Due to the wide variety of shapes and colors, peperomia has become a welcome guest in botanical gardens and living quarters. An evergreen herbaceous plant has more than 1000 species that have been grown as a room crop for many years.
Among the representatives of the genus, both ampelous plants and shrubs are found, which differ significantly in their external characteristics. Caring for peperomia (or dwarf pepper) will not take much time, since it is possible to grow a healthy plant at home, following a few simple rules.
Content
Description of peperomia, dwarf peppers poisonous or not
Peperomia is a large genus of evergreen herbaceous plants belonging to the family Peppers. The homeland of a popular decorative culture are tropical forests of South America. In its natural habitat, dwarf peppers prefer to grow on trees, snags, rocks and loose peaty soils.
A distinctive feature of representatives of this genus is the delicate aroma of leaves, which can be felt by touching the flower with warm hands. The genus includes approximately 1000 different species, which differ in size, shape and color of the leaves. All varieties were conditionally divided into 3 main groups, according to the growth of their shoots. You can meet ampelous, bushy and erect peperomia.
As a rule, peperomia are stunted plants with bright foliage, of the most diverse shapes and colors. A distinctive feature of all representatives of the genus are fleshy stems, which are densely covered with opposite leaves of a single shape. Despite the fact that peperomy is grown as an ornamental deciduous crop, the plant quite often produces inflorescences resembling elegant spikelets or a rat tail in shape.
The shrub does not contain any toxins or poisons, making it completely safe even for children and animals. Accidental ingestion of its parts in the stomach will not cause any symptoms of poisoning.
 You may be interested in:
You may be interested in:Names of varieties of peperomia with a description
Knowing the names of the species, and looking at the photos of various representatives of such a large genus, each grower will be able to choose his ideal option for growing a house.
Chisel
Peperomia Dolotovidnaya - a low succulent shrub, consisting of several dense stems, on which fleshy narrow leaves are alternately located. The shape of the leaf plate is reminiscent of ajar pea pods of light green color. Due to this similarity with legumes, it was popularly called Happy Bob.
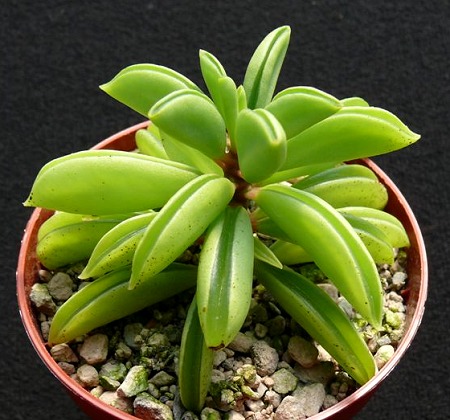

The leaves of the bush are collected in a star-shaped rosette. The plant blooms with small elegant flowers of white-green color. The height of the erect stems of the bush grown indoors, rarely reaches 60 cm.When choosing this variety, it is worth considering that the juicy stems of the bush begin to lignify with age.
Puckered
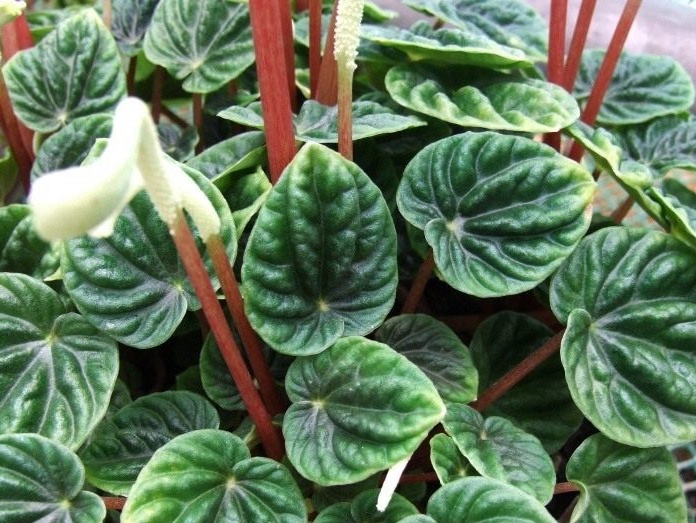
Wrinkled, or Wrinkled, peperomia differs from its relatives in its miniature size and sheets with a large number of convex veins that give them a wrinkled appearance. Plant height rarely reaches even 15 cm. The color of leaf plates varies from green to crimson shades, depending on the hybrid.
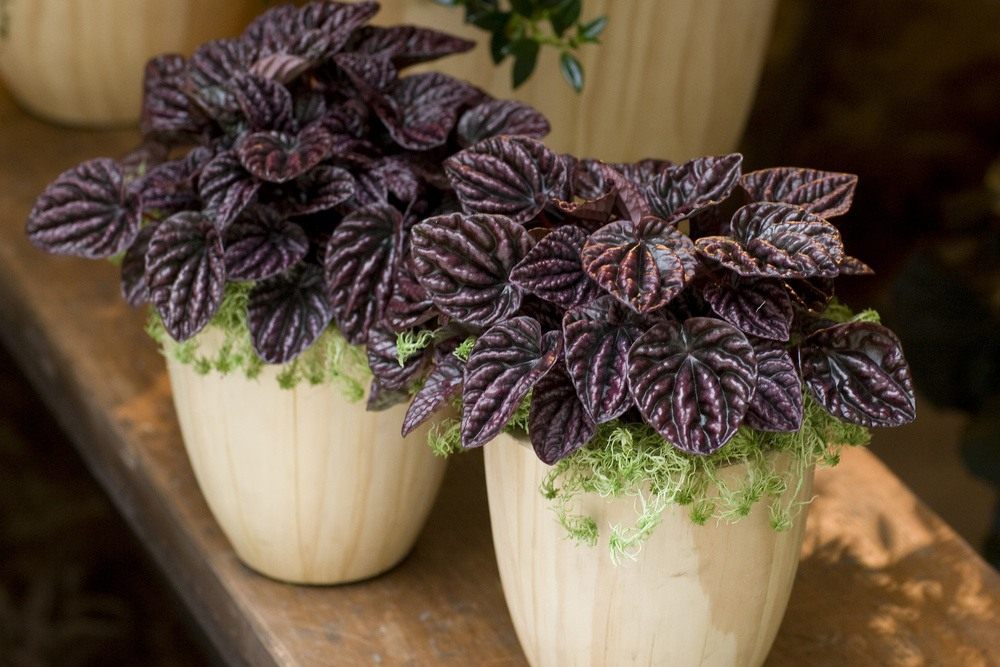

There are also variegated representatives whose foliage is painted in several colors at once. The plant does not have a pronounced dormant period, therefore, with proper care, it can delight with its spike-like flowering all year round. The flowers are white vertical shoots that significantly rise above the foliage.
 You may be interested in:
You may be interested in:Head
Head-headed peperomy is an ampel plant with drooping or creeping shoots, on which oval-shaped short-leaved leaves are alternately located. Leaf plates of the plant have a bright green color, especially when grown in partial shade. Representatives of this species do not differ in large size and grow in height only up to 25 cm.
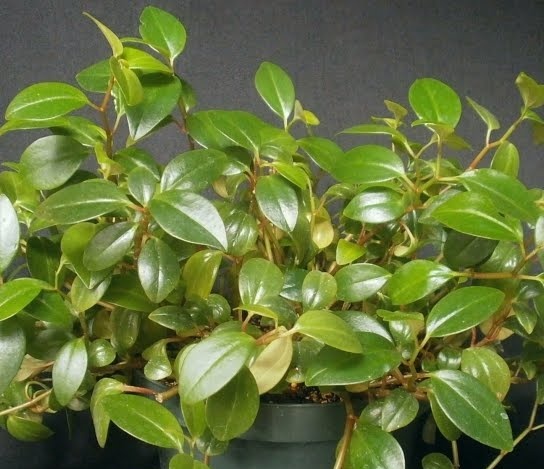

The inflorescence is a tight spikelet, on the surface of which there are subtle, not possessing decorative value, small flowers. Many flower growers intentionally remove the nondescript peduncles of the plant, as they take a lot of energy from the bush.
Tupolate
Tupolate peperomia is a perennial herb with thick and strong shoots, the height of which can reach 40 cm. This species is distinguished by unusual petiole leaf plates in the form of an oval with a cut top. Dense leathery leaves are most often colored dark green, but variegated varieties can also be found.
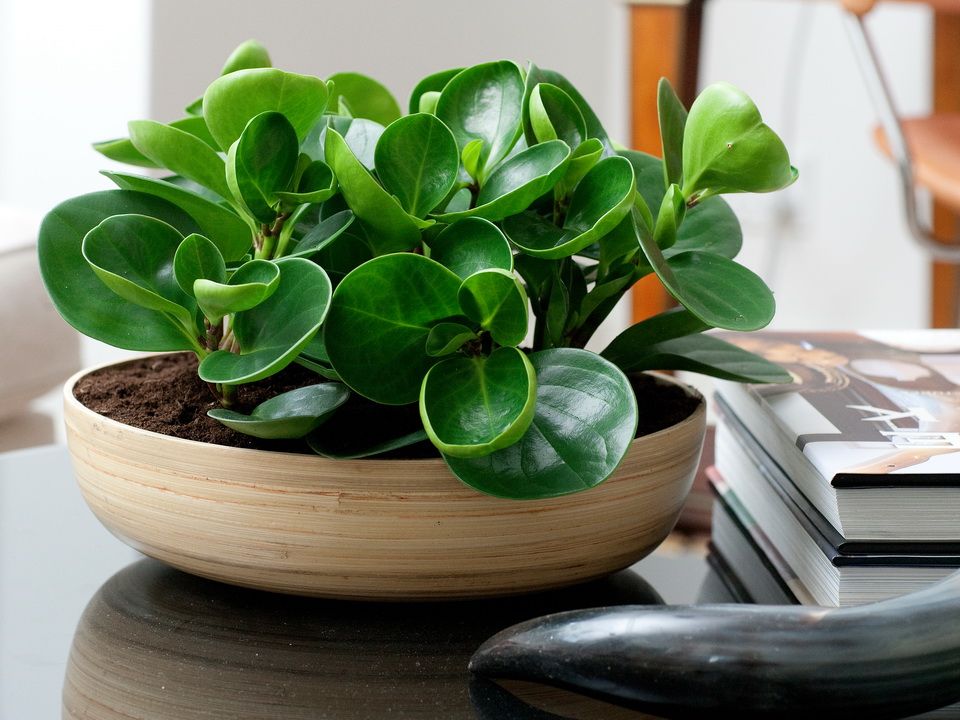

The surface of the sheet is shiny, thanks to a light wax coating. Initially upright shoots begin to line along the surface of the soil as they grow. This species belongs to flowering ornamental crops, but its inconspicuous spike-shaped inflorescence is not the goal when grown.
Caperata lilian
Kaperata variety lilian is a compact shrub, distinguished not only by its fleshy foliage, but also by its snow-white flowering. Snow-white inflorescences towering above the green mass of the bush are often compared with a lily bud. It is thanks to this similarity with the Liliaceae that this dwarf pepper variety got its name.
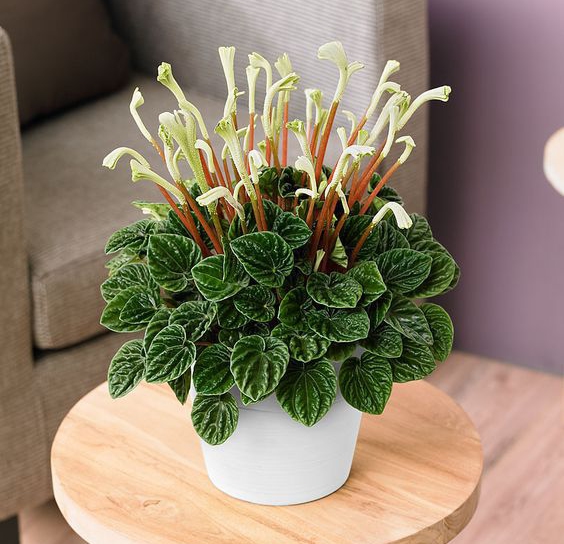

The flowers themselves are located on bright raspberry stems. As the inflorescences ripen, small dry berries appear on their tops, which are easily separated from the plant. Dark green shriveled leaves resemble a slightly rounded heart in shape.
Watermelon
Papperomy Silvery, or Watermelon - one of the most spectacular representatives of its kind. A miniature plant with short-sexed red stems attracts attention due to the unusual color of its leaf plates. The alternation of silver and bright green stripes makes the foliage look like a watermelon peel, due to which the plant got its popular name.
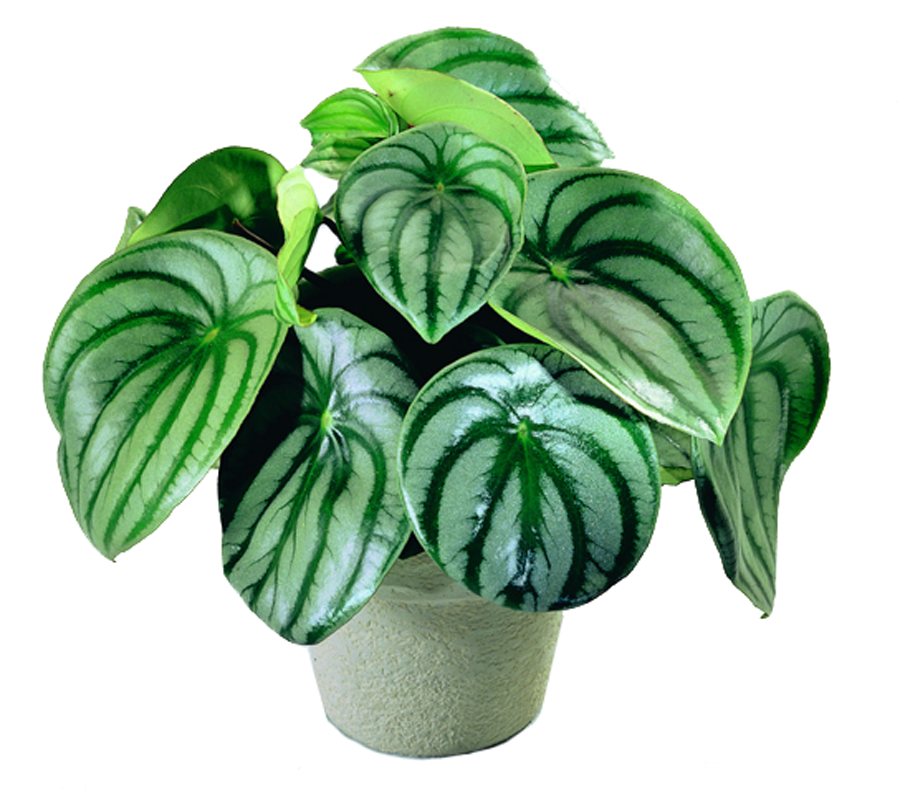

Despite the compactness of the shrub, whose height does not reach even 12 cm, its leathery ovoid leaves can grow up to 8 cm in length. Inflorescences of this species appear unexpectedly and look like thin spikelets of white-green color.
Leafy
Pereskelistny peperomia is a rather large decorative culture, characterized by hard leathery leaves of elliptical shape with 3 arcuate veins. Regular small leaves with a slightly pointed end, gathering 3-5 pieces, form whorls.The length of each sheet is rarely more than 5 cm.
Shiny leaves, as a rule, are painted in green shades, however, variegated varieties are also found, which are rarely grown at home. Also a distinctive feature of the bush is its fleshy erect stems of a reddish hue, which eventually begin to take root in the lower nodes.
Peperomia flower care at home
Peperomia is a popular indoor flower, to provide proper care, which even a beginner grower can. However, to maintain the decorative bush for many years, it is recommended to familiarize yourself with some of the nuances of its cultivation.
 You may be interested in:
You may be interested in:Lighting
Peperomia prefers to grow in the conditions of diffused illumination. However, species with a solid green color can be safely grown in partial shade, since a large amount of light will lead to fading of the green mass of the plant. But variegated varieties, on the contrary, need brighter lighting, otherwise they will lose their decorative appearance.
Temperature and humidity
Peperomia is a thermophilic plant, the optimum temperature of the content of which ranges from 20-25 ° C. Florists recommend maintaining a constant room temperature all year round. However, in the absence of such a possibility, the flower may be kept at a temperature not lower than 16 ° C. The plant does not tolerate drafts, so in winter it is recommended to move it as far as possible from the window.
Peperomia is absolutely not demanding on air humidity. In a particularly dry period, the surface of the bush can be periodically sprayed with warm water to enhance decorativeness.
Watering and feeding
The flower belongs to drought-tolerant plants and does not respond well to waterlogging of the soil. This is especially true for species with fleshy leaves, which contain their own supply of fluid. Watering the shrub as the soil dries, you can protect it from stagnation of water in the pot. For irrigation, it is better to use well-maintained water, the temperature of which is several degrees higher than the temperature in the room.
The shrub needs regular fertilizing with complex mineral fertilizers. During the period of active growth, it is recommended to feed the bush once every 2 weeks. In winter, the amount of top dressing can be halved.
Flowering Care
The period of flowering of peperomia, as a rule, occurs in the summer. At this time, the flower needs additional hydration, which can be achieved by abundant watering (but without flooding) and regular spraying. The appearance and maintenance of the life of inflorescences takes away a lot of strength from the bush, due to which it can lose part of its foliage.

For this reason, most flower growers prefer to remove flower stalks even at the time of their formation. Such a manipulation will protect the plant from dropping foliage, which will preserve the decorative appearance of the bush. In addition, many believe that plant inflorescences do not have a particular aesthetic benefit.
Pruning and pinching
The pruning procedure depends heavily on the type of flower. When growing ampelous varieties, it is recommended to cut off the central vegetation without affecting the extreme shoots.After trimming the central shoots, only a third of their previous length should remain.

As a result of this procedure, young shoots will begin to grow actively, which will positively affect the appearance of the plant. By pinching the longest stem of erect varieties, their bushiness can be significantly increased. One pinching procedure stimulates the appearance of 2-4 new shoots. Shrub varieties do not need pruning or pinching.
 You may be interested in:
You may be interested in:Diseases and pests of a houseplant
Failure to comply with the basic recommendations of agricultural technology during the cultivation of peperomia can cause pain in the flower:
- Most often, the plant affects root rot, which is accompanied by decay of its root system. The cause of the disease is excessive watering and low room temperature. To treat the disease, the flower must be transplanted into a new soil mixture, having previously removed all affected parts of the roots. Finally, gray rot can be dealt with by treating the flower with a fungicidal solution.
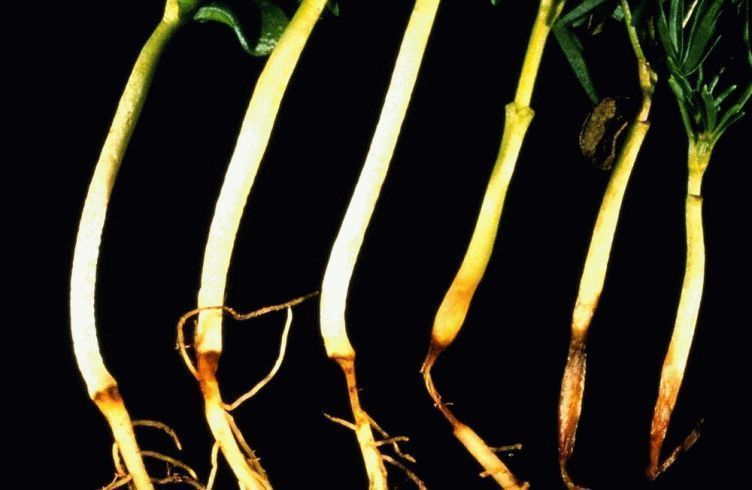
Root rot - Dwarf virus - a specific disease that prevents the flower from developing normally, disrupting its life cycle and leading to curvature of the leaves. This disease is incurable.
- Keeping the plant in a hot room leads to thrips damage. The presence of insects can be determined by brown spots on the leaves. Processing the plant with fungicides and transplanting it into a new soil will help get rid of pests.
- Excessively dry indoor air causes the flower to become infected with a spider mite. The pest can be detected by the thin web that covers the plant. With the timely detection of insects, they can be dealt with by treating the plant with a soapy solution.
How to propagate and transplant peperomia
A flower can multiply at once in several ways: apical or stem shoots, leafy cuttings, seeds and division of the bush:
- Propagation by dividing the bush is one of the easiest and fastest ways to get a new plant. To do this, it is enough to manually divide the root system of the flower into 2 parts and plant each of the parts in separate pots.
- As a handle, you can use pieces of apical and stem shoots with one node. Before planting the cuttings in the ground, it must be placed in water for 48 hours to let the roots out. After two days, the seedlings can be transplanted into the soil mixture for further rooting.

Flower propagation - The plant is quite easily propagated by leafy cuttings. As a planting material, it is important to choose a powerful and completely healthy leaf. A leaf with a petiole rather quickly takes root in clean, defended water. After the appearance of the first roots, the sheet can be easily transplanted into a constant container.
- A flower is rarely propagated using seeds, as this is a fairly long process. Seeds are best sown in a moist soil mixture consisting of sand and leafy soil. Seeds will not germinate unless they are provided with greenhouse conditions, so the container with seedlings must be covered with plastic wrap or glass. Regular moistening of the soil substrate and periodic ventilation of the seedlings will allow the seeds to give the first shoots.
Transplantation Stages:
- Put a drainage layer 2-4 cm wide at the bottom of the pot. You can use pebbles, expanded clay, crushed stone or charcoal as a material for drainage.
- Fill 2/3 of the pot capacity with a mixture of peat, sand and humus, taken in equal quantities.
- Carefully place the flower in a new container.
- Fill the voids of the pot with soil.
- Water the flower.
As a container for peperomia, it is recommended to take a wide shallow pot, the diameter of which will be 1.5-2 cm larger than the previous one.
Common Growing Questions
Growing peperomia for the first time, flower growers quite often come across questions regarding the characteristics of its cultivation.
Dwarf pepper is a miniature indoor culture that, with proper care, is able to maintain its decorative appearance for many years. Gentle watering without flooding, the absence of drafts and stable room temperature are the key to the healthy development of the plant.






 10 beautiful annuals that bloom all summer
10 beautiful annuals that bloom all summer Sow in the ground, without seedlings: 10 beautiful and unpretentious flowers
Sow in the ground, without seedlings: 10 beautiful and unpretentious flowers Platicodon planting and outdoor care
Platicodon planting and outdoor care Hosta - planting and care in the open ground in the Urals
Hosta - planting and care in the open ground in the Urals