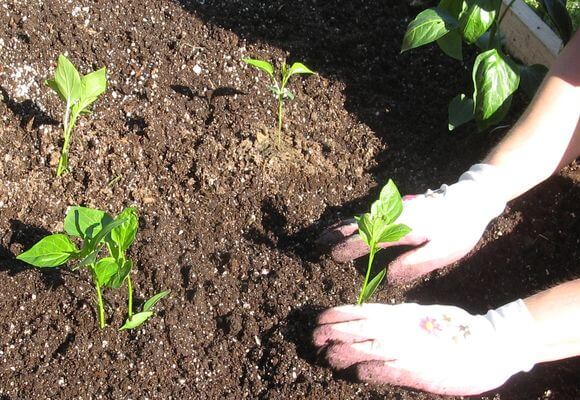

Planting is done in several alternative ways. The landing technology is as follows:
- Two-line tape suggests a distance between rows of 200-400 mm, tapes - up to half a meter, peppers - 200-300 mm.
- The square-nest provides for landing in one hole of two plants, according to the scheme of 0.6 × 0.6 m.
- Chess technology is produced according to the scheme 200 × 200 mm or 300 × 300. In this case, the rows are shifted by half the gap.
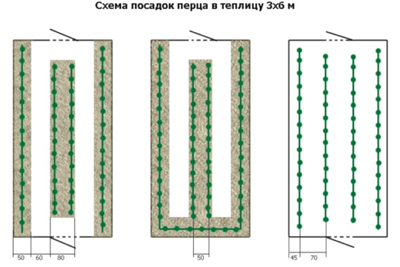
Scheme of planting pepper in a greenhouse
Temperature and lighting
Sprouted shoots from seeds are transplanted into the greenhouse from the second decade of March to the third of April. Soil temperature must be at least + 15 ° C. After germination, the mode is maintained at + 25 ° C - during the day and + 18 ° C - at night.
Top dressing, watering and loosening the soil
After transplanting into sheltered ground, the plant is fed twice before flowering with diluted 1:10 diluted chicken water in water or a nitrofoska solution (1 tbsp. / Bucket of water). When the ovary is formed, it is recommended to use phosphorus-potassium top dressing. Fertilizers should not contain elements of chlorine, it affects the pepper in a negative way.
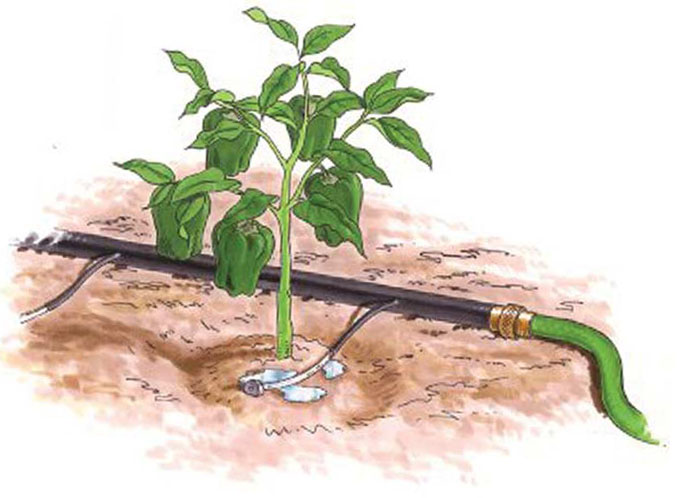
Before the appearance of buds, seedlings are watered no more than once every three days, after the formation of fruits - every other day. To do this, use half a bucket of water heated in the sun on each trunk. After the next watering, the soil is loosened to provide the roots with oxygen and maintain soil moisture.
Formation and support
After planting pepper in a greenhouse near each plant, a wooden support peg intended for garter of the bush is driven in. The formation of no more than 3 stems or plucking of the central flower will increase the productivity of the crown to increase the number of fruit ovaries. It is not recommended to leave more than 20 fruits on one bush.
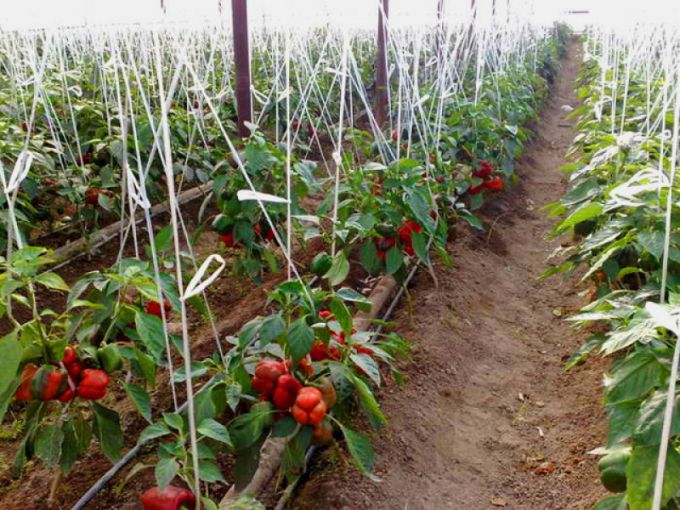

Why tall peppers do not grow peppers in a greenhouse
Growing peppers seems a thankless task, and for beginners it seems completely impossible. If you carefully study the recommendations, a novice gardener will also collect a good crop, you just have to prepare the soil and plant the plants correctly.
Mistakes in agricultural technology and care
Often, pepper does not grow in the greenhouse, because the vegetable was planted in unprepared or cold ground, the mandatory conditions were violated during the vegetation of the plant. The most common causes are:
- lack of nitrogen and phosphorus fertilizers in the soil;
- daytime temperature drops below 28 degrees Celsius, nighttime - 10 ° C, which entails the withering of peppers;
- plants are watered with cold water or the morning watering regimen is not maintained;
- the room is not aired;
- they didn’t stepchain at the right time, as a result of which the juices went into the side shoots;
- after watering, the earth near the trunk does not loosen, which makes it difficult to access oxygen.
Diseases and Pests
Compliance with the rules of agricultural technology prevents the appearance of diseases and pests in the greenhouse. The main ones are:
- Vertex rot. The disease disappears after adding ash under the plant.
- Verticillin wilt appears in the absence of soil disinfection.
- The column is carried by aphids or ticks. The plant should be removed and burned, and the earth cavity filled with a solution of manganese.
- Anthracnose is treated with systemic fungicides.
- With the appearance of alternariosis - black mold, the bush is treated with Bordeaux fluid.
 You may be interested in:
You may be interested in:To combat aphids, phosphorus-potassium fertilizers and ventilation after irrigation are used.
Common Growing Questions
Tall bushes of sweet pepper grown in sheltered soil have good yields. However, for their flowering, growth and ripening, strict adherence to agrotechnical measures is necessary, which consists in the proper cultivation of the soil before sowing, planting, pinching and garter stems to the trellis.



 Calorie pepper stuffed with meat and rice - BZHU per 100 grams
Calorie pepper stuffed with meat and rice - BZHU per 100 grams Gorky pepper - the best varieties for open ground
Gorky pepper - the best varieties for open ground Hot pepper seeds - the best varieties for open ground and reviews
Hot pepper seeds - the best varieties for open ground and reviews Capsicum tincture for hair - how to use and reviews
Capsicum tincture for hair - how to use and reviews